Russia's Victory Day Parade 2015: List of aircraft on display
| a | |||||
| |
|||||
Armies
in the world - Russia Victory Day Parade Military Aircraft |
|||||
| Russia's Victory Day Parade 2015: List of aircraft on display | |||||
The 2015 Moscow Victory Day Parade will take place in Red Square in Moscow on 9 May 2015that will be held in honor of the 70th anniversary of the Allied victory in World War II. Russia’s state-of-the-art aircraft will be presented to the public on an unique fly past column. More than 20 different aircraft will perform aerial display, such as the Tu-160 bomber and the newly-developed Su-35 multirole fighter aircraft. |
|||||
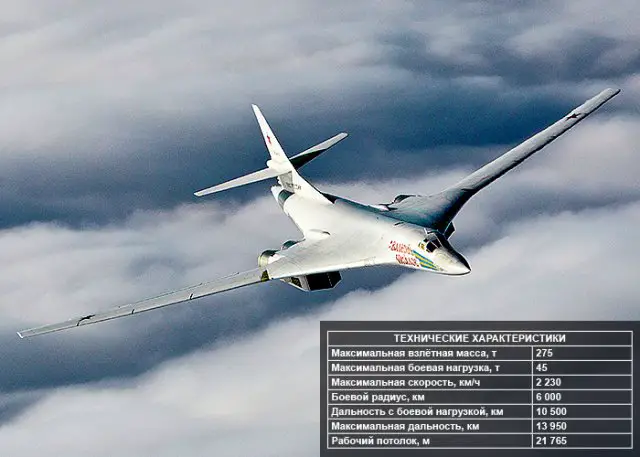
The
Tupolev Tu-160
(NATO reporting code: Blackjack) is a supersonic, variable-sweep wing
heavy strategic bomber designed by the Tupolev Design Bureau in Russia.
Currently, modernization of the Tu-160 bomber and its equipment with new
types of weapon systems is underway. The Russian Air Force will receive
more than 10 modernized Tu-160
Blackjack strategic bombers by 2020, the Defense Ministry
said on Tuesday, February 7, 2012. The modernized version, Tu-160M, features
new weaponry, improved electronics and avionics, which double its combat
effectivness. |
|||||
The
Mil Mi-26
(NATO reporting name: Halo) is a Russian heavy transport helicopter designed
by the Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant which is in service with several different
civilian and military operators. It is the largest and most powerful helicopter
to have gone into series production. The Mi-26
heavy transport helicopter is designed to airlift troops and material,
and transport cargoes inside or outside the fuselage. The transport, troop-carrying,
medevac, flight-refuelling are available. |
|||||
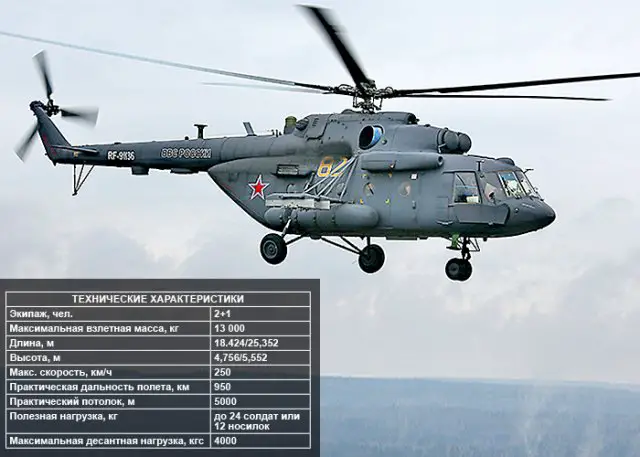 Mil Mi-8 multirole helicopter |
|||||
The
Mil Mi-8 (NATO reporting name: Hip) is a Soviet-designed medium twin-turbine
transport helicopter. There are numerous variants, including the Mi-8T
which is armed with rockets and anti-tank guided missiles, in addition
to carrying 24 troops. The latest Mi-8/17 military transport helicopter
family includes the Mi-8MTV-5 made at Kazan Helicopters and the Mi-8AMTSh
made at Ulan-Ude Aviation Plant. |
|||||
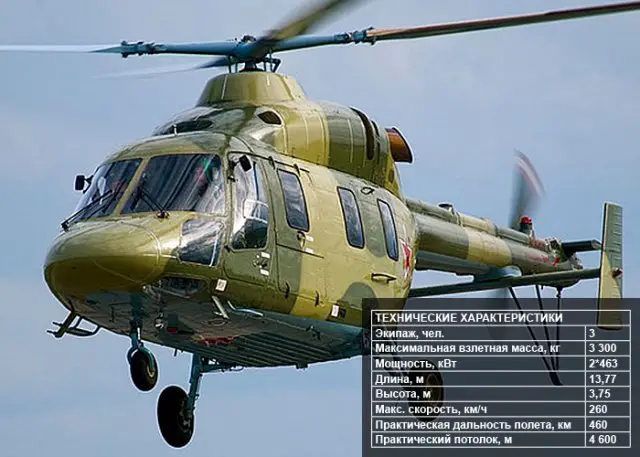
Ansat-U,
a trainer variant of the Ansat
helicopter, is being produced by Kazan Helicopters for the Russian Air
Force. Kazan was selected to supply Ansat-U training helicopters to the
Russian armed forces in September 2001. The assembly of the first Ansat-U
prototype was completed in April 2004. Following the completion of tests,
the full scale production of Ansat-U was authorised in December 2008.
