JF-17 Thunder / CAC FC-1 Xiaolong Fierce Dragon
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
JF-17 Thunder Multi-Role fighter aicraft
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
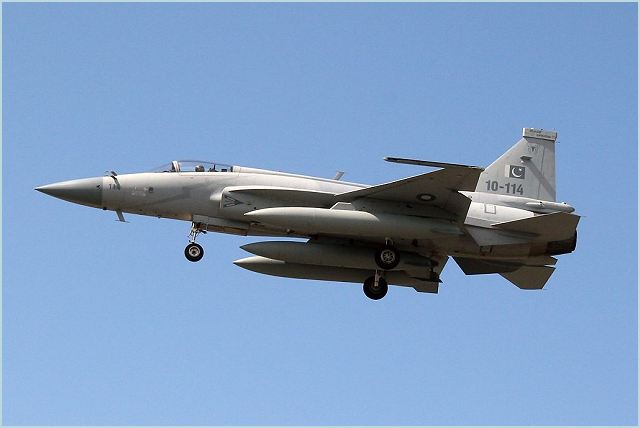
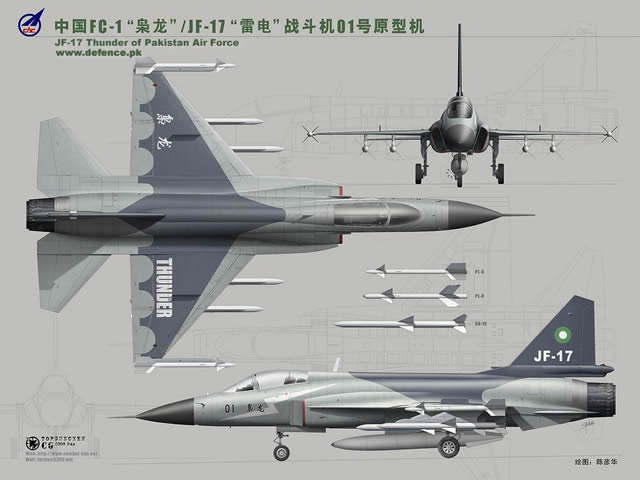
The PAC JF-17 Thunder, or CAC FC-1 Xiaolong (Fierce Dragon), is a light-weight, single-engine, multi-role combat aircraft developed jointly by the Pakistan Air Force, the Pakistan Aeronautical Complex (PAC) and the Chengdu Aircraft Industries Corporation (CAC) of China. Its designation "JF-17 Thunder" by Pakistan is short for "Joint Fighter-17", while the designation "FC-1 Xiaolong" by China means "Fighter China-1 Fierce Dragon". Pakistan Aeronautical Complex (PAC) holds the exclusive rights of 58% of JF-17 airframe co-production work. A comprehensive infrastructure comprising state of the art machines and required skilled human resource has very quickly been developed at the Complex. The final assembly and flight testing of the aircraft was the first JF-17 co-production activity to start at PAC. The first PAC produced aircraft was handed over to Pakistan Air Force in November 2009. Since then, aircraft are being produced regularly to meet the required schedule. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
JF-17 Thunder is only in service with the PAF: 50 aircrafts projected ( to an eventual 250 aircrafts final order). China only built 4 aircrafts for evaluation purposes. As of 2013 Argentina is said (according to IHS Janes) to discuss about a joint-production deal with CAC for a local production of the FC-1. Main versions: JF-17 Block I: first batch of aircraft produced in China for Pakistan JF-17 Block II: Ordered by the PAF in 2011 as a variant with "enhanced features" JF-17 Block III: The block III will feature more advanced avionics and engine. It will be a twin seat variant. Induction is expected to start around 2016 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The airframe is of semi-monocoque structure, constructed primarily of aluminium alloys. High strength steel and titanium alloys are partially adopted in some critical areas. The airframe is designed for a service life of 4,000 flight hours, or 25 years, the first overhaul being due at 1,200 flight hours.Block 2 JF-17s incorporate greater use of composite materials in the airframe to reduce weight.The mid-mounted wings are of cropped-delta planform. Near the wing root are the LERX, which generate a vortex that has the effect of providing more lift to the wing at high angles of attack encountered during combat manoeuvres. A conventional tri-plane empennage arrangement is incorporated, with all-moving stabilators, single vertical stabiliser and rudder, as well as twin ventral fins. The flight control surfaces are operated by a computerised flight control system (FCS), which also adjusts the slats/flaps for improved manoeuvring. Up to 3,629 kg (8,000 lb) of ordnance, equipment and fuel can be mounted under the hardpoints, two of which are on the wing-tips, four under the wings and one under the fuselage. Two bifurcated air inlets, one on either side of the fuselage behind and below the cockpit, provide the engine's air supply. The position and shape of the inlets is designed to give the required airflow to the jet engine during manoeuvres involving high angles of attack. A DSI design is used to simultaneously prevent boundary layer airflow entering the inlet and decelerate supersonic airflow.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionic | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The software written for the JF-17's avionics totals more than one million lines of instructions, incorporating the concept of open architecture. Rather than using the Ada programming language, which is optimised for military applications, the software is written using the popular civilian C++ programming language to better use the large number of civilian software programmers available. The aircraft's glass cockpit incorporates an electronic flight instrument system (EFIS) and a wide-angle holographic head-up display (HUD), which has a minimum total field of view of 25 degrees. The EFIS is made up of three colour multi-function displays (MFD) providing basic flight information, tactical information and information on the engine, fuel, electrical, hydraulics, flight control and environment control systems. The HUD and MFD can be configured by the pilot to show any of the available information. Each MFD is 20.3 cm (8 in) wide and 30.5 cm (12 in) tall, arranged side-by-side in a portrait orientation. The central MFD is placed lower down to accommodate an up-front control panel between it and the HUD. The aircraft also includes a health and usage monitoring system and automatic test equipment. The aircraft has a composite FCS consisting of conventional controls with stability augmentation in the yaw and roll axis and a digital fly-by-wire (FBW) system in the pitch axis. The leading edge slats/flaps and trailing edge flaps are adjusted by the FCS automatically during manoeuvring to increase turning performance. Some sources state that the system has been upgraded to provide fly-by-wire flight control in the roll and yaw axis also, the serial production aircraft having a digital quadruplex (quad-redundant) FBW system in the pitch axis and duplex (dual-redundant) FBW system in the roll and yaw axis. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The JF-17 is powered by a single Russian RD-93 turbofan engine, which is a variant of the RD-33 engine used on the Mig-29 fighter. The engine gives more thrust and significantly lower specific fuel consumption than the turbojet engines fitted to older combat aircraft being replaced by the JF-17. The Guizhou Aero Engine Group has been developing a new turbofan engine, the WS-13 Taishan,Guizhou WS-13. Dry Thrust 51.2 kN / Thrust After Burner 86.37 kN |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
JF-17 can be armed with up to 3,629 kg (8,000 lb) of air-to-air and air-to-ground weaponry, as well as other equipment, mounted externally on the aircraft's seven hardpoints. The under-fuselage and inboard under-wing hardpoints are plumbed, enabling them to carry droptanks of various sizes for extra fuel. Air to Air Missiles: Misiles & Bombs: Guns: 1× 23 mm GSh-23-2 twin-barrel cannon (can be replaced with 30 mm GSh-30-2) |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||





























