- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
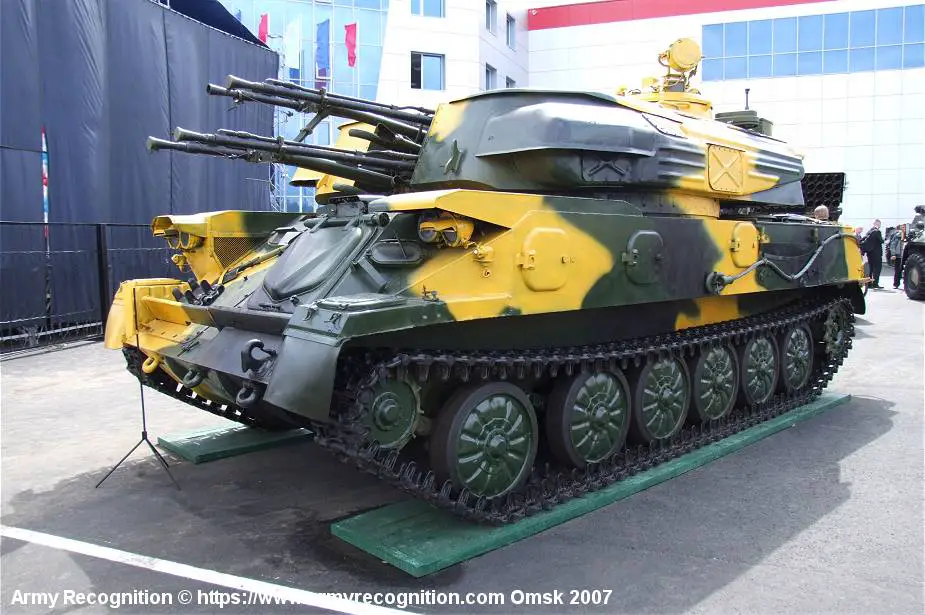
ZSU-23-4 Shilka
ZSU-23-4 Shilka
Self-propelled 23mm anti-aircraft mobile gun system - Russia

Description
The ZSU-23-4 also nicknamed "Shilka" is a Russian lightly armored, self-propelled, radar-guided anti-aircraft weapon system (SPAAG). The ZSU-23-4 Shilka was developed in the early 1960s and was first seen in public during a parade in Moscow in November 1965. The ZSU-23-4 proved highly effective during the 1973 Middle East war and accounted for a large number of Israeli aircraft losses. The ZSU-23-4 was also used in both North and South Vietnam and in the Arabian Gulf War by the Iranian and the Iraqis.
ZSU-23-4 Shilka Russian variants:
- ZSU-23-4V "Shilka" (1968): modernized variant with enhanced reliability of some details, ventilation system case located on the right side of the hull. A Commander vision device was added.
- ZSU-23-4V1 "Shilka" (1970): modernized variant with enhanced reliability of radar system and other details, ventilation system cases located on front bilges of the turret. Guidance-system computer was improved (as well as the accuracy and efficiency of anti-aircraft fire on the move at 40 km/h). It is fitted with a slightly improved diesel engine V-6R-1.
- ZSU-23-4M "Biryusa" (1973): armed with modernized autocannons 2A7M - pneumatic loading was replaced with pyrotechnic loading (unreliable compressor was removed), welded tubes of coolant outlet were replaced with flexible pipes which increased autocannon barrel life from 3500 rounds to 4500 rounds.
- ZSU-23-4MZ "Biryusa" (Z stands for "zaproschik" - inquirer) (1977): equipped with identification friend-or-foe system "Luk". All ZSU-23-4M were upgraded to ZSU-23-4MZ level during scheduled repairs. It should be noted that the army unofficially continued to use the name "Shilka" for all variants of ZSU-23-4.
- ZSU-23-4M2 (1978): so-called "Afghan" variant. Reequipment performed during the Soviet War in Afghanistan for mountain combats. The radar system was removed and night sight was added. Ammunition increased from 2,000 rounds to 4,000 rounds.
- ZSU-23-4M4 (1999): modernized variant developed by Ulyanovsk Mechanical Plant. The vehicle is armed with two additional paired man-portable air-defense systems "Igla" (on each side of the turret) and equipped with laser emission sensors, electron-optical vision devices (including a television system for the driver), and an improved weapon radar system. Mechanical transmission was replaced with hydrostatic transmission, hydraulic boosters were installed. Mobility increased to the level of main battle tanks. First shown to the public during exhibition MAKS-99 in Zhukovsky.