The Ansat-U can carry up to 10 passengers. |
|||||
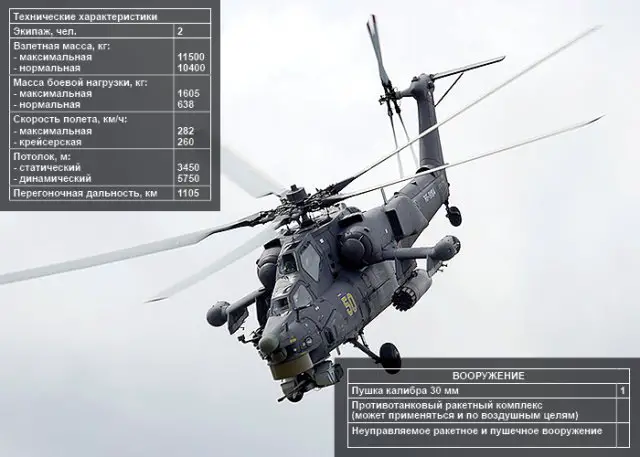
The
Mil Mi-24V/Mi-35
attack helicopter (Hind-E) is a later development of the Mi-24 Hind which
entered production in 1976 and was first seen by the west in the early
1980s. It was armed with the more advanced 9M114 Shturm (AT-6 Spiral).
Eight of those missile are mounted on four outer wing pylons. It was the
most widely produced version with more than 1,500 made. |
|||||
The
Kamov Ka-52 Alligator is a multi-role all-weather
combat helicopter. It is a twin-seat derivative of the Russian-made attack
helicopter Ka-50. The first prototype was unveiled at the aerospace event
Aero India in 1996. The Ka-52 is designed to defeat armor materiel, low-speed
aerial targets, as well as exposed and sheltered manpower in the daytime
and at night. The Ka-52
is equipped with the same weapons as those carried by the Ka-50, including
the Khrizantema (close-in) and the Hermes (long-range) new generation
ATGMs. |
|||||
The
Mil
Mi-28 (NATO reporting name "Havoc") is a Russian
all-weather, day-night, military tandem, two-seat anti-armor attack helicopter.
It is a dedicated attack helicopter with no intended secondary transport
capability, better optimized than the Mil Mi-24 gunship for the role.
The Mi-28N is an upgraded variant fitted with all weather day-night version,
a top-mounted millimeter wave radar station, thermographic camera-TV,
and a laser rangefinder. It is powered by two Russian Klimov TV3-117VMA-SB3
engines (2,500 hp each), produced by the Ukrainian Motor-Sich. |
|||||
 Antonov An-124-100 heavy transport aircraft |
|||||
The
AN-124-100 aircraft has been developed on the basis of the AN-124 “Ruslan”
heavy military transport aircraft. It is the biggest serial heavy lifter
in the world. It is intended for the transportation of heavy and oversized
cargo and various special-purpose vehicles. It was designed by the Antonov
design bureau in the Ukrainian SSR, then part of the Soviet Union. The
Russian Army currently operates 25 An-124 aircraft. |
|||||
 Ilyushin Il-76 "Candid" medium-range military transport aircraft |
|||||
The
Ilyushin Il-76 (NATO reporting name: Candid) is a multi-purpose four-engine
strategic airlifter designed by the Ilyushin design bureau. It was first
planned as a commercial freighter in 1967, as a replacement for the Antonov
An-12. Missions of the aircraft are: to drop paratroopers, carry troop
forces and combat material with crews and armaments, including medium-sized
battle tanks, airlift cargo for troop forces and transport for disaster
relief operations. |
|||||
The
Tupolev Tu-95
(NATO reporting name: Bear) is a four-engine turboprop-powered strategic
bomber and missile platform aircraft. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered
service with the former Soviet Union in 1956 and is expected to serve
the Russian Air Force until at least 2040. The Tu-95MS is a completely
new cruise missile carrier platform based on the Tu-142 airframe. This
variant became the launch platform of the Raduga Kh-55 cruise missile.
