- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
HAWK MIM-23
HAWK MIM-23
Short to medium altitude ground-to-air defense missile system - United States
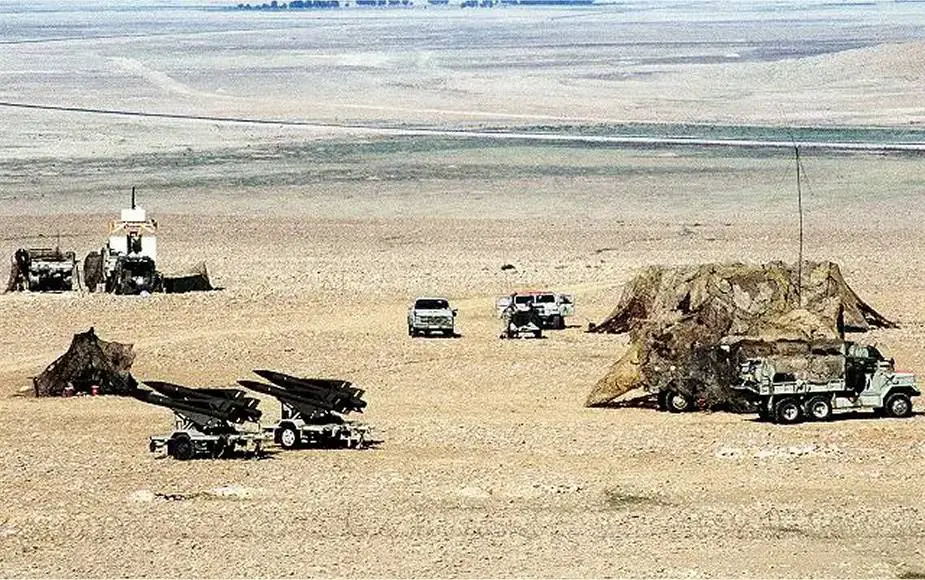

Description
The HAWK (Homing All the Way Killer) MIM-23 is an all-weather low to medium-altitude ground-to-air missile system developed and designed by the American Defence Company Raytheon. The HAWK semi-active radar seeking medium-range SAM system commenced development in 1952 with the US Army awarding a full-scale development contract to Raytheon for the missile in July 1954. Northrop was to provide the launcher and loader, radars and fire control. The first guided test firing took place in June 1956 with the development phase completed in July 1957. Initial Operational Capability (IOC) of the Basic HAWK, MIM-23A, took place in August 1960 when the first US Army battalion was activated. In 1959, a NATO Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed for NATO HAWK between France, Italy, the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany and the US for the co-production of the system in Europe. In addition, special grant aid arrangements were made to deliver European-built systems to Spain, Greece and Denmark and direct sale arrangements of US-built systems were made with Japan, Israel and Sweden. The Japanese sale soon expanded into a country-to-country co-production agreement with production initiated in 1968. In the same region, the US also made grant aid deliveries of HAWK to Taiwan and South Korea. On November 3, 2022, Spain announced the delivery of four MIM-23B I-Hawk Phase III air defense missile systems. On November 4, 2022, the United States announced funding to refurbish HAWK air defense missiles that will be delivered to Ukraine.
Hawk MIM-23 variants:
- HAWK Phase I: Phase I involved the replacement of the CWAR with the AN/MPQ-55 Improved CWAR (ICWAR), and the upgrade of the AN/MPQ-50 PAR to Improved PAR (IPAR) configuration by the addition of a digital MTI (Moving Target Indicator). The first PIP Phase I systems were fielded between 1979 and 1981.
- HAWK Phase II: Developed in 1978 and fielded between 1983 and 1986. upgraded the AN/MPQ-46 HPI to AN/MPQ-57 standard by replacing some of the vacuum tube based electronics with modern solid-state circuits, and added an optical TAS (Tracking Adjunct System). The TAS, designated OD-179/TVY, is an electro-optical (TV) tracking system that increases Hawk operability and survivability in a high-ECM environment.
- HAWK Phase III: The PIP Phase III development was started in 1983, and was first fielded by U. S. forces in 1989. Phase III was a major upgrade that significantly enhanced the computer hardware and software for most components of the system, a new CWAR the AN/MPQ-62, added single-scan target detection capability, and upgraded the HPI to AN/MPQ-61 standard by the addition of a Low-Altitude Simultaneous Hawk Engagement (LASHE) system. LASHE allows the Hawk system to counter saturation attacks by simultaneously intercepting multiple low-level targets. The ROR was phased out in Phase III Hawk units.
