Ka-52 Alligator Hokum B Kamov
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
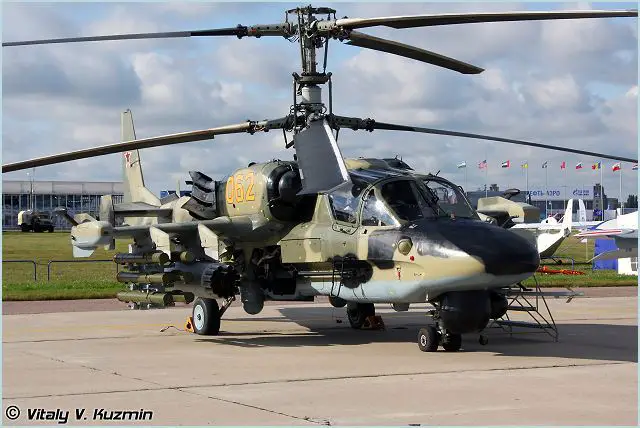
Ka-52 Alligator Hokum B Kamov attack helicopter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
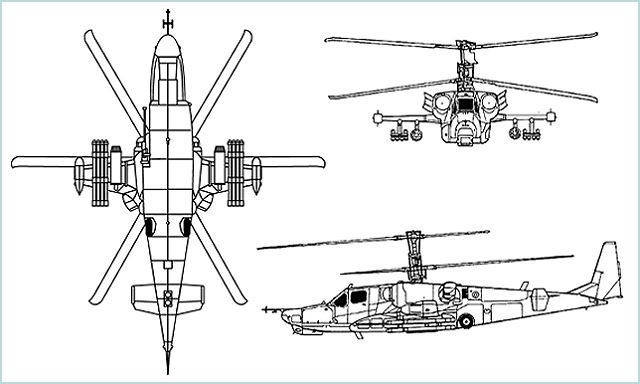
The Kamov Ka-52 Alligator is Russian attack helicopter. The multi-role all-weather combat Ka-52 "Alligator" helicopter is a twin-seat derivative of the Russian-made attack helicopter Ka-50. The first prototype of the Ka-52 was unveiled at the aerospace event Aero India in 1996. The Ka-52 is designed to defeat armor materiel, low-speed aerial targets, as well as exposed and sheltered manpower in the daytime and at night, in VFR (Visulal Flight Rules) and IFR (Instrument Flight Rules) weather conditions. The Ka-52 combat helicopter can be used to defeat targets on the battlefield within wide ranges of launching high-precision supersonic antitank missile systems, including launches from more than a 6-km range within a stand-off zone of air defense artillery and air defense missile systems. The two-seat Ka-52 is capable of carrying out group combat missions, including those involving a combined air strength.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- The Ka-52 is based to the Ka-50.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The crewmembers are accommodated side by side in a common cockpit and each of them can fly the helicopter and control all its systems. The helicopter's two-seat configuration extends the range of combat missions and employment conditions. In terms of airframe and systems, the Ka-52 is 85 percent identical to the Ka-50 helicopter, which facilitates its full-scale production and decreases operation costs. The Ka-52 has been used to develop the Ka-50-2 helicopter version with a tandem seating configuration. The Alligator's other advantages include a high degree of protection for the crew, state-of-the-art automated systems that make piloting easier, and ease of ground maintenance. Powerful armoured protection and ejection seats unique fort its class make the Ka-52 Alligator one of the safest helicopters for crew, while the helmet-mounted target designation system means the helicopter can fly military missions around the clock and at any time of year, significantly reducing pilots' workload.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionics | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Ka-52 Alligator is equipped with state-of-the-art avionics developed mainly by Concern Radioelectronic Technologies, also a Rostec company. The ECM (Electronic countermeasure) equipment is arranged in the pods at wingtips. The heliborne avionics suite enables the crew to perform flight control and air navigation round-the-clock and all the year round The surveillance and fire control systems, including TV, laser and thermal imaging equipment, enable the pilot to detect and defeat targets in the daytime and at night. For night flight, the pilot is provided with night vision goggles. The Ka-52 is equipped with a new integral multifunctional avionics suite incorporating passive/active surveillance and sighting systems. The suite is intended for piloting, air navigation and weapon control. The Ka-52 is equipped with a FAZOTRON cabin desk radio-locator allowing flies in adverse meteorological conditions and at night. The necessary information acquired by this radio-locator is transferred to cabin desk’s multi-functional display screen. The helicopter is equipped with satellite navigation, with colour displays in the cockpit conveying a wide range of information, including a digital map of the terrain.
