Su-24 Fencer Sukhoi
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
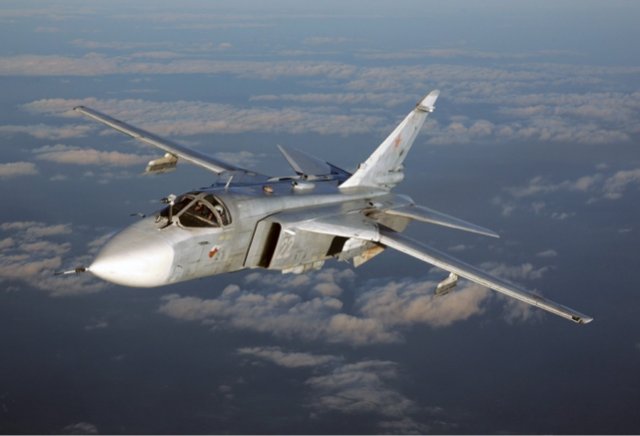
Sukhoi Su-24 / Su-24M Fencer front-line attack aircraft
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Su-24 front-line attack aircraft/interdictor is manufactured by the Sukhoi Design Bureau Joint Stock Company, based in Moscow, and the Novosibirsk Aircraft Production Association, Novosibirsk, Russia. The Su-24M entered service in 1983 and is a development of the Su-24, known by the NATO codename "Fencer". The first production Su-24 went airborne on December 31st, 1971. The Su-24 would not be formally accepted into service until February 6th, 1975.
More than 1,400 of the aircraft were produced in all variants. Today, the Russian Air Force operates 400 upgraded Su-24M/M2 aircraft, but these are being replaced by the Su-34 and are due for complete withdrawal from service in 2020. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- Su-24M: "Fencer-D", includes the addition of inflight refueling and expansion of attack capabilities with even more payload options. Su-24M has a 0.76 m (30 in) longer fuselage section forward of the cockpit, adding a retractable refueling probe, and a reshaped, shorter radome for the attack radar. A new PNS-24M inertial navigation system and digital computer were also added. A Kaira-24 laser designator/TV-optical quantum system (similar to the American Pave Tack) was fitted in a bulge in the port side of the lower fuselage, as well as Tekon track and search system (in pod), for compatibility with guided weapons, including 500 and 1,500kg laser-guided bombs and TV-guided bombs, and laser/TV-guided missiles Kh-25 and Kh-29L/T, anti-radar missiles Kh-58 and Kh-14 (AS-12 'Kegler') and Kh-59 (AS-13 'Kingbolt')/Kh-59M TV-target seeker guided missiles.
- Su-24M2: "Fencer-D", Next modernization of Su-24M introduced in 2000 with the “Sukhoi” program and in 1999 with the “Gefest” program. The modernized planes are equipped with new equipment and systems. As a result, they get new capabilities and improved combat efficiency, including new navigation system (SVP-24), new weapons control system, new HUD (ILS-31, like in Su-27SM or KAI-24) and expanding list of usable munitions (Kh-31A/P, Kh-59MK, KAB-500S). The last batch of the Sukhoi was delivered to the Russian VVS in 2009. Modernization continues with the program “Gefest”. All frontline bombers Su-24 in the Central Military District (CVO) received new sighting and navigation systems SVP-24 in 2013. - Su-24MK: export version of the Su-24M. - Su-24MR: "Fencer-E", dedicated tactical reconnaissance variant. Su-24MR retains much of the Su-24M's navigation suite, including the terrain-following radar, but deletes the Orion-A attack radar, the laser/TV system, and the cannon in favor of two panoramic camera installations, 'Aist-M' ('Stork') TV camera, RDS-BO 'Shtik' ('Bayonet') side-looking airborne radar (SLAR), and 'Zima' ('Winter') infrared reconnaissance system. - Su-24MP: "Fencer-F", dedicated electronic signals intelligence (ELINT) variant, intended to replace the Yak-28PP 'Brewer-E'. The Su-24MP has additional antennas for intelligence-gathering sensors, omitting the laser/TV fairing, but retaining the cannon and provision for up to four R-60 (AA-8) missiles for self-defense. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Su-24's external design owed much to both the T6 prototypes as well as the Su-15 "Flagon" from which it was directly developed from.