Technical Data
| Components |
|
The Hawk system consists of a large number of component elements. These elements were typically fitted on wheeled trailers making the system semi-mobile. The Hawk missile is transported and launched from the M192 towed triple-missile launcher. A self-propelled Hawk launcher, the SP-Hawk, was fielded in 1969, which simply mounted the launcher on a tracked M727 (modified M548), however, the project was dropped and all activity terminated in August 1971.
|
| Missile |
|
The missile is propelled by a dual thrust motor, with a boost phase and a sustain phase. The MIM-23A missiles were fitted with an M22E8 motor which burns for 25 to 32 seconds. The MIM-23B and later missiles are fitted with an M112 motor with a 5-second boost phase and a sustain phase of around 21 seconds. The M112 motor has greater thrust, thus increasing the engagement envelope. The Hawk missile has a slender cylindrical body and four long chord-clipped delta-wings, extending from mid-body to the slightly tapered boat-tail. Each wing has a trailing-edge control surface. The MIM-23A has a minimum engagement range of 2 kilometers, a maximum range of 25 km, a minimum engagement altitude of 60 meters, a maximum engagement altitude of 11,000 m, and a warhead of 54 kg HE blast/fragmentation.
The MIM-23B has a minimum engagement range of 1.5 kilometers, a maximum range of 35 km, a minimum engagement altitude of 60 meters, a maximum engagement altitude of 18,000 m, and a warhead of 75 kg HE blast/fragmentation. Other improved missiles are also available as the MIM-23C, MIM-23D, MIM-23E/F, MIM-23G/H, MIM-23K/J, and MIM-23L/M. |
