- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
SA-24 Grinch 9K338 Igla-S
SA-24 Grinch 9K338 Igla-S MANPADS
Man-portable air-defense missile system - Russia
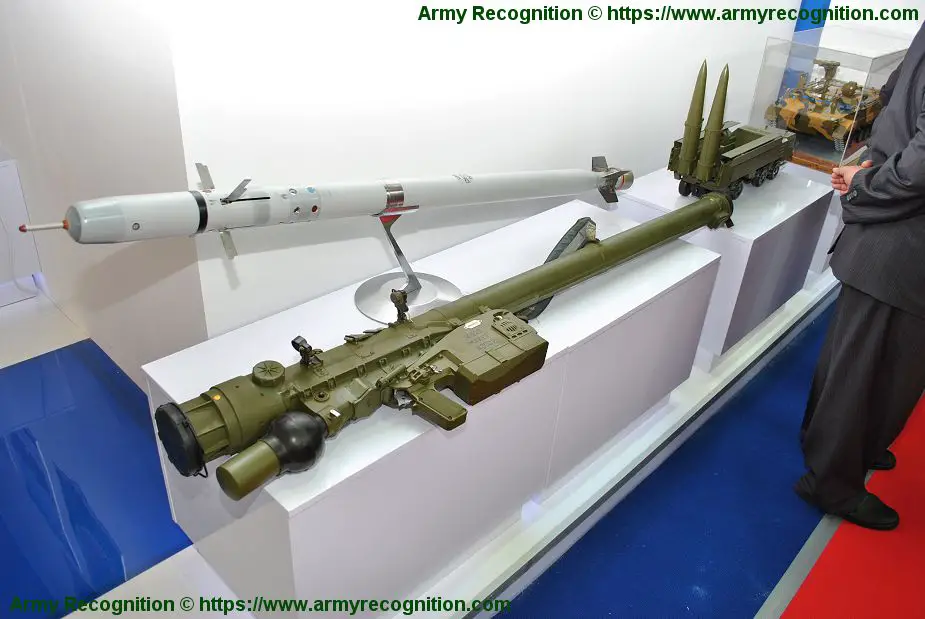

Description
The SA-24 Grinch (Russian name Igla-S 9K338) is the latest generation of Russian portable air defense missile systems. The SA-24 Grinch Igla-S is a further development of the Igla family systems (SA-18 and SA-16). In 2004 the Russian army adopted the new MANPADS - Igla-S (sometimes called "Igla-Super") which is much more sophisticated and efficient in countering air threats. Serial production of the "Igla-S" ("Needle-S") portable antiaircraft missile complex (PAAMC) is conducted at the Degtyarev factory in the city of Kovrov. The "Igla-S" PAAMC by its capabilities is significantly superior to the "Igla" PAAMC, which entered service in 1983.
SA-24 Igla-S variants:
- 9K32 Srela-2 SA-7
- 9K32M Strela-M Sa-7b
- 9K34 Strela-3 SA-14 Gremlin
- 9K310 Igla-1 SA-16 Gimlet
- 9K38 Igla SA-18 Grouse
- 9K310-1 Igla-1M
Technical Data
| Design |
|
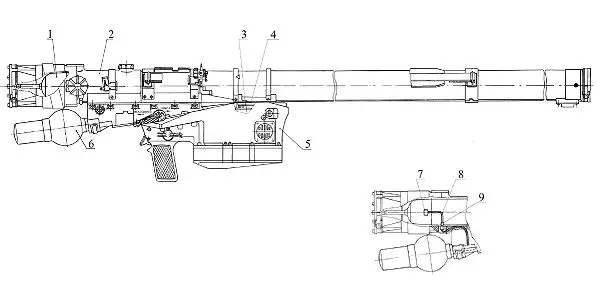
The Igla-S (SA-24 Grinch) system comprises:
- Combat equipment including the 9M342 missile and the 9P522 launching mechanism - Maintenance equipment, including the 9V866-2 mobile test station and the 9F719-2 test set - Training facilities - Night firing devices |
| Missiles |
|
The launcher unit 9P522 fires the missile 9M342. The effectiveness of the 9M342 missile against air targets is attributed to the increase weight of the explosive in the missile's warhead and to the impact/proximity fuze enabling the missile to kill the target both in the event of a direct hit and when it passes at a distance of up to 1.5 m from the target. The target engagement has increased to 6 km compared with the 5.2 km of the Igla (SA-16 / SA-18) system.
