- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
S-500 Prometheus 55R6M Triumfator-M
S-500 Prometheus 55R6M Triumfator-M
Mobile surface-to-air defense missile system - Russia

Description
The S-500 "Prometheus" (Russian name 55R6M Triumfator-M) is the latest generation of Russian-made surface-to-air defense missile system developed by the Russian defense company Almaz-Antey. According to Russian sources, the S-500 is an advanced version of the S-400 with dedicated components designed to intercept ballistic missiles at an altitude of up to 200 km. The S-500 is designed for intercepting intercontinental ballistic missiles and for air defense against Airborne Early Warning and Control and jamming aircraft. The S-500 missile will be also able to destroy low-orbit satellites on Earth's thermosphere. The first development of the S-500 was started in 2009 with the first prototype completed in 2012. In 2011, Almaz-Antey announced that the first production system of the S-500 would be completed in 2014. In December 2015, the newspaper website Sputnik released the information that the Russian Armed Forces could receive the first pre-production prototypes of the next-generation S-500 air defense system in 2016. The S-500 is able to destroy aerial targets at a range of up to 600 km (over 370 miles) and simultaneously engage up to 10 targets. The system will be capable of destroying hypersonic and ballistic targets. The S-500’s interceptors will operate at an altitude higher than 185 km. The system will have a response time of about three to four seconds, which is considerably shorter than the S-400 rated at nine to ten seconds. It also has an extended radar range compared to the S-400. Russian Defense Minister Alexei Krivoruchko announced on December 28, 2019, that Russia would start preliminary tests of its latest air defense missile system S-500 Prometheus in 2020. According to a video released by the Russian Ministry of Defense on July 20, 2021, the Russian Army unveiled the S-500 Prometheus, also known as 55R6M "Triumfator-M", the latest generation of Russian-made air defense missile system during a live firing test. According to information published on April 25, 2022, by the Russian press agency TASS, Almaz-Antey Concern has launched batch production of S-500 air defense systems. On February 22, 2024, the S-500 conducted firing tests demonstrating its capability to intercept and destroy hypersonic targets. The S-500 TEL (Transporter Erector Launcher) truck was presented for the first time to the public during the defense exhibition Army-2024 that was held near Moscow in August 2024. On December 18, 2024, General Valery Gerasimov, the Chief of the General Staff of the Russian Federation, announced the formation of Russia's first regiment equipped with the highly advanced S-500 'Prometheus' air defense missile system.
S-500 missile variants:
- No variants at this time.
Technical Data
| Missile Launcher Unit |
|
The 77P6 Self Propelled Transporter Erector Launcher (TEL) of the S-500 Prometheus appears to be based on the proposed 9A82MK TELAR for the S-300VMK 9M82M Giant missile. According to the video released by the Russian Ministry of Defense on July 20, 2021, the S-500 TEL is equipped with two Missile Launch Tubes/Transport Containers mounted at the rear of the truck chassis. In the firing position, two hydraulic jacks are lowered to the ground on each side of the truck chassis and the missile containers are placed on vertical to the rear side.
|
| Missiles |
|
The S-500 Prometheus uses two new types of missile: the 77N6-N and 77N6-N1. They can be fitted with an inert warhead designed to destroy nuclear warheads by force of impact, it’s to say by hitting them with precision at great speed. The 77N6-N and 77N6N-N1 are reportedly able to fly at a hypersonic speed of 5 to 7 kilometers per second, allowing them to intercept hypersonic cruise missiles. These missiles seem to use a hit-to-kill method, meaning they will directly attack targets through physical impact as opposed to relying on a fragmentation warhead. These missiles could have a range of 600 km. The S-500 also features advanced communication systems with secured communication links on variable frequencies that shield itself from electronic warfare.