| Radar and control systems |
| The Streit Group Scorpion 4x4 MRAP is motorized with a Cummins 6 Cylinders ISBE 6.7L engine developing 300 hp at 1,500 rpm. The Scorpion can run at a maximum road speed of 110 km/h with a maximum cruising range of 800 km. The Scorpion can climb a gradient of 60% and a side slope of 40%. The vehicle can cross a river with a maximum depth of 1.5 m. |
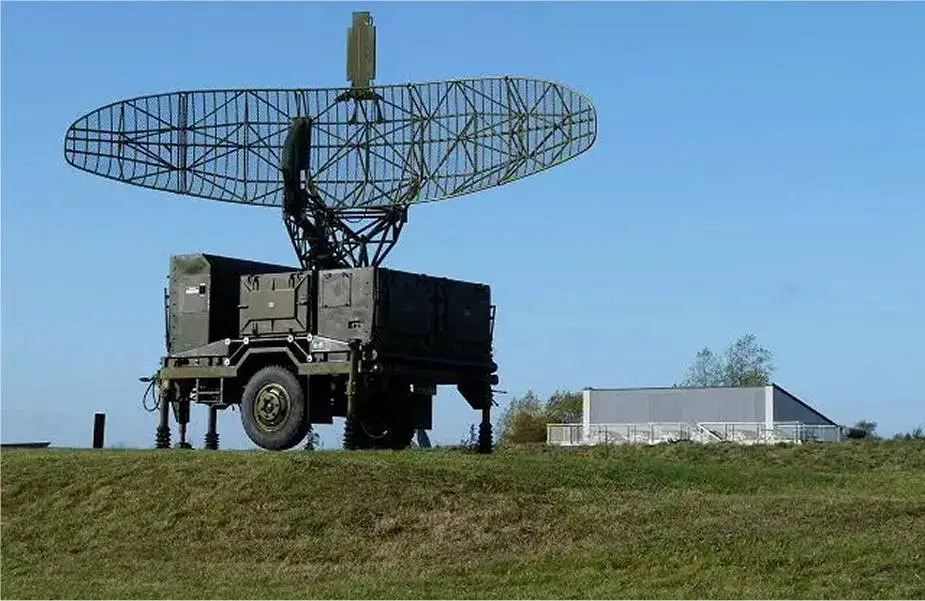
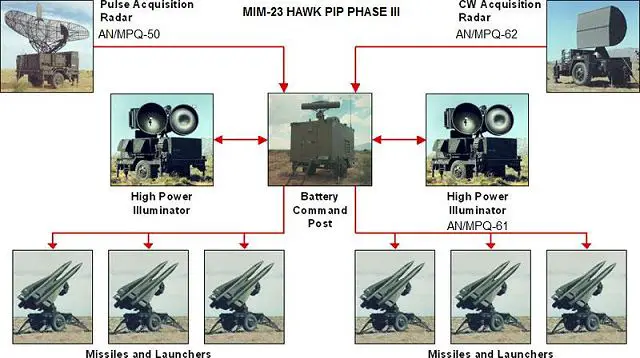
| The latest version of Hawk Phase-III battery consists of: - One PAR Pulse Acquisition Radar AN/MPQ-50: The PAR is the primary source of high- to medium-altitude aircraft detection for the battery. The C-band frequency allows the radar to perform in an all-weather environment. The radar incorporates a digital MTI to provide sensitive target detection in high-clutter areas and a staggered pulse repetition rate to minimize the effects of blind speeds. The PAR also includes several ECCM features and uses off-the-air tuning of the transmitter. In the Phase III configuration, the PAR is not modified. |
 |
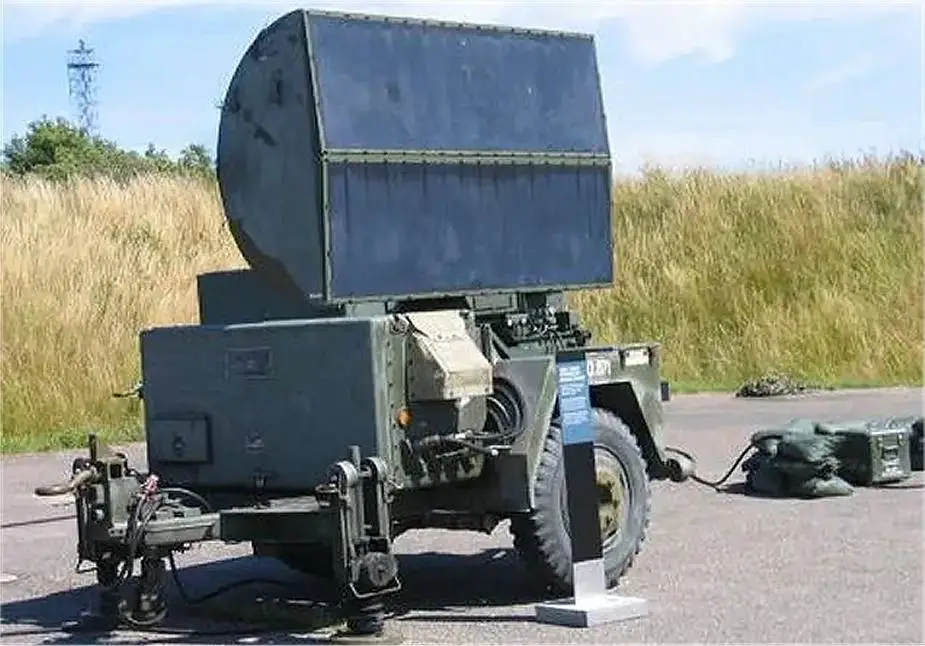
| - One Continuous Wave Acquisition Radar (CWAR): This X Band Continuous wave system AN/MPQ-55 is used to detect targets. The unit comes mounted on its own mobile trailer. The unit acquires targets through 360 degrees of azimuth while providing target radial speed and raw range data. |
 |
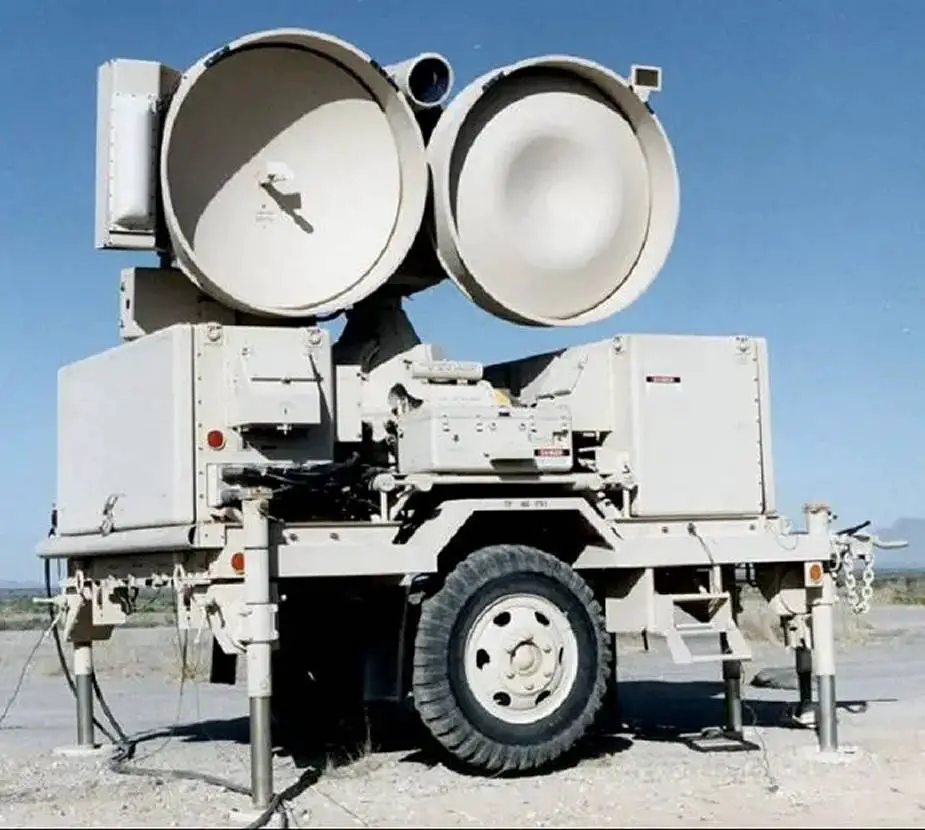