Known to NATO as the Bear-H and was referred to by the U.S. military as
a Tu-142 for some time in the 1980s before its true designation became
known. |
|||||
The
Tupolev Tu-22
(NATO reporting name: Blinder) was the first supersonic bomber to enter
production in the Soviet Union. Manufactured by Tupolev, the Tu-22 entered
service with the Soviet military in the 1960s, and the last examples were
retired during the 1990s. The Tu-22M3
is an improved variant of the basic version of Tu-22. The Tu-22M3 long-range
bomber is intended to destroy ground and large marine targets (primarily
aircraft-carrier task forces) with supersonic air-to-surface missiles
in the entire spectrum of application conditions in operational and tactical
depth of enemy defenses. |
|||||
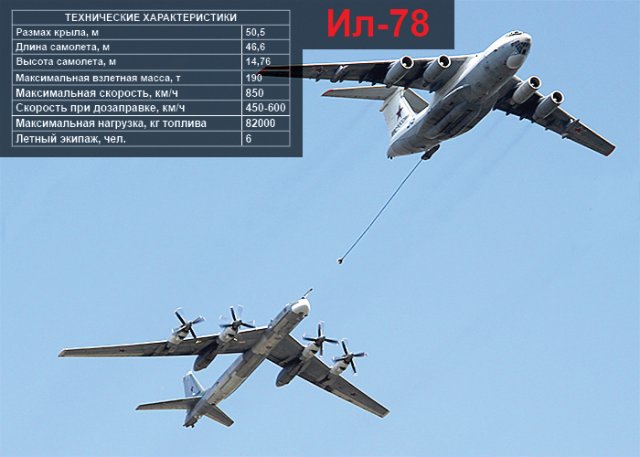 Ilyushin Il-78 aerial refuelling tanker aircraft |
|||||
The
Ilyushin Il-78 (NATO reporting name Midas) is a four-engined aerial refuelling
tanker based on the Il-76. The maiden flight of Il-78 took place on 26
June 1983 and the aircraft entered into service in 1984. About 53 aircraft
are currently operational worldwide. The Il-78 aircraft can refuel a maximum
of four planes simultaneously on the ground. It can also be used as a
military transport aircraft for air drop and air landing of cargo and
crew. |
|||||
The
Sukhoi Su-30SM fighter aircraft is a specialised
version of the thrust-vectoring
Su-30MKM and MKI variants for the Russian military,
produced by the Irkut Corporation. The new version has been upgraded based
on Russian military requirements for radar, radio communications systems,
friend-or-foe identification system, ejection seats, weapons, and other
aircraft systems.The aircraft is equipped with the Bars-R radar and the
wide-angle HUD. |
|||||
The
Su-35 (NATO code name: Flanker-E) is a single-seat,
twin-engined multifunctional fighter aicraft designed and manufactured
by the Russian Aviation Industry Sukhoi. Intended to gain air superiority
and engage aerial and ground targets when performing autonomous and group
combat actions, by day and night, in VFR and IFR weather conditions. Its
first flight took place on February 19, 2008. The Su-35S
received upgraded avionics and various modifications were performed to
the airframe. |
|||||
The
Mikoyan MiG-29 (NATO name Fulcrum) is a fourth-generation
jet fighter aircraft. Developed in the 1970s by the Mikoyan Design Bureau,
it entered service with the Russian Air Force in 1983, and remains in
use in many other nations. The MiG-29SMT
is an upgrade package for first-generation MiG-29s (9.12 to 9.13) containing
enhancements intended for the MiG-29M variant. Additional fuel tanks in
a further enlarged spine provide a maximum flight range of 2,100 km on
internal fuel. The weapons load was increased to 4,500 kg on six underwing
and one ventral hardpoints, with similar weapon choices as for the MiG-29M.
The upgraded aircraft can also accomidate non-Russian origin avionics
and weapons. |
|||||
The
Sukhoi Su-34
(NATO reporting name: Fullback) is a Russian twin-engine, twin-seat strike
fighter. It is intended to replace the Sukhoi Su-24. Based on Sukhoi Su-27
"Flanker", the Su-34 is designed primarily for tactical deployment
against ground and naval targets, but it can also carry out air-to-air
missions (interception/air superiority), as a secondary role. The Russian
Air Force completed the final stage of the state tests of the Su-34 on
19 September 2011.The aircraft entered service in early 2014. |
|||||
The
Su-24 (NATO reporting name: Fencer) is a supersonic,
all-weather attack aircraft/interdictor developed in the Soviet Union.
