- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
Gepard - Cheetah SPAAG
Gepard - Cheetah SPAAG
Self-propelled 35mm anti-aircraft gun tracked armored vehicle - Germany
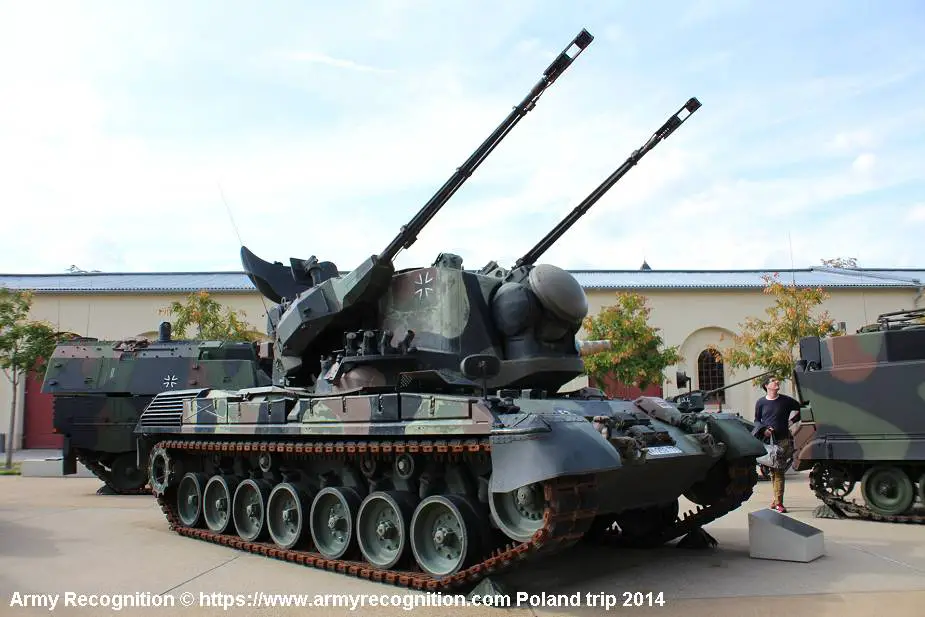

Description
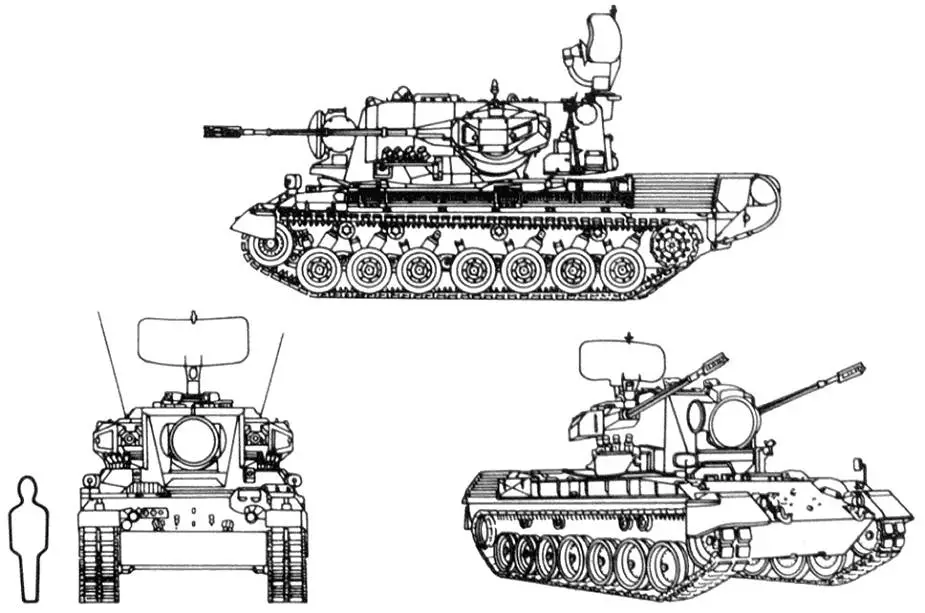
The Gepard also nicknamed Cheetah, is a self-propelled anti-aircraft cannon that was developed by the German company Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) between 1976 and 1980. The development of the Gepard started in the 1960s and it was fielded in the 1970s. The anti-aircraft vehicle has been upgraded several times with the latest electronics. The Gepard is based on the Leopard 1 Main Battle Tank (MBT) tracked chassis fitted with a two-man turret armed with two 35 mm Oerlikon Contraves KDA cannons. The German Army took delivery of 420 systems. The Gepard was also exported to Belgium and the Netherlands. Currently, the self-propelled anti-aircraft cannon is still in service with Brazil, Chile, Jordan, Romania, and Qatar. Late in 1998 the German MoD (Ministry of Defense) stated that it was to donate 43 Gepard 35 mm SPAAG to the Romanian Army as well as maintenance and training equipment. The German Army delivered the first systems to Romania in 1999. In December 2020, it was announced that a license had been issued for the export of a total of 15 Gepard anti-aircraft tanks to Qatar. Furthermore, four automatic cannons, 30 tubes, 16,000 rounds of ammunition, and 45 breechblocks will be delivered as spare parts. In February 2022, it was announced that KMW will deliver 50 decommissioned Gepard anti-aircraft tracked armored vehicles to Ukraine, to counter the invasion by Russia. On April 26, 2022, the German government