| - One HPIR High Power Illuminating Radar: The early AN/MPQ-46 High Power Illuminator (HPIR) radars had only two large dish-type antennas side by side, one to transmit and one to receive. The HPIR automatically acquires and tracks designated targets in azimuth, elevation, and range. It also serves as an interface unit supplying azimuth and elevation launch angles computed by the Automatic Data Processor (ADP) in the Information Coordination Centre (ICC) to the IBCC or the Improved Platoon Command Post (IPCP) for up to three launchers. |
 |
| - One ROR Range Only Radar: Pulse radar (AN/MPQ-37 or AN/MPQ-51 Phase II) automatically comes into operation if the HPIR radar cannot determine the range, typically because of jamming. The ROR is difficult to jam because it operates only briefly during the engagement, and only in the presence of jamming. |
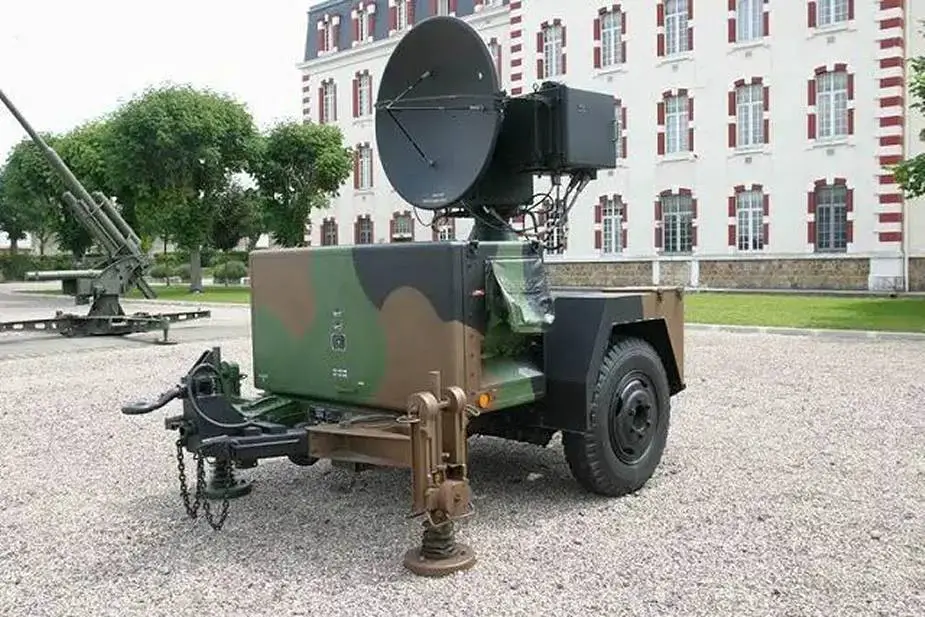 |
| - BCC Battery Control Central: The BCC provides the facilities for the man/machine interface. The Tactical Control Officer (TCO) is in command of all the BCC operations and maintains tactical control over all engagement sequences. The TCO monitors all functions and has the authority and facilities to enable or pre-empt any engagement or change established priorities. The tactical control assistant assists the TCO in the detection, identification, evaluation, and coordination with higher commands. The tactical control console gives these two operators the necessary target and battery status information and controls required. |
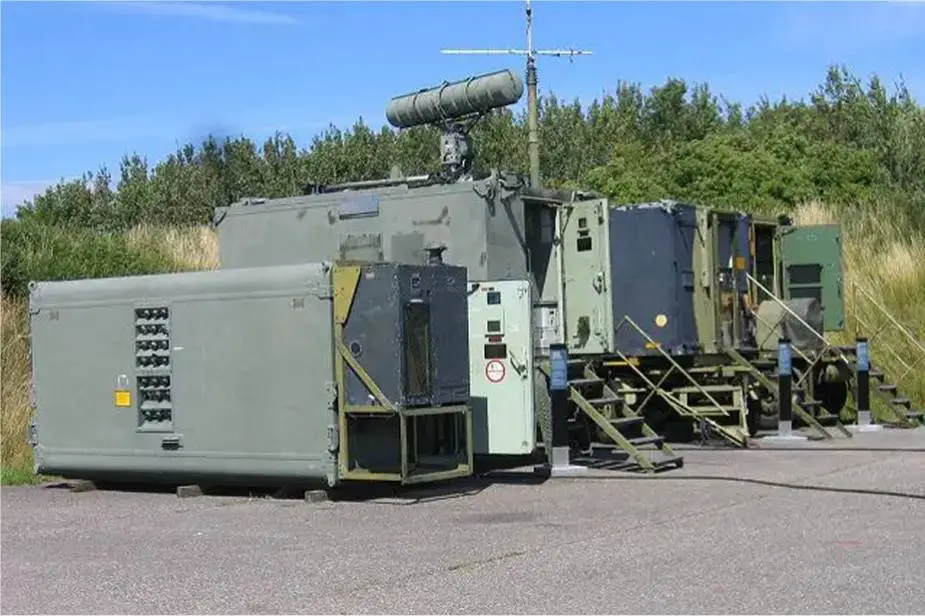 |