The Su-24
has two Saturn/Lyulka AL-21F-3A afterburning turbojet engines with 109.8
kN (24,700 lbf) thrust each, fed with air from two rectangular side mounted
intakes with splitter plates/boundary-layer diverters. The Su-24's fixed
armament is a single fast-firing GSh-6-23 cannon with 500 rounds of ammunition,
mounted in the fuselage underside. The gun is covered with an eyelid shutter
when not in use. The warload includes various nuclear weapons. Two or
four R-60 (NATO AA-8 'Aphid') infrared missiles are usually carried for
self-defense by the Su-24M/24MK. |
|||||
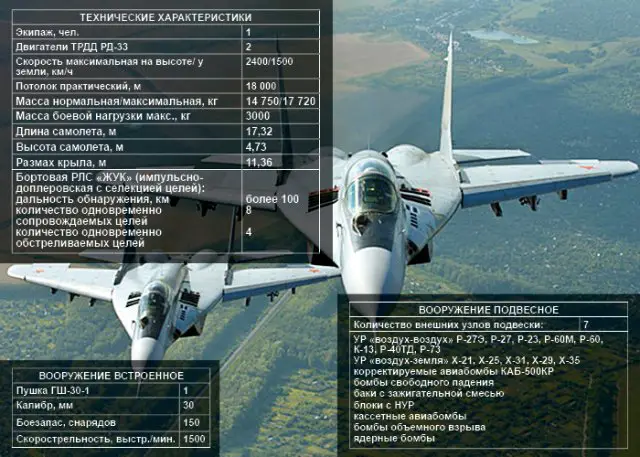
The
Mikoyan
MiG-31 (NATO code: Foxhound) is a Russian made supersonic
fighter aircraft developed to replace the MiG-25 "Foxbat". The
MiG-31 was designed by the Mikoyan design bureau based on the MiG-25.
MiG-31 can work efficiently in all weather conditions while fulfilling
visual flight rules (VFR) and instrument flight rules (IFR), day and night.
It is equipped with state-of-the-art digital avionics. The MiG-31
was the first soviet fighter aircraft to have true look-down and shoot-down
capability. |
|||||
The
Sukhoi Su-25
(NATO reporting name: "Frogfoot") is a single-seat, twin-engine
jet aircraft developed in the Soviet Union by the Sukhoi Design Bureau.
It was designed to provide close air support for the Soviet Ground Forces.
The first prototype made its maiden flight on 22 February 1975. After
testing, the aircraft went into series production in 1978. The Su-25SM
upgrade is aimed at expanding their combat capabilities, enhancing lethality
and slashing operating and maintenance burden. The plane's navigational
accuracy is improved by an order of magnitude while its ordnance's efficiency
is increased two to three times. The upgrade increases combat payload
on the new MBD3-U2T-1 bomb racks up to 5,000 kg and expands their ordnance
list allowing R-73E air-to-air guided missiles and S-13T rockets. The
Laser targeting system is replaced with a modernized version with a limited
video camera channel, no Zoom or Night Vision Video features like those
in the Su-39's Kair Fire Control based system. The old style Reflector
Sight(with Telescopic Bomb Sight) is replaced with an LCD screen and an
Electronic Heads Up Display. |
|||||
The
Sukhoi Su-27 (NATO reporting name: Flanker) is a
twin-engine fighter aircraft designed by the Russian Company Sukhoi. There
are several related developments of the Su-27 design. The first 'Flanker-A'
prototypes flew on May 20, 1977 and entered service as the 'Flanker-B'
in 1984. The Sukhoi Su-27 is in service not only in Russia but also in
China and Vietnam. The Su-27's basic design is aerodynamically similar
to the MiG-29, but it is substantially larger. The Su-27
is equipped with a Phazotron N001 Zhuk coherent pulse-Doppler radar with
track-while-scan and look-down / shoot-down capability. The fighter also
has an OLS-27 infrared search and track (IRST) system in the nose just
forward of the cockpit. |
|||||
The
Yakovlev
Yak-130 is a russian made subsonic two-seat new-generation
aircraft intended for basic and advanced flight training of air school
trainee pilots to fly fourth- and fifth-generation combat aircraft, for
maintaining flying skills of pilot personnel of regular air units, and
flying combat missions in local armed conflicts. Development of the plane
began in 1991, and the maiden flight was conducted on 26 April 1996. As
an advanced training aircraft, the Yak-130 is able to replicate the characteristics
of several 4+ generation fighters. It can also perform light-attack and
reconnaissance duties, carrying a combat load of 3,000 kg. |
|||||