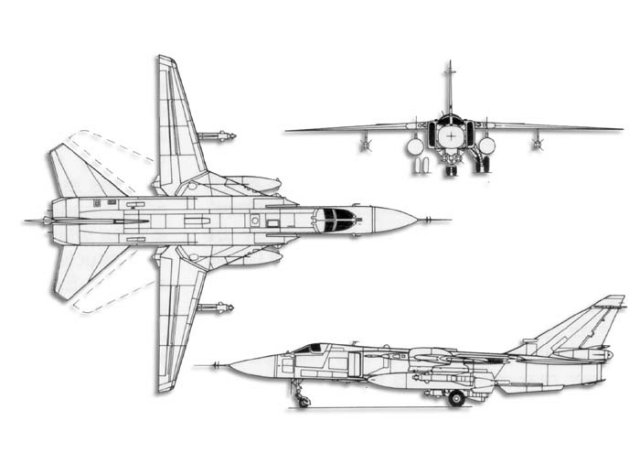
The wings are high-mounted, variable, swept-back, and tapered. The wing sweepback angle varies from 16° to 69°, with respect to the wing leading edge with four outer-wing panel fixed positions of 16°, 35°, 45° and 69°. There are twin turbofan engines. The air intakes are tapered away from the body, rectangular-shaped, and mounted on the body forward of the wings' leading edges. There are twin exhausts. The fuselage is long, slender, with pointed, solid nose, and rectangular-shaped body from the air intakes to the exhausts. There are two belly fins and four pylons. There is a bubble canopy. The dorsal spine extends from the cockpit to the tail. The tail fin is swept-back and tapered with square tip. The flats are high-mounted on the fuselage, swept-back, and tapered with angular tips. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Propulsion
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Su-24 is powered by a pair of Saturn/Lyulka AL-21F-3A series turbojet engines delivering 16,860 lbs of thrust each on dry and 24,675lbs of thrust with afterburner. It could hit a maximum speed of 1,320 km/h at sea level and up to 1,550 km/h at higher altitudes. Radius was limited to 2,775 km for ferry operations and 1,050 km for combat operations (without external fuel tanks). The Su-24 can carry different fuel tanks to increase service range, such as PTB-2,000 (1,860 l) or the PTB-3,000 (3,050 l).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Avionics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Avionics of the Su-24 Fencer were sophisticated by the standards of the time. The core of the avionics suite was the PNS-24 Tigr navigation-attack (nav-attack) system, which integrated a number of avionics subsystems. Avionics subsystems included:
- An Orion-A pulse-Doppler radar in the nose for navigation and targeting. - A built-in Chaika (Seagull) targeting system, with electro-optic sight and radio datalink for the Kh-23 / AS-7 Kerry and Kh-25 / AS-10 Karen radio-guided ASMs. The external assembly for the Chaika system was under the nose. Targeting laser-guided weapons required, as mentioned, carriage of a Fantasmagoria-series targeting pod on a wing pylon. A terrain-following system with a Relyef (Profile) terrain-following radar coupled to an autopilot and an infrared sensor mounted just in front of the windscreen are also fitted on the aircraft. - A Filin-N defensive countermeasures system, including a Beryoza (Birch) SPO-15 radar warning receiver (RWR), with distinctive antenna fairings on the sides of the top of the tailfin and alongside the engine inlets; an SPS-161 jammer with an antenna under the brake parachute fairing; and a Geran-F (Germanium-F) jammer with an antenna under the rudder and under the nose. - Short, medium, and long range radio navigation aids, along with a gyro-based inertial reference system (IRS); HF & VHF radios; identification friend or foe (IFF) transponder; instrument landing system (ILS); and flight data recorder. The Su-24M variant was fitted with the Kaira-24 laser designator for use with precision guided ordnance delivery replacing the original electro-optical sighting system. The greatest benefit of the M-variant lay in the implementation of a new weapons control system known under the name of PNS-24M Tiger NS. A ninth