- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
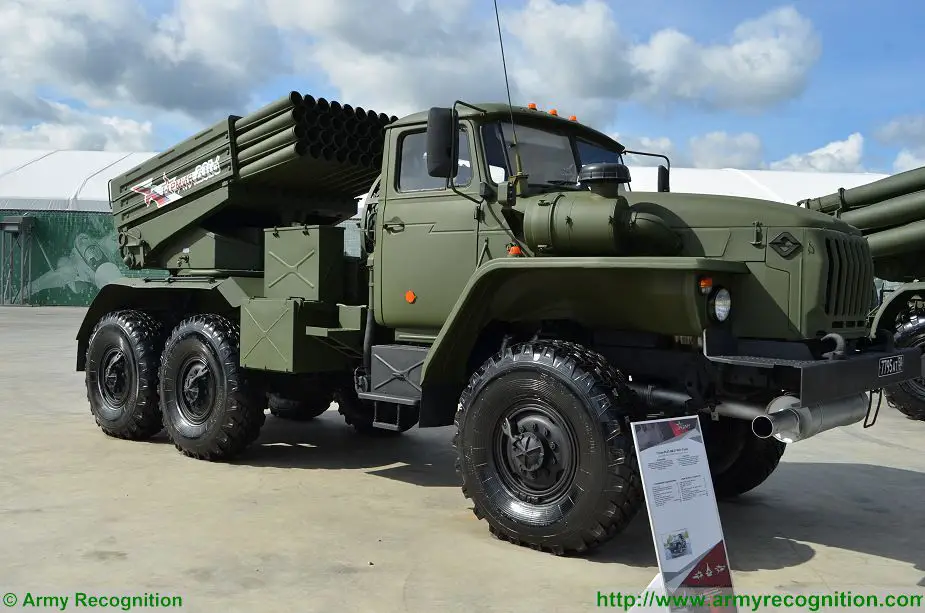
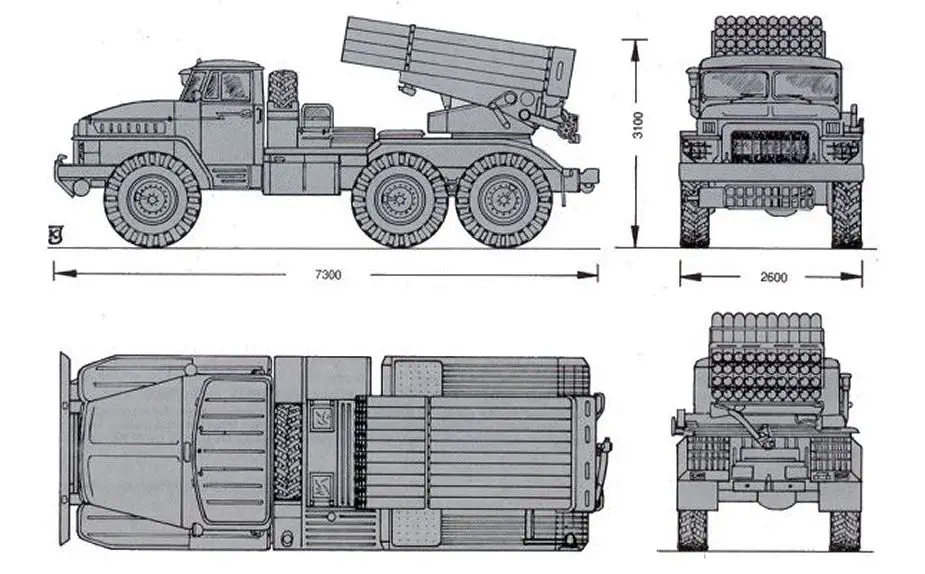
BM-21 GRAD 9K51
BM-21 GRAD 9K51 MLRS
122mm Multiple Launch Rocket System - Russia

Description
The BM-21 Grad is a Soviet truck-mounted 122-mm multiple rocket launcher, developed in the early 1960s. The development of the 122 mm BM-21 Grad divisional-level RSZO took place in the mid-1950s under the guidance of the Splav Scientific Production Concern at Tula. The BM-21 122 mm multiple rocket launcher (MRL) system entered into service with the Soviet Army in 1963 to replace the aging 140 mm BM-14 system. The main role of the BM-21 Grad system is to support the division with suppressive fire to counter anti-tank missile, artillery and mortar positions, destroy strong points and eliminate enemy nodes of resistance on the immediate battlefield.
BM-21 GRAD Variants:
- BM-21 "Grad": Original 40-round launcher, mounted on a Ural-375D truck.
- BM-21-1: Some systems use the Ural-43201 5t truck chassis with KamAZ-740 diesel engine of 210 hp.
2B17 or also BM-21-1: This upgrade was presented for the first time in 2003 and was developed by Motovilikha Plants from Perm. The system is fitted with a satellite navigation system NAP SNS, automated fire control system ASUNO, APP laying system and can fire a new generation of rockets with a range of 40 km. The truck is the Ural-43201.