| - ICC Information Coordination Central: The ICC is the fire-control data processing and operational communications center for the battery. It provides rapid and consistent reactions to critical targets. Automatic detection, threat ordering, the IFF (Identification Friend or Foe Transceiver) followed by automatic target assignment and launch functions are provided by the ICC. The ICC contains an ADP (Automatic Data Processor), IFF, and battery terminal equipment, and communications equipment. The ADP comprises an Electronic Data Processor (EDP) and a Data Take-Off unit (DTO). The DTO forms the interface between the other system equipment and EDP. With the exception of inputs from a solid-state reader and outputs to a printer, all communications with the ECP are through the DTO. The EDP is a militarized, general-purpose digital computer especially adapted to this role. |
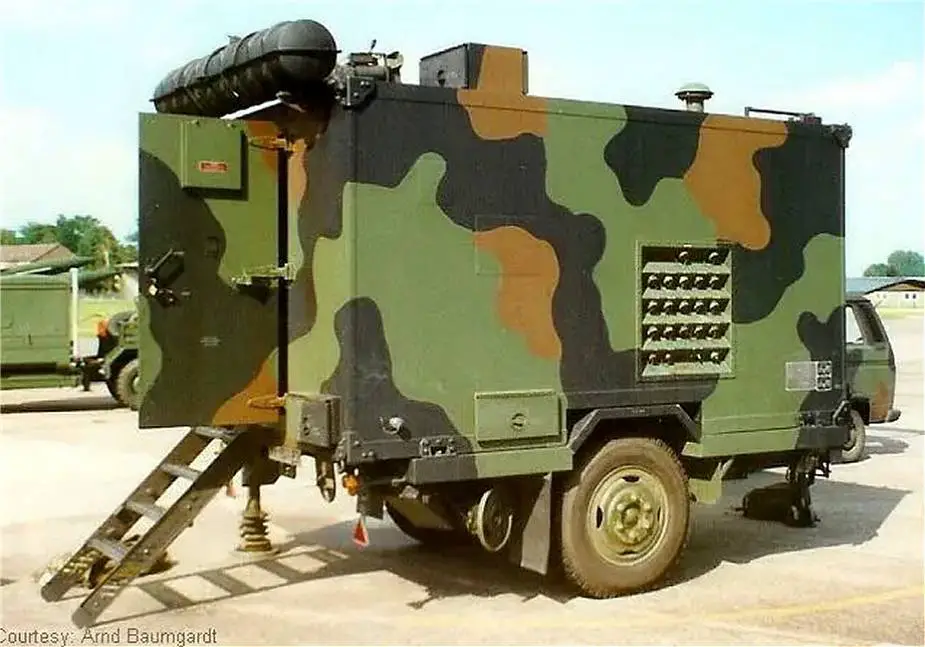 |
| - Platoon Command Post PCP: The PCP is used as the fire-control center and command post for the AFU (Assault Fire Unit). It can also be used to replace an ICC. The PCP provides manual and automatic target processing, IFF, intra-unit, intra-battery and army air defense command post communications and the displays and fire-control equipment for the three-man crew. It is essentially an ICC with a tactical display and engagement control console, a central communications unit, a status indicator panel, and an automatic data processor. The tactical display and engagement control console provides the man/machine interface for the AFP (Assault Fire Platoon). |
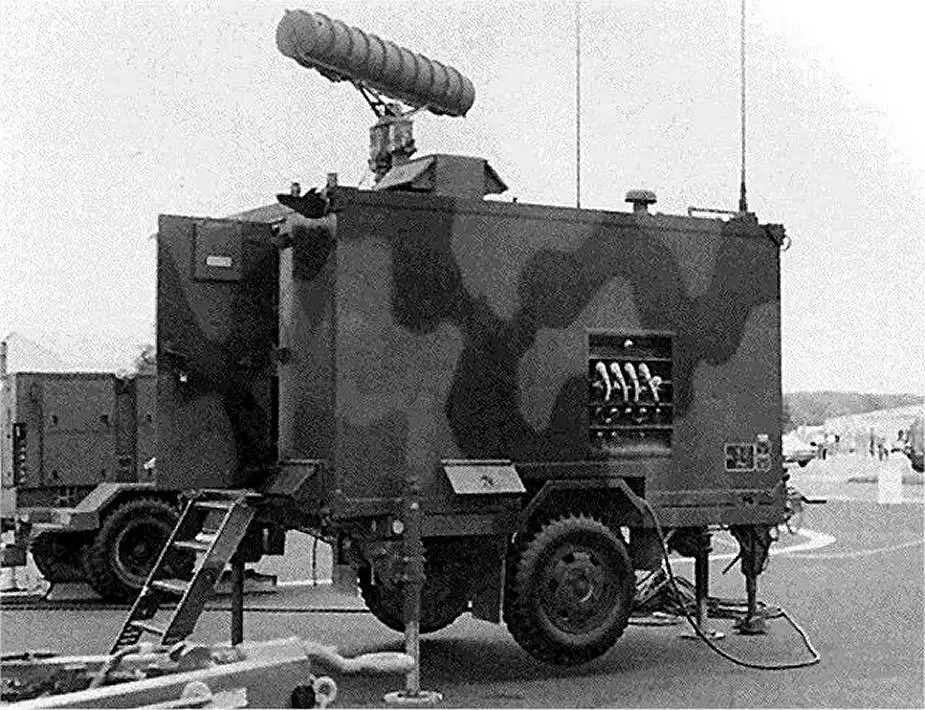 |