hardpoint was added to the design. Defensive measure were also improved with the new "Karpaty" system, incorporating the "Mak" infrared sensor on the upper fuselage surface amidships. The first production Su-24M went airborne on June 20th, 1979 with full acceptance into service coming in 1983. The Su-24M2 upgrades included a new SV-24 computer, liquid crystal displays, ILS-31 head-up display, digital moving map and global positioning system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The eight weapons pylons beneath the Su-24's fuselage, wing gloves and outer wing panels can carry a wide variety of weaponry, ranging from tactical and defence-suppression bombs and missiles through to nuclear weapons. The Su-24 basic version can carry several different air-to-surface missiles: Kh-23 or Kh-23M (NATO codename AS-7 Kerry) radio-command guided missiles (range 5km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-28 (AS-9 Kyle) and Kh-58 passive radar-homing missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried). It can also carry up to two Vympel R-60 (AA-8 Aphid) IR-homing air-to-air missiles with a range of 3km. Fencer attack aircraft can also carry laser guided bombs (KAB-500KR, KAB-500L) and conventional air bombs (AB-100, AB-250 (M54), AB-250 (M62), AB-500M-54, ODAB-500PM). 55mm S-5, 80mm S-8 or 120mm S-13 rocket pods can also be fixed on hardpoints.
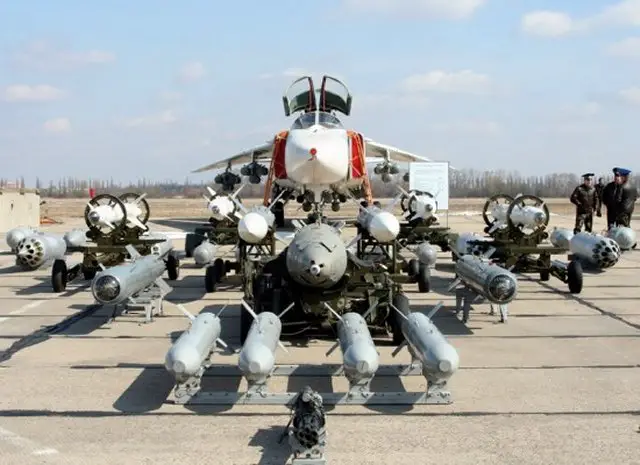 The Su-24M aircraft is armed with: Kh-25L (AS-10 Karen) laser-guided missiles (range 20km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-29LT (AS-14 Kedge) laser / TV-guided missiles (range 10km; up to three missiles carried); Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) passive radar-homing missiles (range 180km; up to two missiles carried); and Kh-59 (AS-13 Kingbolt) TV-command-guided missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried). The Su-24M aircraft is armed with: Kh-25L (AS-10 Karen) laser-guided missiles (range 20km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-29LT (AS-14 Kedge) laser / TV-guided missiles (range 10km; up to three missiles carried); Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) passive radar-homing missiles (range 180km; up to two missiles carried); and Kh-59 (AS-13 Kingbolt) TV-command-guided missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried). The aircraft can carry up to three gun pods with 23mm Gsh-6-23 guns, which have a rate of fire of 9,000 rounds a minute and fire unit of 500 rounds. 400 Russian Air Force Su-24M were upgraded to M2 standard with navigation and weapons systems to enable launch of new versions of Kh-29 and other missiles. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
Su-24 Fencer Sukhoi
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sukhoi Su-24 / Su-24M Fencer front-line attack aircraft
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Su-24 front-line attack aircraft/interdictor is manufactured by the Sukhoi Design Bureau Joint Stock Company, based in Moscow, and the Novosibirsk Aircraft Production Association, Novosibirsk, Russia. The Su-24M entered service in 1983 and is a development of the Su-24, known by the NATO codename "Fencer". The first production Su-24 went airborne on December 31st, 1971. The Su-24 would not be formally accepted into service until February 6th, 1975.