approved the delivery of 50 Gepard anti-aircraft vehicles to Ukraine to fight the invasion of Russian troops. On May 20, 2022, Germany announced the delivery of 15 Gepard 35mm self-propelled anti-aircraft gun armored vehicles to Ukraine. On July 25, 2022, Ukrainian Defense Minister Oleksiy Rezniko announced that the Ukrainian army had received three Gepard vehicles from Germany. A total of 30 Gepard air defense armored vehicles will be delivered to Ukraine. On December 1, 2022, Germany announced a new delivery of seven Gepard anti-aircraft gun systems to Ukraine. As of March 14, 2023, Germany has already delivered 34 Gepards to Ukraine. During an interview with the newspaper "Welt" on June 22, 2023, German Brigadier General Christian Freuding, who serves as the Head of the Situation Center Ukraine within the German Ministry of Defense, confirmed Germany's commitment to strengthen Ukraine's air defense with 45 additional Gepard anti-aircraft armored vehicles.
Gepard Cheetah variants:
- PRTL (PantserRupsTegenLuchtdoelen translating to "ArmourTrackAgainstAirtargets"): Dutch version of the Gepard is fitted with an X band search radar which has a range of 15 km and an X/Ka band tracking radar which has a range of 13 km. A bank of six 76 smoke grenade dischargers is mounted on either side of the turret.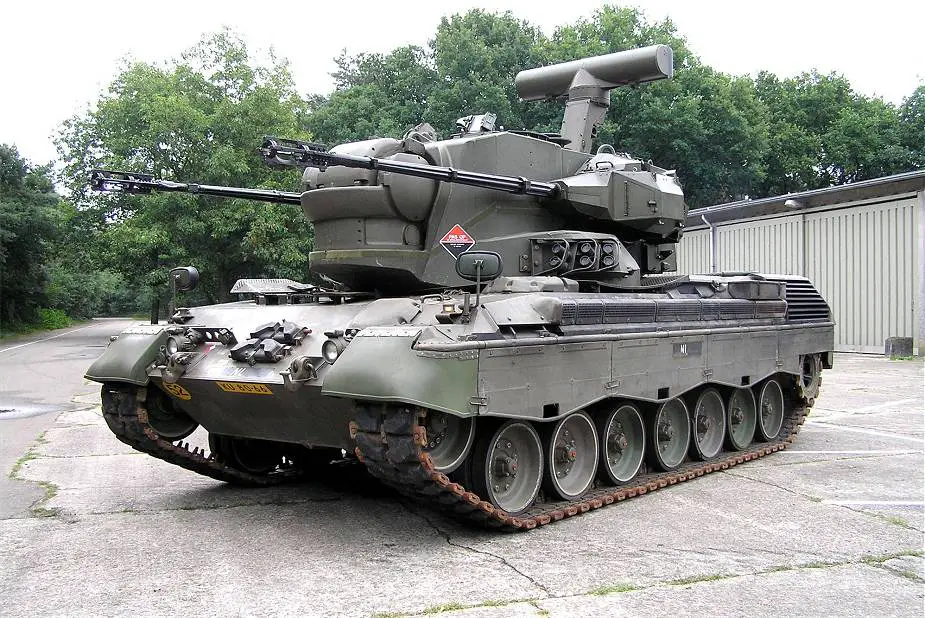
Technical Data
| Armament |
|
The Gepard is fitted with a two-man turret armed with two Oerlikon Contraves 35 mm KDA cannons which have a cyclic rate of fire of 550 rds/min. One 35mm cannon is mounted externally on either side of the turret and the anti-aircraft ammunition is fed via fixed and moving chutes which are hermetically sealed from the fighting