CH-47F Chinook
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
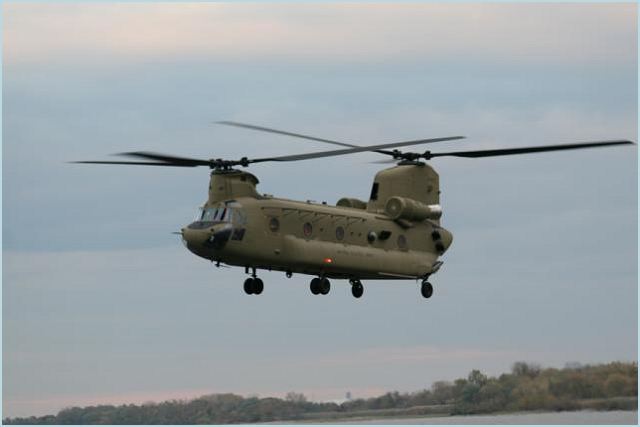
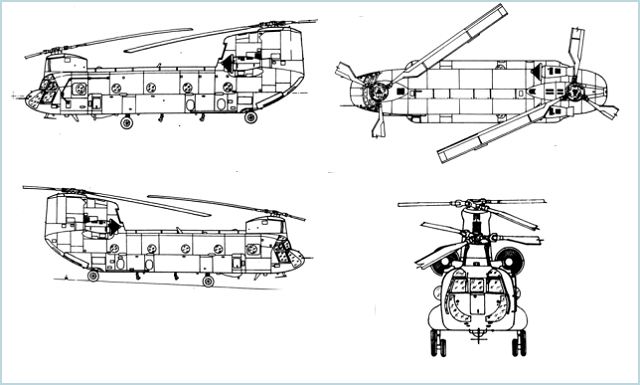
CH-47F Chinook transport helicopter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The CH-47F is an improved and more powerful version of the CH-47. The U.S. Army's first major design leap was the now-common CH-47D, which entered service in 1982. The first CH-47F, an upgraded D model, took it maiden flight in 2001. The first production rolled out on 15 June 2006 at Boeing's facility inRidley Park, Pennsylvania, and first flew on 23 October 2006. Boeing has delivered 48 F-model helicopters to the U.S. Army through August 2008; at that time Boeing announced a five-year contract with the Army, worth over $4.8 billion for 191 more, plus 24 options. In February 2007, the Netherlands became the first international customer, ordering six CH-47Fs, expanding its current fleet to 17. The Netherlands also plans to upgrade its current 11 CH-47Ds to the CH-47F configuration. On 10 August 2009, Canada signed a contract to purchase 15 CH-47Fs for delivery in 2013–14, entering service with the Royal Canadian Air Force. On 15 December 2009, Britain announced its Future Helicopter Strategy, including the purchase of 24 new CH-47Fs to be delivered from 2012. Australia ordered seven CH-47Fs in March 2010 to replace its six CH-47Ds between 2014 and 2017. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Main Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- CH-47A: The all-weather, medium-lift CH-47A Chinook was powered initially by Lycoming T55-L-5 engines rated at 2,200 horsepower (1,640 kW) but then replaced by the T55-L-7 rated at 2,650 hp (1,980 kW) engines or T55-L-7C engines rated at 2,850 hp (2,130 kW).
- ACH-47A: The ACH-47A was originally known as the Armed/Armored CH-47A (or A/ACH-47A). It was officially designated ACH-47A by U.S. ArmyAttack Cargo Helicopter and unofficially Guns A Go-Go. Four CH-47A helicopters were converted to gunships by Boeing Vertol in late 1965. - CH-47B: The CH-47B was an interim solution while Boeing worked on a more substantially improved CH-47C. CH-47B was powered by two Lycoming T55-L-7C 2,850 shp (2,130 kW) engines. It featured a blunted rear rotor pylon, redesigned asymmetrical rotor blades, and strakes along the rear ramp and fuselage to improve flying characteristics. - CH-47C: The CH-47C featured more powerful engines and transmissions. Three versions of the "C model" were built. The first had Lycoming T55-L-7C engines delivering 2,850 shp (2,130 kW). The "Super C" included Lycoming T55-L-11 engines delivering 3,750 shp (2,800 kW), an upgraded maximum gross weight of 46,000 lb (21,000 kg) and a pitch stability augmentation system (PSAS). - CH-47D: The CH-47D shares the same airframe as earlier models, the main difference being the adoption of more powerful engines. Early CH-47Ds were originally powered by two T55-L-712 engines, the most common engine is the later T55-GA-714A. With its triple-hook cargo system, the CH-47D can carry heavy payloads internally and up to 12,000 kg externally. The D-model was first introduced into service in 1979. - MH-47D: The MH-47D variant was developed for special forces operations and has in-flight refueling capability, a fast-rope rappelling system and other upgrades. - MH-47G: The MH-47G Special Operations Aviation (SOA) version is currently being delivered to the U.S. Army. It is similar to the MH-47E, but features more sophisticated avionics including a digital Common Avionics Architecture System (CAAS). The CAAS is a common glass cockpit used by different helicopters such as MH-60K/Ls, CH-53E/Ks, and ARH-70As. The MH-47G also incorporates all of the new sections of the CH-47F. - CH-47J: The CH-47J is a medium-transport helicopter for the Japan Ground Self-Defense Force (JGSDF), and the Japan Air Self-Defense Force(JASDF). The differences between the CH-47J and the CH-47D are the engine, rotor brake and avionics. To use it by the general transportation, SAR and disaster activity like U.S. forces. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back menu | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The CH-47F design features alterations to the airframe structure to reduce the effects of vibration, as well as other structural enhancements the cockpit, cabin, aft section, pylon and ramp. The cabin provides 42m³ of cargo space and 21m² of cargo floor area and can accommodate two HMMWVs (high-mobility multipurpose wheeled vehicle) or an HMMWV together with 105mm howitzer and gun crew. The main cabin can hold from 33 fully equipped troops to 50 troops, according to the seating arrangements and equipment being carried. For medical evacuation, the cabin can accommodate 24 litters (stretchers). Ramp operations can be carried out on water using an optional power-down ramp and water dam configuration.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionics and equipment | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The CH47F is fitted with EW avionics including a Rockwell Collins Common Avionics Architecture System (CAAS) cockpit, and BAE Systems' Digital Advanced Flight Control System (DAFCS). The Rockwell Collins digital cockpit is fitted with the common avionics architecture system (CAAS) with improved electrical, avionics and communication systems. CAAS includes: five multi-function displays, moving map display; digital modem; BAE Systems digital advanced flight control system (DAFCS); data transfer system storing preflight and mission data.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The CH-47F is powered with a new 3,630 kW horsepower T55-GA-714A Honeywell engines, an upgraded airframe featuring greater single-piece construction for lower maintenance requirements. The CH-47F can fly at speeds of over 282 km/h with a payload of more than 9,500 kg. The operating range of CH-47F is increased to 609 km
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The CH-47F can be armed with three machine guns: two in the crew door on the starboard side and one window-mounted on the port side.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back menu | ||||||||||||||||||||||