More than 1,400 of the aircraft were produced in all variants. Today, the Russian Air Force operates 400 upgraded Su-24M/M2 aircraft, but these are being replaced by the Su-34 and are due for complete withdrawal from service in 2020. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- Su-24M: "Fencer-D", includes the addition of inflight refueling and expansion of attack capabilities with even more payload options. Su-24M has a 0.76 m (30 in) longer fuselage section forward of the cockpit, adding a retractable refueling probe, and a reshaped, shorter radome for the attack radar. A new PNS-24M inertial navigation system and digital computer were also added. A Kaira-24 laser designator/TV-optical quantum system (similar to the American Pave Tack) was fitted in a bulge in the port side of the lower fuselage, as well as Tekon track and search system (in pod), for compatibility with guided weapons, including 500 and 1,500kg laser-guided bombs and TV-guided bombs, and laser/TV-guided missiles Kh-25 and Kh-29L/T, anti-radar missiles Kh-58 and Kh-14 (AS-12 'Kegler') and Kh-59 (AS-13 'Kingbolt')/Kh-59M TV-target seeker guided missiles.
- Su-24M2: "Fencer-D", Next modernization of Su-24M introduced in 2000 with the “Sukhoi” program and in 1999 with the “Gefest” program. The modernized planes are equipped with new equipment and systems. As a result, they get new capabilities and improved combat efficiency, including new navigation system (SVP-24), new weapons control system, new HUD (ILS-31, like in Su-27SM or KAI-24) and expanding list of usable munitions (Kh-31A/P, Kh-59MK, KAB-500S). The last batch of the Sukhoi was delivered to the Russian VVS in 2009. Modernization continues with the program “Gefest”. All frontline bombers Su-24 in the Central Military District (CVO) received new sighting and navigation systems SVP-24 in 2013. - Su-24MK: export version of the Su-24M. - Su-24MR: "Fencer-E", dedicated tactical reconnaissance variant. Su-24MR retains much of the Su-24M's navigation suite, including the terrain-following radar, but deletes the Orion-A attack radar, the laser/TV system, and the cannon in favor of two panoramic camera installations, 'Aist-M' ('Stork') TV camera, RDS-BO 'Shtik' ('Bayonet') side-looking airborne radar (SLAR), and 'Zima' ('Winter') infrared reconnaissance system. - Su-24MP: "Fencer-F", dedicated electronic signals intelligence (ELINT) variant, intended to replace the Yak-28PP 'Brewer-E'. The Su-24MP has additional antennas for intelligence-gathering sensors, omitting the laser/TV fairing, but retaining the cannon and provision for up to four R-60 (AA-8) missiles for self-defense. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Su-24's external design owed much to both the T6 prototypes as well as the Su-15 "Flagon" from which it was directly developed from.
The wings are high-mounted, variable, swept-back, and tapered. The wing sweepback angle varies from 16° to 69°, with respect to the wing leading edge with four outer-wing panel fixed positions of 16°, 35°, 45° and 69°. There are twin turbofan engines. The air intakes are tapered away from the body, rectangular-shaped, and mounted on the body forward of the wings' leading edges. There are twin exhausts. The fuselage is long, slender, with pointed, solid nose, and rectangular-shaped body from the air intakes to the exhausts. There are two belly fins and four pylons. There is a bubble canopy. The dorsal spine extends from the cockpit to the tail. The tail fin is swept-back and tapered with square tip. The flats are high-mounted on the fuselage, swept-back, and tapered with angular tips. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Propulsion
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Su-24 is powered by a pair of Saturn/Lyulka AL-21F-3A series turbojet engines delivering 16,860 lbs of thrust each on dry and 24,675lbs of thrust with afterburner. It could hit a maximum speed of 1,320 km/h at sea level and up to 1,550 km/h at higher altitudes. Radius was limited to 2,775 km for ferry operations and 1,050 km for combat operations (without external fuel tanks). The Su-24 can carry different fuel tanks to increase service range, such as PTB-2,000 (1,860 l) or the PTB-3,000 (3,050 l).