|
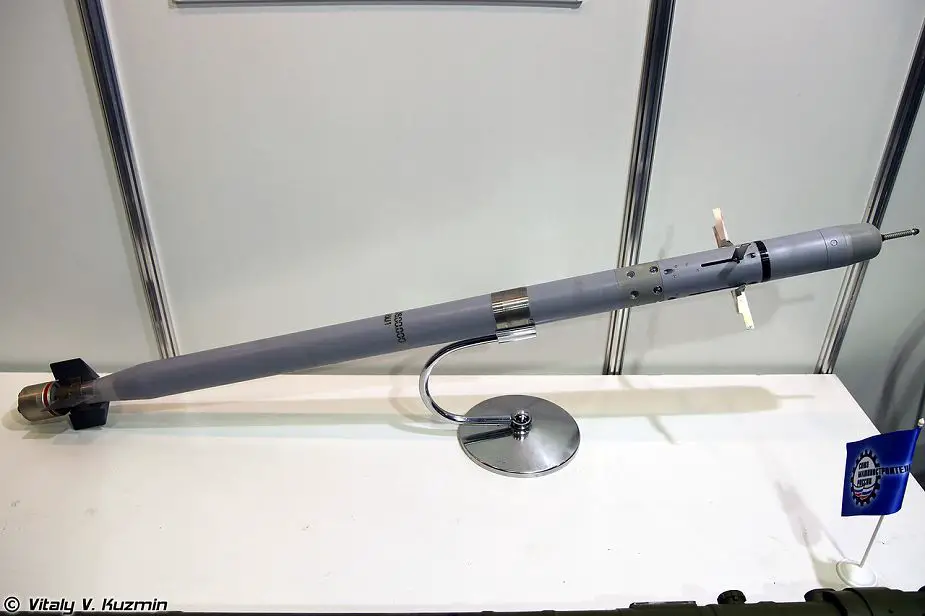 9M342 missile for SA-24 Igla-S |
| Operations |
| When engaging slow or straight-receding targets, the operator tracks the target with the iron sights in the launch tube and applies a half-trigger. The shooter then pulls the trigger fully and immediately applies lead and super elevation. This method is called manual engagement. An automatic mode, which is used against fast targets, allows the shooter to fully depress the trigger in one pull followed by immediate lead and super elevation of the launch tube. The 9V866-2 and 9F719-2 maintenance facilities can be used to check the missile and the launching mechanisms of the Igla and Igla-1 MANPADS. The 9P522 launcher can be used to fire the Igla and Igla-S portable SAM system. The 9M342 missile can be mounted on different platforms using control equipment and launching modules of the Strelets (9S846) set. |
| Combat use |
| The SA-24 Grinch Igla-S man-portable air defense missile (MANPADS) system is designed for use against visible targets such as tactical aircraft, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles, cruise missiles, head-on or receding, in the presence of natural (background) clutter and countermeasures. The SA-24 Grinch Igla-S features high effectiveness and increased range against small targets, such as cruise missiles and remotely piloted vehicles. The SA-24 Grinch Igla-S is able to engage targets at night |
Specifications
| Armament | Type of targets |
| One 9M343 missile | tactical aircraft, helicopter, UAV and cruise missile |
| Country users | Missile |
| Brazil, India, Iraq, Libya, Russia, Venezuela. | Weight: 10.8 kg Weight Warhead: 2,5 kg Warhead type: HE Fragmentation Flight speed: 570 m/s Altitude: 10 - 3,500 m |
| Combat Weight | Reaction Time |
| 17 kg ready to fire | 5 to 10 sec. |
| Target engagement | Guidance system |
| 500 to 6,000 m | Passive IR homing device and night vision (operating in the medium IR range) |
| Operator | Dimension missile |
| 1 | Length: 1,63 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
Pictures - Video



























