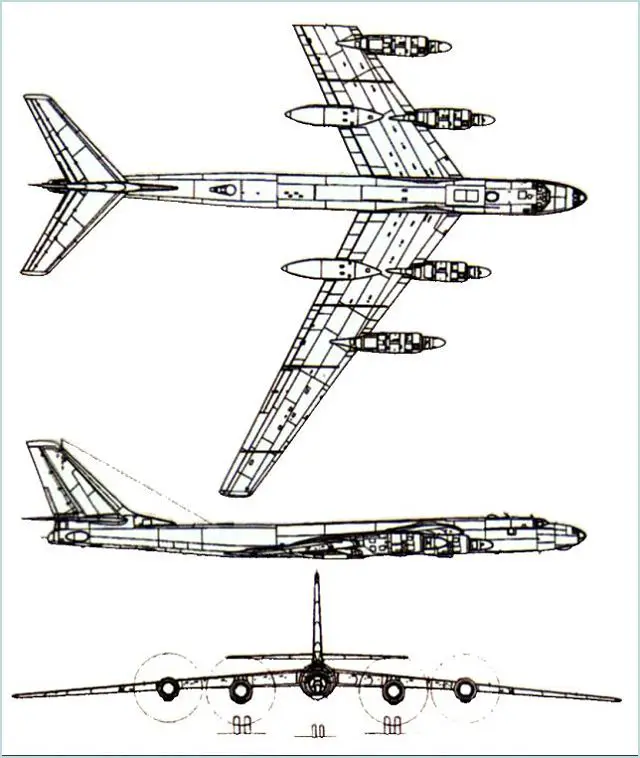
Tu-95 Tupolev Bear
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Tu-95 Tu-95MS Tupolev Bear strategic bomber aircraft
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Tupolev Tu-95 (NATO reporting name: Bear) is a four-engine turboprop-powered strategic bomber and missile platform aircraft. First flown in 1952, the Tu-95 entered service with the former Soviet Union in 1956 and is expected to serve the Russian Air Force until at least 2040. Intended for destruction of critical targets with nuclear missiles in remote military and geographical areas and in the deep rear of continental theaters of military operations. TheTu-95 strategic bomber aircraft can accomplish combat missions by day and night, in VFR and 1FR weather conditions, any season and all climates. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main variants: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- Tu-95M: Basic variant of the long-range strategic bomber and the only model of the aircraft never fitted with a nose refuelling probe. Known to NATO as the Bear-A.
- Tu-95K22: Conversions of the older Bear bombers, reconfigured to carry the Raduga Kh-22 missile and incorporating modern avionics. Known to NATO as the Bear-G. - Tu-95K: Designed to carry the Raduga Kh-20 air-to-surface missile. - Tu-95KD: The Tu-95KD aircraft were the first to be outfitted with nose probes. Known to NATO as the Bear-B. - Tu-95MR: Bear A modified for photo-reconnaissance and produced for Naval Aviation. Known to NATO as the Bear-E - Tu-95MS: Completely new cruise missile carrier platform based on the Tu-142 airframe. This variant became the launch platform of the Raduga Kh-55 cruise missile. Known to NATO as the Bear-H and was referred to by the U.S. military as a Tu-142 for some time in the 1980s before its true designation became known. - Tu-142: Maritime reconnaissance/anti-submarine warfare derivative of Tu-95. Known to NATO as the Bear-F. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Tu-95MS represents a cantilever mid-wing monoplane with a swept wing (from 20 to 65°) and tail, and a three-strut nosewheel landing gear.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionic and combat systems | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Tu-95MS is equipped with an aiming and navigation system including a radar. To protect aircraft from threats in the aft hemisphere, an aiming radar is placed in the aft fuselage to provide automatic target search, tracking, as well as the aiming of two 23mm GSh-23 guns to destroy enemy aircraft. In addition, the bombers self-defense complex includes IR flare/chaff dispensers. Infrared sensors of the Mak-UT IR sensor missile approach warning system are installed under the nose sections and on the top surface of the fuselage above the wings.Electronic countermeasures pods are pylon mounted on the port and starboard side of the tail gunner's station and fairings are visible on each side of the weather radar on the nose section.
The Tu-95MS bomber is currently being modernized. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The powerplant consists of four NK-12MP turboprop engines with tractor coaxial four-bladed variable-pitch propellers. Engine high characteristics and perfect aerodynamic configuration allow the aircraft to continue the flight mission even if two engines fail. In this case, negative thrusts are eliminated by the system of automatic propeller feathering. Fuel is stored in 8 integral fuel tanks in the right and left outer wings. Three intra fuselage rubber tanks are arranged in the wing center section and the aft fuselage. In case of failure of fuel pumps' power supply, fuel can be fed to the engines by gravity. The refueling probe intended for inflight refueling is located in the nose fairings upper part. The Tu-95 has a maximum level speed of 650km per hour and an unrefuelled combat radius of 6,400km. With one in-flight refuelling, the aircraft has a combat radius of 8,200km.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The weapon bay accommodates a multistation missile launcher capable to fire six strategic cruise missiles. The Tupolev Tu-95 bomber aircraft can also be equipped with conventional free-fall bombs. The Tu-95MS Bear H is capable of carrying six KH-55 Granat (Nato designation AS-15 Kent) nuclear-armed long-range cruise missiles with a range of 3,000km. The missiles are mounted on a catapult launch drum in the bomb bay. Alternatively, the Tu-95 can carry 14 Kh-SD anti-ship missiles with a range of 600 km or eight conventionally armed Kh-101 air launch cruise missiles, which have a range of up to 3,000 km. The rear gun compartment is fitted with a twin barrelled GSh-23L autocannon in tail turret. The Tu-92 can carry 15,000 kg of missiles, including the Raduga Kh-20, Kh-22, Kh-26, and Kh-55 air-to-surface missiles.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||





