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Avionics
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Avionics of the Su-24 Fencer were sophisticated by the standards of the time. The core of the avionics suite was the PNS-24 Tigr navigation-attack (nav-attack) system, which integrated a number of avionics subsystems. Avionics subsystems included:
- An Orion-A pulse-Doppler radar in the nose for navigation and targeting. - A built-in Chaika (Seagull) targeting system, with electro-optic sight and radio datalink for the Kh-23 / AS-7 Kerry and Kh-25 / AS-10 Karen radio-guided ASMs. The external assembly for the Chaika system was under the nose. Targeting laser-guided weapons required, as mentioned, carriage of a Fantasmagoria-series targeting pod on a wing pylon. A terrain-following system with a Relyef (Profile) terrain-following radar coupled to an autopilot and an infrared sensor mounted just in front of the windscreen are also fitted on the aircraft. - A Filin-N defensive countermeasures system, including a Beryoza (Birch) SPO-15 radar warning receiver (RWR), with distinctive antenna fairings on the sides of the top of the tailfin and alongside the engine inlets; an SPS-161 jammer with an antenna under the brake parachute fairing; and a Geran-F (Germanium-F) jammer with an antenna under the rudder and under the nose. - Short, medium, and long range radio navigation aids, along with a gyro-based inertial reference system (IRS); HF & VHF radios; identification friend or foe (IFF) transponder; instrument landing system (ILS); and flight data recorder. The Su-24M variant was fitted with the Kaira-24 laser designator for use with precision guided ordnance delivery replacing the original electro-optical sighting system. The greatest benefit of the M-variant lay in the implementation of a new weapons control system known under the name of PNS-24M Tiger NS. A ninth hardpoint was added to the design. Defensive measure were also improved with the new "Karpaty" system, incorporating the "Mak" infrared sensor on the upper fuselage surface amidships. The first production Su-24M went airborne on June 20th, 1979 with full acceptance into service coming in 1983. The Su-24M2 upgrades included a new SV-24 computer, liquid crystal displays, ILS-31 head-up display, digital moving map and global positioning system. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The eight weapons pylons beneath the Su-24's fuselage, wing gloves and outer wing panels can carry a wide variety of weaponry, ranging from tactical and defence-suppression bombs and missiles through to nuclear weapons. The Su-24 basic version can carry several different air-to-surface missiles: Kh-23 or Kh-23M (NATO codename AS-7 Kerry) radio-command guided missiles (range 5km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-28 (AS-9 Kyle) and Kh-58 passive radar-homing missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried). It can also carry up to two Vympel R-60 (AA-8 Aphid) IR-homing air-to-air missiles with a range of 3km. Fencer attack aircraft can also carry laser guided bombs (KAB-500KR, KAB-500L) and conventional air bombs (AB-100, AB-250 (M54), AB-250 (M62), AB-500M-54, ODAB-500PM). 55mm S-5, 80mm S-8 or 120mm S-13 rocket pods can also be fixed on hardpoints.
 The Su-24M aircraft is armed with: Kh-25L (AS-10 Karen) laser-guided missiles (range 20km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-29LT (AS-14 Kedge) laser / TV-guided missiles (range 10km; up to three missiles carried); Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) passive radar-homing missiles (range 180km; up to two missiles carried); and Kh-59 (AS-13 Kingbolt) TV-command-guided missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried). The Su-24M aircraft is armed with: Kh-25L (AS-10 Karen) laser-guided missiles (range 20km; up to four missiles carried); Kh-29LT (AS-14 Kedge) laser / TV-guided missiles (range 10km; up to three missiles carried); Kh-31P (AS-17 Krypton) passive radar-homing missiles (range 180km; up to two missiles carried); and Kh-59 (AS-13 Kingbolt) TV-command-guided missiles (range 90km; up to two missiles carried). The aircraft can carry up to three gun pods with 23mm Gsh-6-23 guns, which have a rate of fire of 9,000 rounds a minute and fire unit of 500 rounds. 400 Russian Air Force Su-24M were upgraded to M2 standard with navigation and weapons systems to enable launch of new versions of Kh-29 and other missiles. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||





