| - M192 Launcher unit (LCHR): LCHR supports up to three ready-to-fire missiles and is activated only on the initiation of the fire cycle. When the fire button is activated in the BCC or PCP, several launcher functions occur simultaneously: the launcher slews to designated azimuth and elevation angles, power is supplied to activate the missile gyros, electronic and hydraulic systems, the launcher activates the missile motor and launches the missile. The launcher is equipped with electronic cutouts and sensing circuits that allow firing in all emplacement situations. |
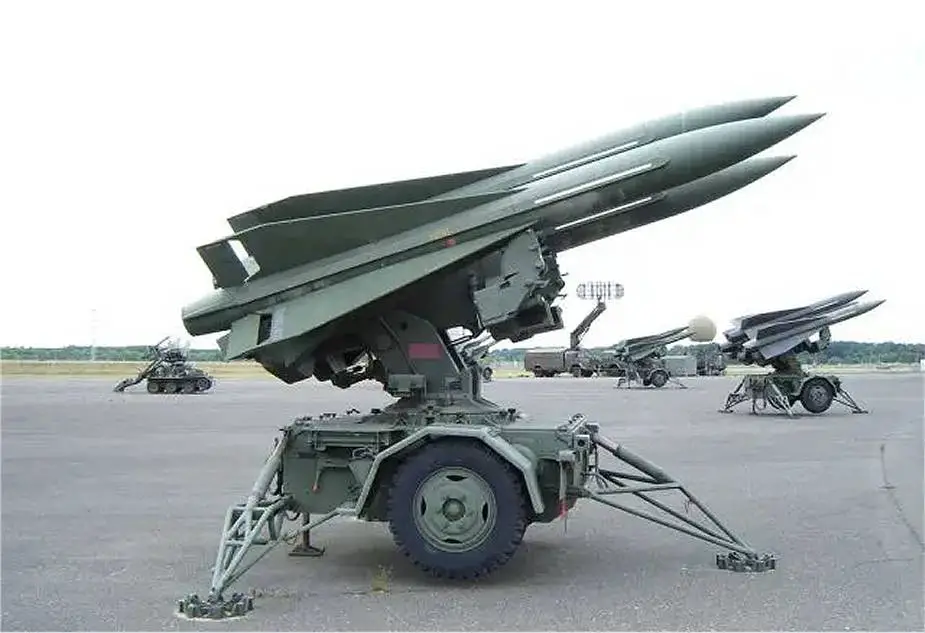 |
| Combat Use |
| The Hawk system consists of seven major components. Its Information Coordination Central (ICC) and Battery Control Central (BCC) perform critical command and control functions, including automatic data processing, friend or foe identification, and digital voice and data communications. The Pulse Acquisition Radar (PAR) AN/MPQ-35 or AN/MPQ-50 (Hawk phase II), is a search radar with a 20 rpm rotation, for high/medium altitude target detection. Continuous Wave and Pulse Acquisition Radars (CWAR) AN/MPQ-34 or AN/MPQ-55 (Hawk phase II) provide low-to-medium-altitude target detection, while the High Power Illuminator tracks and illuminates targets (HIPIR) AN/MPQ-33-39 or AN/MPQ-46 (Hawk phase I) or AN/MPQ-57 (Hawk Phase II) or AN/PQ-61 (Hawk phase III). The Hawk missile performs the target-kill function, providing a formidable defense against fixed and rotary-wing aircraft, cruise missiles, and short-range tactical ballistic missiles. The