According to the Russian defense industry, the S-500 will be also able to fire the 53T6M missile, also called PRS-1M, a new hypersonic interceptor developed by Russia as part of the A-135 missile defense system and intended as the replacement for the 53T6 endo-atmospheric interceptor. The new interceptor is capable of reaching a top speed of 4 kilometers per second, which means Mach 14, and simultaneously destroying up to 10 ballistic missiles. The system will have a response time of about three to four seconds, which is considerably shorter than the S-400 rated at nine to ten seconds. The S-500 is also able to launch extended-range missile 40N6M and the existing missiles used by the S-400 including the 40N6 which has a range of 380 km, 48N6 that can reach a target at a maximum range of 250 km, and 9M96 which has a range of 120 km. |
| Mobility |
| All battery components of the S-500 Prometheus are carried on hardened BZKT BAZ-6909 family vehicles, in 6 x 6, 8 x 8, 10 x 10 configurations. The BAZ-6909 is a family of all-terrain truck chassis produced and manufactured by the Russian Company Bryansk Motor Vehicle Plant. This family includes 6x6, 8x8, and 10x10 heavy high mobility trucks, prime movers, artillery tractors, with a payload capacity of 13-21 t. The mobile launcher unit TEL (Transporter Erector Launcher) is based on the chassis of BAZ-69096 trucks in a 10x10 configuration. The BAZ-6909 can run at a maximum speed of 70 km/h with a maximum cruising range of 500 km. |
| Command and Control Vehicles |
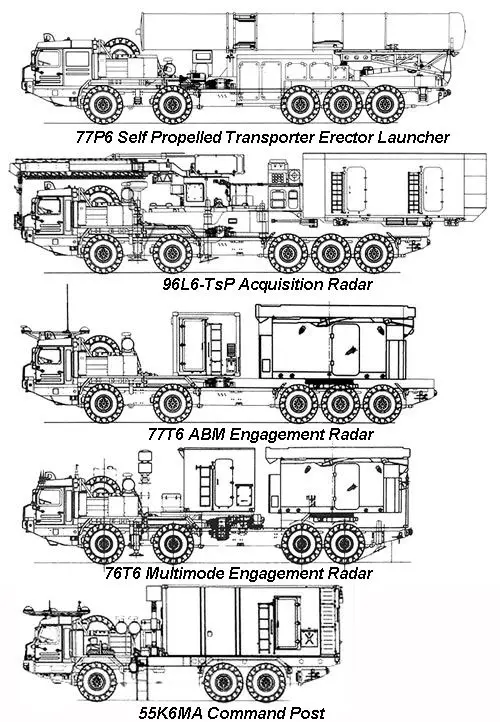
| The S-500 Prometheus is expected to use the following radars: the 91N6A(M) acquisition and battle management radar, the revised 96L6-TsP acquisition radar, and the new 76T6 multimode engagement and 77T6 ABM engagement radars. The 96L6-TsP Acquisition Radar is a direct derivative of the 96L6-1 series used as a battery acquisition radar in the S-400. Battle management and ABM acquisition will be performed by the 91N6A(M) Big Bird Acquisition and Battle Management Radar, an evolution of the 64N6E series, typically used to support multiple S-300P/S-400 batteries. Two battery command post types are listed, the 55K6MA which is clearly an evolution of the S-400 55K6E battery command post, and the 85Zh6-2, which may refer to a command post for an extended battery. The S-500 battery could include: - an undisclosed number of 77P6 TEL Transporter Erector Launcher - 55K6MA and 85Zh6-2 Command Posts - 91N6A(M) "Big Bird" Acquisition and Battle Management (ABM) Radar - 96L6-TsP acquisition Radar - 76T6 Multimode Engagement Radar - 77T6 AMB Engagement Radar - 40V6MT Universal Mobile Mast System |
Specifications
| Type | Armament |
| Long-range surface-to-air defense missile system | Each TEL with two missiles in an individual container |
| Country users | Range missile |
| Russia | 77N6-N: 600 km ballistic missile, 400 km air targets 77N6-N1 : |
| Designer Country | Guidance System |
| Russia | Command and active radar |
| Deployment Time | Radar and Command Stations |
| To deploy the system from the traveling position to set system assets: 5 - 10 min At ready from deployed position : 3 min |
Command posts 55K6MA and 85Zh6-2 on BAZ-69092-12 6x6; the acquisition and battle management radar 91N6A(M), a modification of the 91N6 (Big Bird) towed by the BAZ-6403.01 8x8 tractor; the 96L6-TsP acquisition radar, an upgraded version of the 96L6 (Cheese Board) on BAZ-69096 10x10; the multimode engagement radar 76T6 on BAZ-6909-022 8x8; the ABM engagement radar 77T6 on BAZ-69096 10x10; |
Details View
 |
|
Pictures - Video

