Technical Data
| Armament |
|
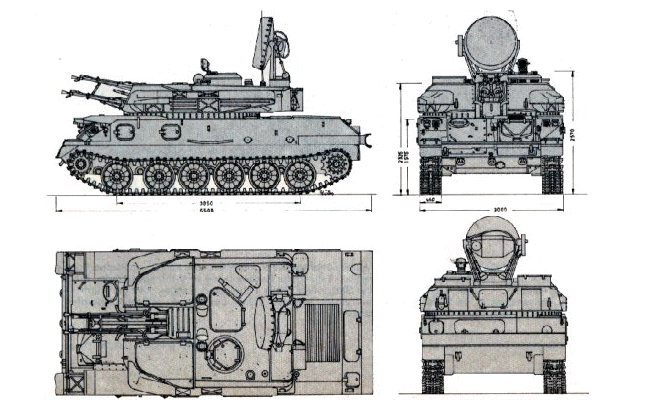
The main armament of the ZSU-23-4 Shilka is composed of four AZP-23 23 mm canons with an elevation of +85° to - 4°, and a 360° turret traverse. The 23 mm canon is gas operated with a vertically moving breech-block locking system that drops to unlock and has a cyclic rate of fire of 800 to 1,000 rounds per minute per barrel. The ZSU-23-4 Shilka can engage targets using only one or two of the four canons. The cannons have an effective range of up to 2.5 km against aerial targets and up to 2 km against ground targets. The maximum firing range of the autocannons is around 4 km, but their accuracy and effectiveness decrease significantly beyond the effective range.
The ZSU-23-4 carries a total of 2,000 rounds of ammunition for its autocannons. The ammunition is typically loaded into belts, with each belt containing 250 rounds. The autocannons can fire up to 3,400 rounds per minute, giving the ZSU-23-4 a high rate of fire and the ability to engage multiple targets simultaneously. The ammunition used in the ZSU-23-4 is typically high-explosive incendiary (HEI) rounds, which are designed to explode on impact and create a high-velocity spray of shrapnel. This makes them highly effective against both aerial and ground targets, as the shrapnel can cause significant damage to the target. In addition to HEI rounds, the ZSU-23-4 can also be equipped with armor-piercing incendiary (API) rounds, which are designed to penetrate armored targets. The ZSU-23-4 can also be equipped with tracers, which make it easier for the gunner to track the trajectory of the rounds and adjust their aim accordingly. |
| Design and protection |
|
The ZSU-23-4 is built on the chassis of the MT-LB, a Soviet-made armored tracked vehicle. A large turret is mounted to the center of the chassis. The commander, gunner, and range operator are seated in the large square turret. The guns and ammunition are in the forward part of the turret and separated from the crew by a gas-tight and armored bullhead. Access to the guns and ammunition is by two large hatches, one on either side of the turret roof, which is hinged in the center and open vertically. The all-welded hull of the ZSU-23-4 is divided into three compartments, the driver at the front, combat at the center, and the engine at the rear. The armor protection is 15 mm at 55° for the glacis plate, and hull sides and 10 mm for the hull rear and the turret sides.
|
| Mobility |
| The ZSU-23-4 Shilka is based on the GM-575 tracked vehicle chassis, which used components from the PT-76 light amphibious tank. The engine and the transmission are at the rear of the hull as is the DG4M-1 gas turbine coupled to a manual gearbox with 5 forwards and 1 reverse gears. The torsion bar suspension system consists of six single rubber-tired road wheels with the idler at the front and the drive sprocket at the rear. There are no track return rollers. |
| Combat equipment |
| The ZSU-23-4 Shilka is equipped with an NBC system with an air filtration unit, fire-fighting equipment, TNA-2 navigational system, infrared vision device, R-123 radio set, R-124 intercom and electric power supply system consisting of a DG4M-1 single-shaft gas turbine engine and a direct-current generator. The ZSU-23-4 is equipped with a radar system mounted at the rear of the turret which is used to help it detect and track aerial targets. The radar is known as the "Gun Dish" radar. It operates in the X-band frequency range and has a range of up to 18 km, depending on the altitude and size of the target. The radar is capable of tracking multiple targets simultaneously, which is essential for effective anti-aircraft operations. When a target is detected by the radar, the information is sent to the tracking and targeting system, which calculates the target's speed, altitude, and direction of travel. The gunner then uses this information to aim the autocannons and engage the target. |
Specifications
| Armament | Armor |
| Four 23 mm automatic canons | Maximum 15 mm |
| Country users | Weight |
| Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Armenia, Belarus, Bulgaria, Congo, Cuba, Egypt, Russia, Ecuador, Ethiopia, Georgia, Guinea-Bissau, Hungary, India, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Laos, Libya, Morocco, Mozambique, Nigeria, North Korea, Peru, Poland, Somalia, Syria, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, Vietnam, Yemen, Zimbabwe. | 19,000 kg |
| Designer Country | Speed vehicle |
| Russia | 44 km/h on road |
| Combat equipment | Range vehicle |
| NBC protection,fire-fighting equipment, infrared night vision, electric power supply, firing control system and radar. | 260 km |
| Crew | Dimensions |
| 4 | Length: 6,54 m; Width: 2,95 m; Height: 2,25 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pictures - Video



