launchers, in addition to their missile aiming function, support pre-launch commands and transport the missiles in tactical situations. A typical HAWK battery consists of 1 PAR Radar, 1 CWAR Radar, 2 HPIR radars, 1 ROR Radar, 1 ICC Information Coordination Central, one BCC Battery Control Central, one AFCC Assault Fire Command Console, one PCP Platoon Command Post, two launcher section controls and six M192 launcher units with 18 missiles. Phase III HAWK battery consists of one PAR radar, one CWAR radar, 2 HIPIR radars, one FDC Fire Distribution Center, one IFF Identification Friend or Foe Transceiver, six DLN: Digital Launchers with 18 missiles. |
Specifications
| Armament | Propulsion |
| Low to medium-altitude ground-to-air missile | dual-thrust solid fuel booster sustainer rocket motor |
| Country users | Launch Weight |
| France, Greece, Iran, Israel, Italy, Japan, Kuwait, Netherlands, Egypt, Jordan, Morocco, Romania, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Spain, South Korea, Sweden, Taiwan, Turkey, Ukraine, United Arab Emirates | MIM-23A: 584 kg MIM-23B: 627.3 kg |
| Designer Country | Warhead Missile |
| United States | MIM-23A: 54 kg HE blast/fragmentation MIM-23B: 75 kg HE blast/fragmentation |
| Guidance System | Range Missile |
| semi-active radar homing with proportional navigation | MIM-23A: 2,000 to 32,000 m MIM-23B: 1,500 to 40,000 m |
| Speed Missile | Dimensions Missile |
| Mach 2.7 | Length: 5.08 m; Diameter: 0.37 m; Wing span: 1.19 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pictures - Video

























