NH90
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NH90 Multi-Mission helicopter
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
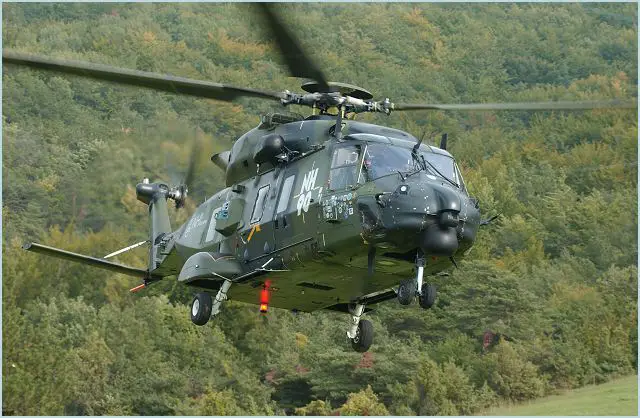
The NH90 is a European military helicopter designed against NATO requirements to meet a long term need. The NH90 meets the latest safety standards and is able to operate in harsh military environments, over land and sea, day or night. In 1985 five European nations signed a memorandum of understanding covering a NATO helicopter for the 90s, or NH 90. The UK dropped out of the programme in 1987 in favor to the EH 101, leaving France, Germany, Italy and the Netherlands in the project by means of NH Industries. This was established in France in 1992 to control a collaborative programme involving Eurocopter France (with NFT [Norway] as a risk-sharing partner from 1994), Agusta, Eurocopter Deutschland and Fokker. The NH90 entered service in 2006 and has been selected as a medium multi-role helicopter by 14 nations. The first NH90s were delivered by late 2006 to the German Army. These were followed by Italian and Finnish helicopters in 2007. Later during 2007, the Italian and French navies started to receive their NFH versions and the first Swedish NH90s were also delivered. On 18 December 2007 the first two MRH 90 aircraft were delivered to the Australian Defence Force. The Royal Netherlands Navy got its first NH90 NFH in April 2010. Norway started to receive their NH90s in November 2011. New Zealand received their first two NH90s in December 2011. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The common core air vehicle of the NH90 is based on a twin engine, four blade main rotor design and incorporates innovative features to provide true multi-role capability; Carbon fibre fuselage with twin doors and rear ramp, composite rotor blades, modular avionic system integrated within a full glass cockpit. The NH90 is designed to be as versatile as possible. With a spacious cabin, large sliding side doors each side, a rear ramp and a modular cabin design, it can be configured to specific missions and re-roled quickly. It is also designed to be survivable with a specific focus on ballistic tolerance and self protection, both necessities when operating in a combat environment. Up to 20 troops or 12 stretchers can be carried in the NH-90's TTH cabin. Small tactical vehicles such light armoured vehicle can be carried, with access via a hydraulic rear ramp. Up to 2,500kg of cargo can be carried onboard.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Avionic | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The NH90 uses an Advanced control of helicopter systems, communication suite and flight, navigation and mission aids to enable a high crew output. Configurable screens provide necessary information and simplified controls reduce crew workload to focus on safety and mission success. The NH90 is equipped with decoy-based countermeasures system developed by MBDA which provides active protection across the entire threat spectrum, and especially against IR homing missiles (plus radar and other homing methods). The system can operate automatically or semi-automatically in association with a missile detector or RWR system. The tactical system and digital map generator produced by the Company Dornier offers a real time digital terrain map, scanned maps and aeronautical information for navigation purposes. As an option, it can provide real time data transmission. At the front, the NH90 is fitted with a FLIR thermal imager piloting and navigation aid developed by Alenia Marconi. The pilot is equipped with a 3rd generation night vision HMSD (Helmet Multi Display), produced by Thales Avionics, enables the pilot to carry out night tasks. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Two engine types are available to increase the NH 90's export potential. The first of five flying and one ground-test prototypes was the French-assembler PT 1 that first flew on 18 December 1995 with RTM 322 engines. The NH-90 features a 4-bladed main rotor with blades made from composite materials and the hub from titanium and a 4-bladed tail rotor assembly. The NH90 is now is powered by 2 Rolls-Royce/Turbomeca RRTM322-01/9, or two General Electric/Fiat Avio T700/T6E1 turbo-shaft engines.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The Nato frigate helicopter can be armed with anti-submarine torpedoes, air-to-surface missiles and air-to-air missiles. The TTH NH90 version can be armed with internal pintle mounted machine gun (7.62 or 12.7 mm) and ¦20mm cannon in pod.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
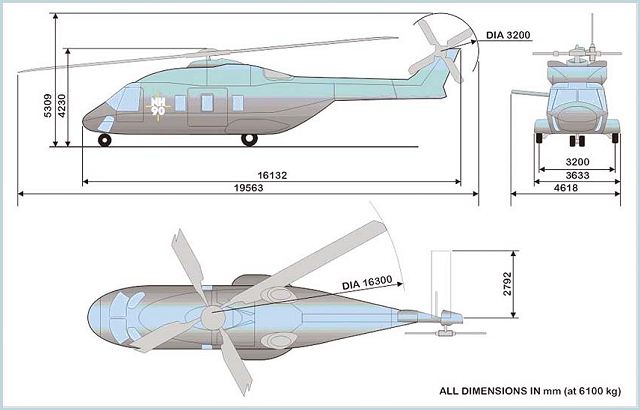
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Video NH90 TTH Tactical Troop Transport Multi-Mission helicopter
{youtube}HYl8u3lPdas{/youtube} |
||||||||||||||||||||||
































