Lasta-95 Yugolmport
| a | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
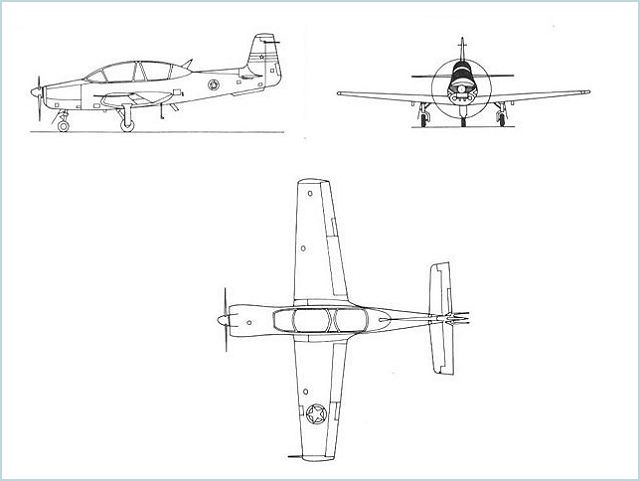
LASTA-95 YugoImport Advanced training aircraft
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
“LASTA-95” aircraft is designed for selection, initial and basic training of pilots, it offers low landing and takeoff speeds and pilot-friendly handling, forgiving potential errors by inexperienced pilots. This training aircraft is distributed and marketed by the Serbian company YugoImport. In view of a domestic requirement and the potential for a strong export market, the Yugoslav government issued a directive to industry for the development of a new and highly maneuverable tandem-seat prop trainer. This was seen as a preferable option for the replacement of Utva 75, in use by the Yugoslav Air Force in the basic training role. The first prototype was completed by the spring of 1985. And, following completion of the initial testing phase, the first flight was achieved on September 2, 1985. Even at this stage the Lasta prototype has seen substantial changes; in the choice for a new propeller, changes in the weight and balance and an improved fuel and hydraulic system. In January 1989, was issued a modified version - Lasta 2, a lighter, with shorter fuselage and a new electronics system including fire control Ferranti ISIS D-282. By early 1990s Utva, and her partner, have produced enough parts for the completion of 10 pre-production airframes. At the same time the Yugoslav Air Force has decided to cut the requirement to only 6 examples, and the remaining four were left unassembled and crated. The initial batch airframes received serials in the 54151 - 54156 range. Due to space and time constraints the Aviation Test Center, in Batajnica, could only accept 2 airframes for testing. These tests have established aircraft suitability and a recommendation for initial production was issued. With the early break-up of Yugoslavia, and the ensuing civil war, testing and production were abandoned and the airframes preserved at Utva factory in Pancevo. In late 2009, it was announced that Iraq would purchase 20 Lasta 95 aircraft. The Serbian Air Force is also interested in purchasing 16 Lasta 95's. The first three Lasta 95s were transferred to Iraq on August 5, 2010. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
-• BASIC VERSION OF THE AIRCRAFT is built against the requirements for aerobatic category loads of (nz_max = 6.0, nz_min = -3).
• ARMED VERSION OF THE AIRCRAFT is built against the requirements for utility category with loads of (nz_ max = 4.4, nz_ min = -1.8). |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Design | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Aircraft cockpit provides:
• Ergonomic accommodation for 90% of pilots according to current AF & AD standard, in the range of 5 to 95% of pilot statures and comfortable accommodation for 99% of pilots. • Good cockpit visibility and direct visibility of approaching runway (with 2o reserve) from the front seat. Rear seat headroom of minimum 100 mm. • Ergonomically built pilot seat, adjustable in height, accepts back-carried pilot parachute, provided with harness that secures the pilot in all stages of flight but allows normal handling of all cockpit controls, as well as rapid and easy aircraft evacuation on the ground and in the air. • Adjustable pedals. • Pilot rescue by normal cockpit evacuation (without ejection seat), by piercing of cockpit canopy with detonating cutter. • Aircraft flying in basic instrumental flight training from the front cockpit. Provided with instrumental flying simulation system which can be easily mounted and removed. Fuel installation: • Integral wing fuel tanks fitted ahead of front spar • Collecting tank in fuselage • Jet supply pump • Auxiliary electric pump • Fuel unbalance cock • Fire protection cock Hydraulic system features: • Designed for landing gear retracting/extending and powering the braking system. • Hydraulic system is featuring with simplicity and lightweight; system is powered by electro-hydraulic generator that does not use power of aircraft engine, equipped with auxiliary hand pump and reliable and simple hydraulic connectors. Landing gear features: • Enables takeoff and landing on concrete and prepared grass runways. Retracted and extended by hydraulic actuators. • Emergency mechanical release. • Main wheel tire dimensions 380 ? 150. • Nose wheel tire dimensions 330 ? 130. • Disc brakes fitted to main wheels. • Differentially controlled braking. • Nose strut view. Electrical equipment: • Electric circuit 28V DC. • Main source: Alternator 2 kW. • Auxiliary source: Ni-Cd battery 17 Ah. • Engine starting by external generator or by battery. • Alternating current system (115/26 V, 400 Hz) by means of static converter of 50 VA. • Lighting: • Position lights • Landing spotlight • Taxi lights • Anti-collision light |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Armament | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lasta-95 weapons system:
• The aircraft can perform training in gunning, rocketing and bombing with application of collimator sight (optionally, upon customer’s request, with optoelectronic sight), engaging the following airborne ordnance: • Pods with machine guns cal. 7.62 mm or 12.7 mm • Honeycomb-type multiple rocket launchers 57 mm • 2 x 100 kg aerial bombs: Optionally, aircraft can be used for homeland security misions, as follows: • Light close air support of counterinsurgency operations and • Area patrol / light attack missions Lasta-95 armament: • The aircraft can perform training in gunning, rocketing and bombing with application of collimator sight (optionally, upon customer’s request, with optoelectronic sight), engaging the following airborne ordnance: • Pods with machine guns cal. 7.62 mm or 12.7 mm • Honeycomb-type multiple rocket launchers 57 mm • 2 x 100 kg aerial bombs |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Propulsion | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Engine Lycoming AEIO-540-L1B5D main features:
• Six cylinders • Flat, opposed • Direct fuel injection • Air cooling • Designed for aerobatic flying • Propeller Hartzell twin-bladed • Maximum continuous output (H = 0 at 2700 r.p.m.) 220 kW |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accessories | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Controls is feturing with:
• All control surfaces are mechanically controlled. • Flaps and all three trimmers electrically actuated. • Electric trimmers for rudder and ailerons. • Mechanical, spring-loaded trimmer for elevator. Other mechanical controls: • Engine • Fuel • Cockpit canopies • Landing gear, emergency • Cockpit heating and ventilation • Armament controls Electronic equipment: The aircraft is outfitted with modern electronic equipment that meets all current international standards and provides the following main functions: • Two-way radio communication air-ground and air-air in VHF range, with frequency spacing of 25 and 8.33 kHz, with minimum output of 10 W, simultaneous reception of all audio signals in both cockpits and enabling permanent communication between two pilots. |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specifications | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
a a
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
{youtube}DdMIf4W3Jf8{/youtube}
|
||||||||||||||||||||||