compartment. Each cannon is loaded with 310 rounds of anti-aircraft and 20 rounds of armor-piercing ammunition. The electrically driven turret is powered by a 40 kW generator driven by a 4-cylinder, 3.8 liter Mercedes-Benz OM 314 multi-fuel engine. The cannons of the Gepard can fire a full range of ammunition including HEI (High-explosive incendiary), HEI-T (High-explosive incendiary Tracer), HEI (BF), SAPHEI-T (Armor Piercing/High Explosive/Incendiary with Tracer), FAPDS (Frangible Armor Piercing Discarding Sabot), APDS-T, APFSDS-T (Armor-piercing fin-stabilized discarding sabot with Tracer), TP/TP-T (Target Practice Tracer Projectile) and AHEAD (Advanced Hit Efficiency And Destruction). The cannons have a maximum firing range of 5,500 m with FAPDS ammunition. A bank of four 76 mm smoke grenade dischargers is mounted on either side of the turret.
|
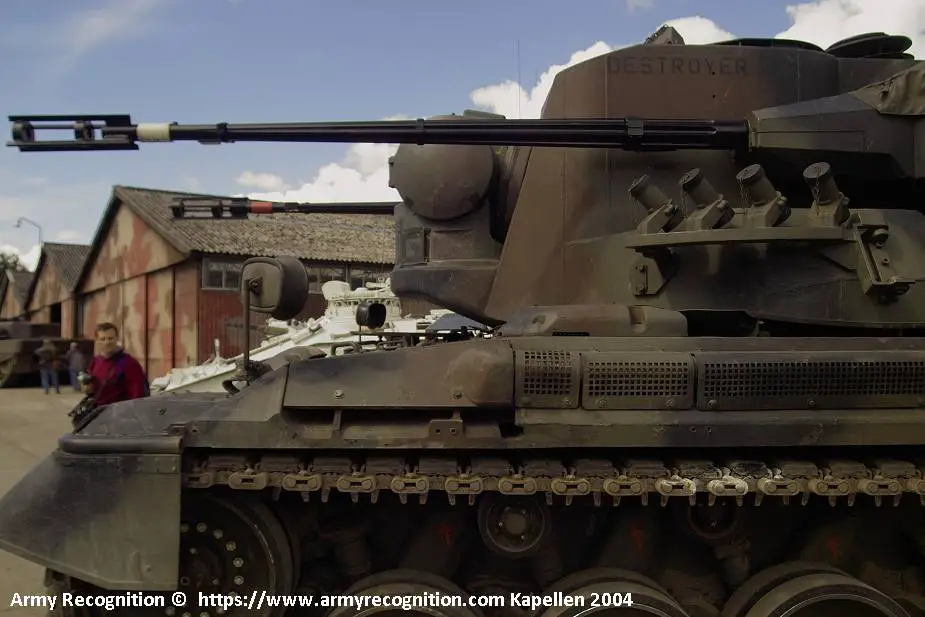 Close view of the 35mm automatic cannon mounted on each side of the turret |
| Design and protection |
|
The Gepard is based on the tracked armored chassis of the Leopard 1 MBT (Main Battle Tank), the original turret is removed and replaced by a two-man anti-aircraft gun system. It has a crew of three including a driver, commander, and gunner. The driver is seated at the front of the hull on the right side with a Daimler-Benz OM314 95 hp auxiliary power unit, for which the exhaust pipe runs along the left side of the hull to the rear. The two-man turret is mounted in the center of the hull with the commander seated on the left and the gunner on the right. The turret and the hull of the Gepard are on all-welded steel construction to provide protection against the firing of small arms and artillery shell splinters.
