Russia designs Liana space intelligence and guidance system
Military space technologies rose to a new level in the past decades. A group of satellites can monitor and coordinate joint operation of combat units. Sophisticated ground, airborne and space systems are designed to intercept and disable spacecraft. Specific attention is paid to guidance, the Independent Military Review writes.
Follow Air Recognition on Google News at this link
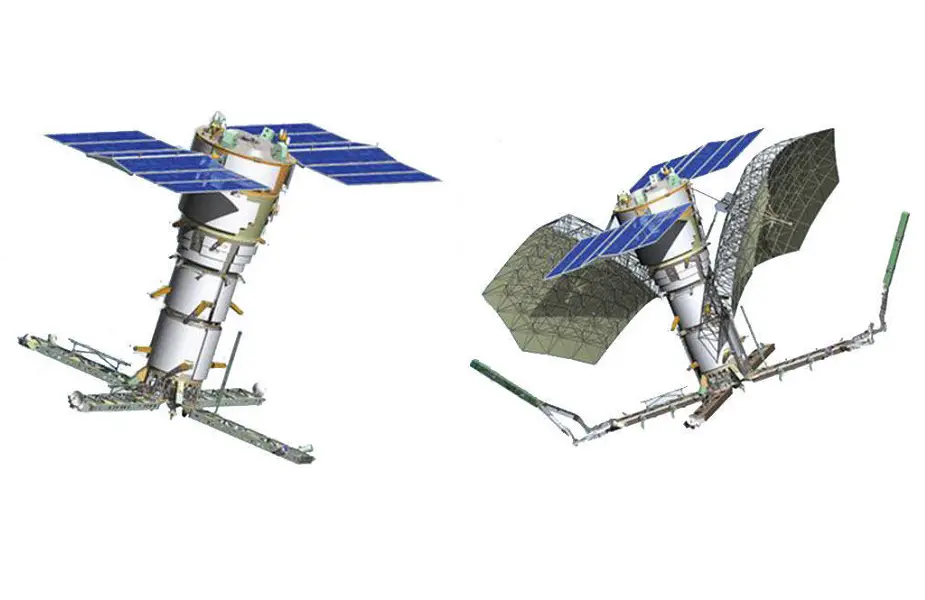 Liana satellites survey the sea theater of warfare and detect hostile warships and submarines. The intelligence provides data on military activities of foreign countries in various parts of the globe. Here, an artistic render of Lotos S1 and Pion reconnaissance satellites. (Picture source: KB Arsenal)
Liana satellites survey the sea theater of warfare and detect hostile warships and submarines. The intelligence provides data on military activities of foreign countries in various parts of the globe. Here, an artistic render of Lotos S1 and Pion reconnaissance satellites. (Picture source: KB Arsenal)
Russia is designing Liana space intelligence system to replace outdated Legenda, which was created in 1970s to monitor hostile aircraft-carrying forces. Imperfect optical technologies of Legenda could detect only major objects. However, the Military Academy of the Russian General Headquarters said Legenda effectively determined the actions of the British Navy in the Falkland conflict. After the Soviet collapse Legenda was not upgraded and the group of 30 spacecraft finally degraded by early 2000s.
Russian scientists began to design a modern satellite system. Numerous disagreements and organizational problems delayed Liana creation for many years. In contrast to the predecessor, Liana is universal and controls practically the whole globe by a small group of satellites.
It operates two types of satellites — Pion and Lotos. There is actually no information about them in open sources. However, modern technologies prompt the missions and capabilities of the spacecraft.
Liana satellites survey the sea theater of warfare and detect hostile warships and submarines. The intelligence provides data on military activities of foreign countries in various parts of the globe. Test ranges, airfields, naval bases, nuclear missile infrastructure, strategic enterprises, groupings of warships and ground forces trigger most interest. Experts said Liana does not depend on the atmospheric conditions and provides coordinates with a 1-km to 10-m precision.
Open sources said the satellites operate in a circular orbit of 800-900 km. It makes them invulnerable to antisatellite weapons. The operation in the top limits of low-altitude orbit helps monitor hostile actions at sea and on the ground and coordinate actions of friendly forces. The system provides guidance for Kalibr cruise missiles, as well as air ballistic Kinzhal and hypersonic Tsirkon. The latter specifically needs precise guidance, as the speed exceeds Mach 8 and radically decreases the fly-in time.
In early 2000s, such capabilities of the Russian space system seemed impossible. New technologies raised the level of space hardware to ensure the balance of forces in the current international situation.
© Copyright 2021 TASS. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.
























