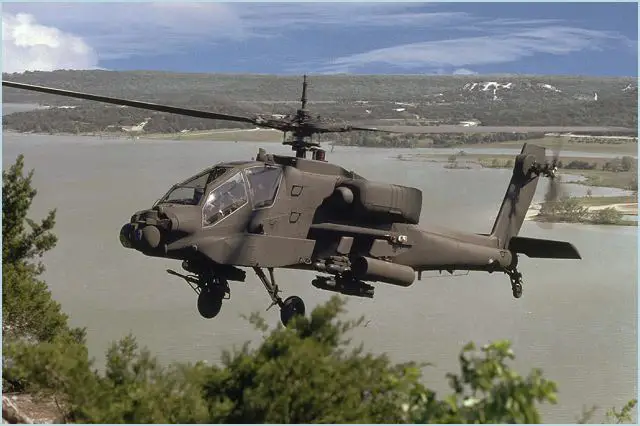
AH-64 Apache
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AH-64 Apache attack helicopter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
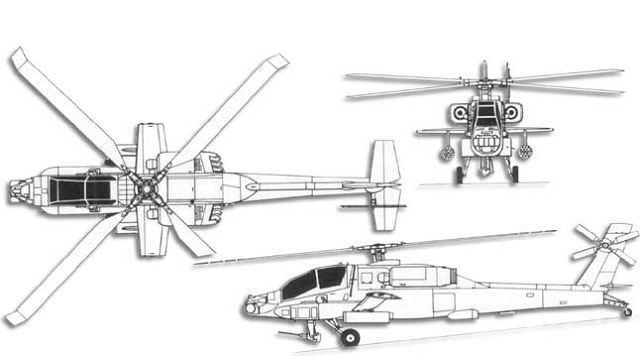
The AH-64 Apache is a four-blade, twin-engine attack helicopter with a tail wheel-type landing gear arrangement, and a tandem cockpit for a two-man crew. The AH-64 is now manufactured by the Company Boeing. Originally, the Apache started life as the Model 77 developed by Hughes Helicopters for the United States Army's Advanced Attack Helicopter program to replace the AH-1 Cobra, and was first flown on 30 September 1975. In all, 12 nations fly, have ordered or have selected AH-64D Apache helicopters for their defense forces. The U.S. Army has ordered more than 600 Apache Longbow aircraft through multi-year contracts and follow-on purchases. Boeing delivered the first U.S. Army Apache Longbow in April 1997, and the first production AH-64D Apache Block III in October 2011. Follow-on orders and upgrades will keep the Apache in production well into the next decade and beyond. International customers include Egypt, Greece, Israel, Japan, Kuwait, The Netherlands Saudi Arabia, Singapore, the United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom, The first international AH-64D Apache was delivered to the Royal Netherlands Air Force in May 1998 and the first international AH-64D Apache Block III was delivered in May 2012. More than 300 new and remanufactured international AH-64Ds have been delivered or are in production. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The first of the upgraded block II Apaches was delivered to the US Army in February 2003. Block II included upgrades to the digital communications systems of 96 A-model Apaches to improve communications within the "tactical internet". In October 2007, Boeing delivered the first extended block II to the US Army.
In July 2005, the US Army awarded Boeing a development contract for block III improvements, which entered service in 2011. In December 2009, the maiden flight test of AH-64D Apache with block III structures was completed. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The crew sits in tandem, with the pilot sitting behind and above the copilot/gunner. Both crew members are capable of flying the aircraft and performing methods of weapon engagements independently. The AH-64 Apache has a four-blade main rotor and a four-blade tail rotor. The crew compartment has shielding between the cockpits, such that at least one crew member can survive hits. The compartment and the rotor blades are designed to sustain a hit from 23-millimeter rounds. The airframe includes some 1,100 kg of protection and has a self-sealing fuel system to protect against ballistic projectiles. The aircraft was designed to meet the crashworthiness requirements of MIL-STD-1290, which specifies minimum requirement for crash impact energy attenuation to minimize crew injuries and fatalities. This was achieved through incorporation of increased structural strength, crashworthy landing gear, seats and fuel system.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionics and equipment | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The AH-64 Apache is fitted with helmet-mounted display, the Integrated Helmet and Display Sighting System (IHADSS); among other abilities the pilot or gunner can slave the helicopter's 30 mm automatic M230 Chain Gun to his helmet, making the gun track head movements to point at where he looks. The AH-64D Longbow Apache is equipped with the Northrop Grumman millimeter-wave Longbow radar. The Longbow fire control radar incorporates an integrated radar frequency interferometer for passive location and identification of radar-emitting threats. The AH-64 Apache is also equipped with an electronic warfare suite consisting of: AN/APR-39A(V) radar warning receiver from Northrop Grumman (formerly Litton) and Lockheed Martin; Lockheed Martin AN/APR-48A Radar Frequency Interferometer Electronic Support target acquisition system; AN/ALQ-144 infra-red countermeasures set from BAE Systems IEWS (formerly Sanders, a Lockheed Martin company); AN/AVR-2 laser warning receiver from Goodrich (formerly Hughes Danbury Optical Systems then Raytheon); AN/ALQ-136(V) radar jammer developed by ITT; and chaff dispensers.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The AH-64 is powered by two General Electric T700 turboshaft engines with high-mounted exhausts on either side of the fuselage. The AH-64 Apache can reach a maximum cruise speed of 293 km/h.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The main armament of the AH-64 Apache includes a 30mm automatic Boeing M230 chain gun is located under the fuselage. It provides a rate of fire of 625 rounds a minute. The helicopter has capacity for up to 1,200 rounds of ammunition. The latest version of the Apache, the AH-64D is armed with the Lockheed Martin / Boeing AGM-114D Longbow Hellfire air-to-surface missiles which has a maximum range from 8 to 12 km. The Apache can be also armed with air-to-air missiles (Stinger, AIM-9 Sidewinder, Mistral and Sidearm) and the advanced precision kill weapon system (APKWS), formerly known as Hydra, family of guided and unguided 70mm rockets.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||

