|
| Mobility |
| The Gepard is powered by an MTU MB 838 Ca M500, 10 cylinder multi-fuel engine developing 830 hp at 2,200 rpm coupled to ZF 4 HP 250 planetary gear shift with hydraulic torque converter, 4 forward and 2 reverse gears. It uses the same suspension and tracks as the Leopard 1 consisting of seven dual light metal rubber-tired road wheels with the drive sprocket at the rear, idler at the front and four track-return rollers on either side. The first, second, third, sixth and seventh road wheel stations are provided with hydraulic shock-absorbers. The Gepard can run at a maximum road speed of 65 km/h with a maximum road cruising range of 550 km and 400 km in off-road conditions. It can climb a gradient of 60 % and a vertical obstacle of 1.15m. It can cross a trench of 3 m and has a fording depth of 2.5 m. |
| Accessories |
| The Gepard is fitted with two radars including pulse Doppler search radar located at the rear of the turret roof and a tracking radar mounted at the front of the turret. In travel position, the search radar is lowered to the rear of the turret. The search radar operates in the E/F bands and has a range of 15 km. The NATO E band is a designation given to the radio frequencies from 2000 to 3 000 MHz while F designates radio frequencies from 3 000 to 4 000 MHz. The search radar rotates at 60 rpm and provides continuous airspace surveillance with an IFF (Identification Friend or Foe) capability. The IFF is an identification system designed for command and control. It uses a transponder that listens for an interrogation signal and then sends a response that identifies the broadcaster. IThe radar can be operated when the vehicle is moving and, when not required it can be folded down behind the rear of the turret to reduce overall height. As soon as an aircraft appears on the scope the crew is alerted. The target is displayed in terms of