The Crossbow (Russian: Arbalet) radar system can overcome military challenges at any time of day or night and in any weather conditions, including deliberate or natural radio electronic interference. Crossbow gives Ka-52 pilots a radar facility map of the local terrain, making it possible to identify and avoid hazardous wet and turbulent zones, and also to rapidly locate targets. Radioelectronic Technologies also supplies the Alligator with Hunter (Russian: Okhotnik) series systems for laser-guided weapons and video imaging processing for missile guidance. Thanks to these systems, the helicopter can rapidly identify and simultaneously engage two targets, guiding Attack (Russian: Ataka) and Whirlwind (Russian: Vikhr) missiles with high accuracy. The SAU-800 autopilot system allows for manual and automatic piloting. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Ka-52 is powered with two uprated 1,863kW Klimov TV3-117VMA-SB3 turboshafts. Two 1,633kW TV3-117VMA turboshafts in prototype. Climbing ability of the helicopter is lower – 8 m/s (10 m/s for its single-seat modification), allowable overload factor is only +3.0 g, in comparison with +3.5 g for Ka-50 version. Hovering ceiling was also reduced from 4,000 m to 3,600 m. Maximum speed (310 km/h) and operational range of 460 km remained unchanged. Like other Kamov helicopters, it features Kamov's characteristic contra-rotating co-axial rotor system, which removes the need for the entire tail rotor assembly and improves the aircraft's aerobatic qualities—it can perform loops, rolls and “the funnel” (circle-strafing), where the aircraft maintains a line-of-sight to the target while flying circles of varying altitude, elevation and airspeed around it. Using two rotors means that a smaller rotor with slower-moving rotor tips can be used compared to a single-rotor design.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
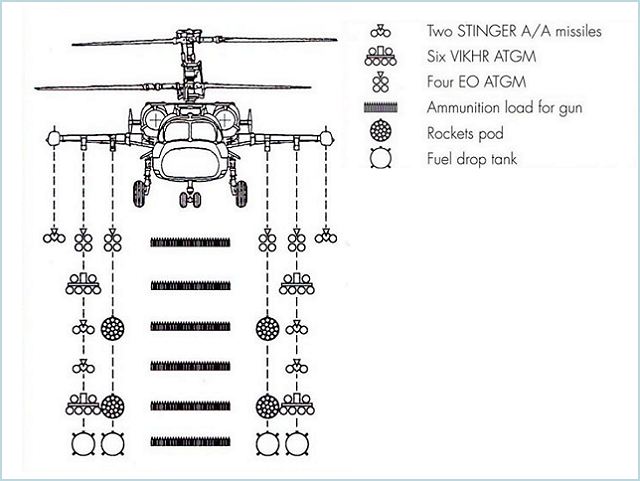
The Ka-52 is equipped with powerful offensive weapons that can be configured for different military missions. The helicopter is equipped with the same weapons as those carried by the Ka-50, including the Khrizantema (close-in) and the Hermes (long-range) new-generation ATGMs. The Ka-52's main armament includes high-precision Vikhr and Ataka ATGMs, a 30mm rapid-firing flexible 2A42 gun mount with an ammunition load of 460 rounds, and S-8 and S-13 aircraft rockets. The rapid-fire unit NPPU-80 with 2A42 30mm gun is located on the helicopter's starboard. For defeating aerial targets, Igla-V missiles, a gun mount, and Vikhr ATGMs are used. The following weapons can be suspended at six underwing hardpoints:
- up to 16 Vikhr ATGMs; - up to 80 S-8 rockets; - up to ten S-13 rockets; - up to four Igla-V missiles; - 23mm gun mount pods; - various aerial bombs. The total weight of the weapons carried on the underwing hardpoints is 2,500 kg. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||































