Shahed 285
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shahed 285 reconnaissance - attack - maritime helicopter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
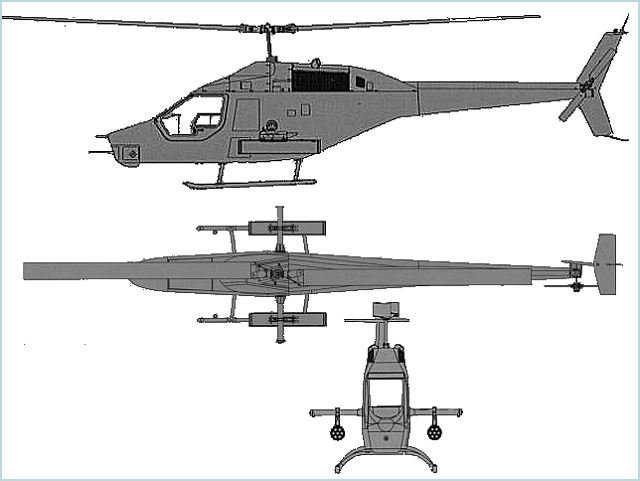
Shahed 285 is a light attack/reconnaissance helicopter developed, designed and manufactured in Iran. It was unveiled on 24 May 2009. It is being produced in three versions: a light reconnaissance version, an attack version and a maritime patrol/anti-ship version. The Shahed 285 was unveiled in May 2009 on the anniversary of the 1982 liberation of the Iranian city Khoramshahr -- which was occupied by Iraqi forces during the 1980-88 war. The IRGC (Islamic Revolution Guards Corps) says the state-of-the-art helicopter is capable of taking part in seaborne and airborne combat operations. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main variants: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
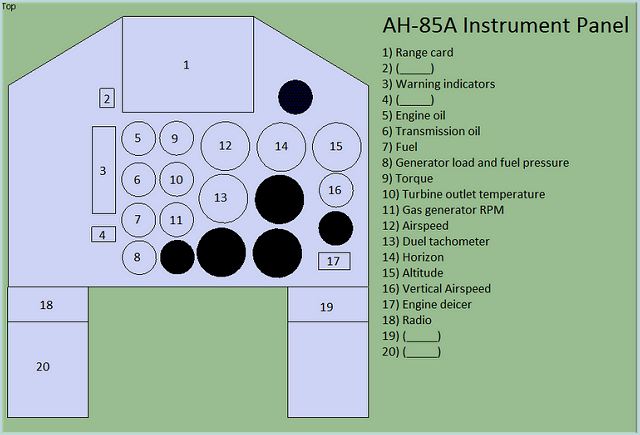
- AH-85A: Light overland version. It is intended for low-intensity policing conflicts or border patrol. Armed with a 7.62 mm machine-gun in the nose and two 70-mm rocket pods on hard-points.
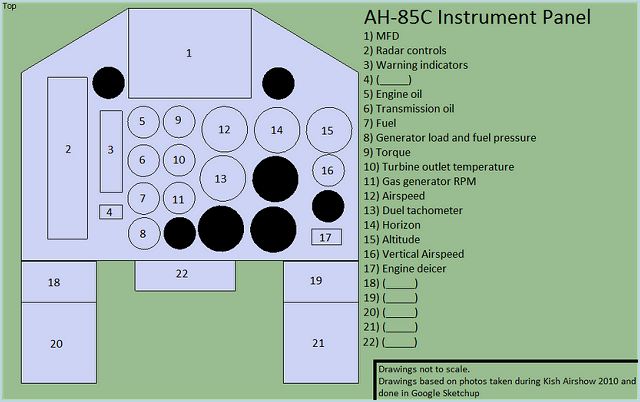
- AH-85B: Heavy overland version. Although it has yet to be seen, this model is said to be intended for "non-symmetrical wars". [11] Nothing further is known. - AH-85C: Naval attack version. Equipped with a basic surface-search radar in it's nose instead of a machine-gun. Also equipped with a slightly different cockpit configuration then the AH-85A. Armament includes either two Kowsar AShMs or eight Sadid-1 missiles. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The body is built of of "non-metallic composite components" which indicates materials like fiberglass, kevlar or other bullet-resistant fabrics, and even some of the lightweight ceramics though latter are exceptionally expensive.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionic and combat systems | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The cockpit uses the basic instrumentation configuration from the Shahed 278 though additional controls can be found running along the left and right hand side of the cockpit.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Shahed 285 prototypes are powered by the Allison 250-C20 engine while the production models are scheduled to be fitted with the more powerful 250-C20B which can be identified by the air splitter on the intakes for the engine which cannot be seen on the prototypes.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
On the side of the fuselage, near the passenger doors, they are two weapons pylons with hard-points for various weapons. The Shahed 285 can carry autocanons, machine guns, guided missiles, anti-armor missiles and air-to-air and air-to-sea missiles.
AH-85A: One 7.62 mm PKMT machine-gun in a chin mount at the front of the helicopter. Twin pylons on either side carry a single LAU-68 rocket launcher each which can fire a total of 14 unguided rockets. AH-85B: This heavier version can be armed with anti-tank guided missile and some heavier gun-pods. AH-85C: No armament, but this version is equipped with a basic surface search radar. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Video Shahed 285 reconnaissance - attack - maritime helicopter
{youtube}ySBz3uex4G8{/youtube} |
||||||||||||||||||||||