azimuth, angle and range and is identified as friend or foe. If the aircraft is hostile, information is passed to the coherent Siemens-Albis pulse Doppler-tracking radar. This radar is mounted on the front of the turret, which has a range of 15 km, operates in the Ku-band, and when not in use can be traversed 180º so that the antenna is facing the front of the turret. The tracking radar tracks the target automatically in terms of azimuth, elevation, and range. At the same time, the search radar is still maintaining a search for other targets. The acquisition range of the tracking radar allows target acquisitions within an angle of about 200º without rotating the turret. Information from the radar system can be transmitted by radio in digital form and displayed on a similar monitor at headquarters. Standard equipment of the Gepard includes a navigation system and CBRN (Chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear defense) protection systems. |
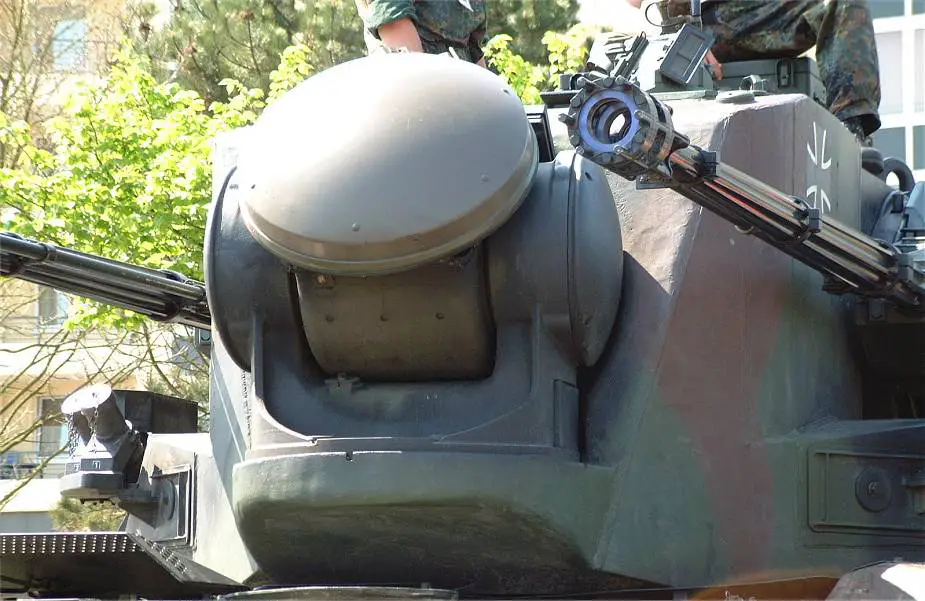 The tracking radar is mounted at the front of the turret |
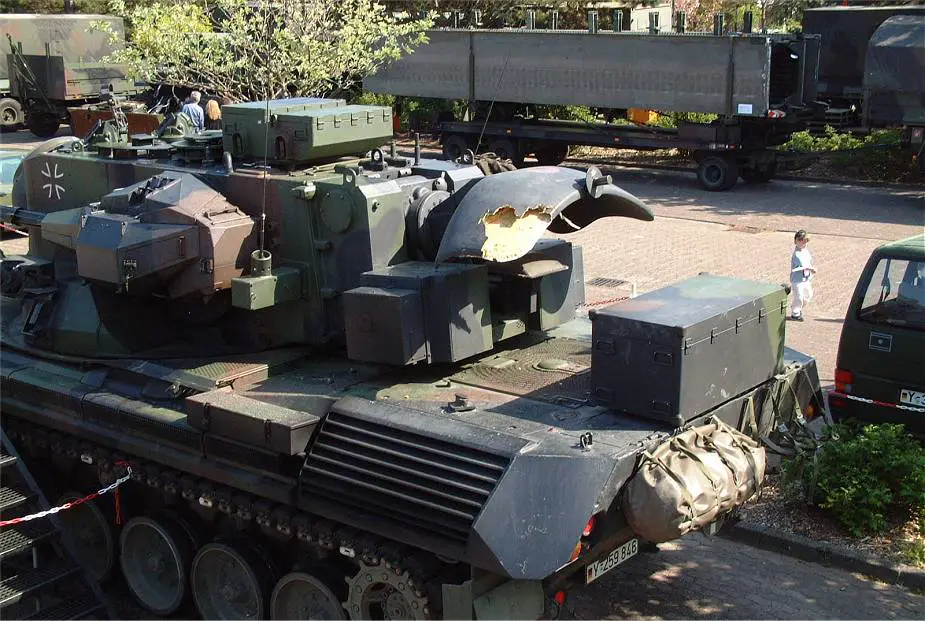 The search radar is mounted at the rear of the turret. In this picture, the radar is lowered at the rear of the hull in travel position. |
Specifications
| Armament | Armor |
| Two 35mm cannons | Protection against the firing of small arms and artillery shell splinters |
| Country users | Weight |
| Brazil, Chile, Jordan, Qatar, Romania, Ukraine | 44,800 kg combat weight |
| Designer Country | Speed vehicle |
| Germany | 65 km/h |
| Accessories | Range vehicle |
| Search radar, tracking radar, navigation system, internal communication system, CBRN protection system | 550 km road - 400 km off-road |
| Crew | Dimensions |
| 3 | Length: 7.73 m; Width: 3.37 m; Height: 4.03 m radar up |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pictures - Video

