- 9P138 "Grad-1": lighter 36-round version, mounted on a six-by-six ZIL-131 chassis. The vehicle with supporting equipment (rockets, transporter 9T450 and re-supply truck 9F380) is referred to as complex 9K55. The 9P138 can only use "short-range" rockets with a range of 15 km. He used to be known in the West as BM-21b or M1976.
- BM-21V "Grad-V" (Vozdushnodesantiy - 'airborne') (NATO designation M1975): Developed for airborne troops in 1969. A GAZ-66B four-by-four truck chassis is fitted with a 12-round 122 mm rocket launcher. The vehicle is sturdy enough to be air-dropped. Parts of the vehicle such as the canvas cab roof can be taken off or folded down to reduce its size during transit. Like the BM-21, the BM-21V has stabilizing jacks on the rear of the vehicle for support when firing. The launch vehicle has the industrial inex of 9P125.
- 9A51 "Prima": 50-round launcher on a Ural-4320 5t chassis. The vehicle together with fire control equipment, the ammunition transporter TZM 9T232M and the new rocket 9M53F is referred to as complex 9K59. Apparently, only a small number was produced.
- 9K132 "Grad-P": Single-round man-portable launcher, which can be reloaded and used again. The rocket itself is a 122mm fin-stabilized rocket, armed with any of the warheads used on BM-21 rockets. The weapon is not often used by the Russian military but is popular with paramilitary and guerrilla forces.
- BM-21PD "Damba" (Protivodiversionnyi): 40-round launcher mounted on Ural-375D or 43201 truck. Developed for the protection of naval bases against underwater infiltrations, uses special ammunition PRS-60 (Protivodiversionnyi Reaktivnyi Snaryad). The vehicle together with the ammunition transporter is referred to as complex DP-62 "Damba".
- A-215 "Grad-M": 22-round naval version, entered service in 1978.
Technical Data
| Armament |
|
The BM-21 GRAD is equipped with a pod of 40 launch tubes of 122 mm caliber arranged in a rectangular shape that can be turned away from the unprotected cab. The rocket tube arrangement is a single rectangular bank of four layers each with 10 tubes. The rocket launcher pod is mounted on a mobile elevatable launcher platform which has elevation from 0 to +55º with traverse being 60º right and 120º left. The rocket launcher weapon system is mounted at the rear of the truck chassis. The launching mechanism is powered by a small generator system inside the truck. It can fire rockets directly from the cab or from a trigger at the end of a 64-meter cable. After firing, the vehicle needs to be reloaded, which can take around 10 minutes with an experienced crew and the appropriate reloading equipment.
|
| Rockets |
|
The BM-21 rockets can be either fired singly or in a salvo lasting six seconds. Manual reloading by the two-man crew takes approximately five minutes. The launcher can traverse a full 360º. The system is limited to firing HE fragmentation-type rockets only. The BM-21 can launch rockets directly from the cab or remotely from outside of the truck cab with a 64-meter cable. Standard rockets have a maximum firing range of 20 km, but with the use of the latest generation of rockets, the range can be increased up to 35/40 km. The rockets can be fired individually or in a salvo. The salvo can be fully launched in as little as 20 seconds.
Various 122mm rockets have been developed for the BM-21 Grad MRLS: - 9M22U HE fragmentation rocket - 9M521 HE fragmentation rocket with enhanced power warhead. In engaging targets, twice effective as 9M22U - 9M522 HE fragmentation rocket with a separable warhead. In engaging targets, six effective as 9M22U - 9M217 rocket with sensor-fuzed submunitions. - 9M218 rocket with HEAT fragmentation submunitions. |
| Design and protection |
| The cabin truck of BM-21 GRAD is not protected. The launch vehicle's cabin accommodates the launch preparation and firing equipment. Individual round, selective ripple or salvo firing is possible from either the cab or from a remote-control unit connected to the vehicle via a 64 m cable. The BM-21 has a crew of six including two soldiers in the 9F37 ammunition resupply vehicle. |
| Mobility |
| The BM-21 is based on a Ural-375D six-by-six truck chassis. The truck Ura-375D is powered by a water-cooled V-8 180 hp gasoline engine ZIL-375. The BM-21 has a maximum road speed of 80 km/h, a road range of up to 800 kilometers, and can cross fords up to 1.5 m deep. |
| Combat Equipment |
| The BM-21 truck has a collapsible canvas cab, removable doors and windscreen, telescopic steering wheel, and tie-down points for aiding parachute dropping and landing. A PG-1M panoramic telescope with a K-1 collimator can be used for sighting. A spare tire is fitted at the rear of the crew cab. |
Specifications
| Armament | Truck |
| 40 launch tubes 122 mm caliber | Ural-375D 6x6 |
| Country users | Weight |
| Afghanistan, Algeria, Angola, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bosnia, Bulgaria, Burundi, Cameroon, Cambodia, RDC, Congo, Croatia, Cuba, Cyprus, Egypt, Ethiopia, Finland, Georgia, Hungary, India, Iran, Israel, Kazakhstan, North Korea, Kyrgyzstan, Lebanon, Libya, Mali, Mongolia, Morocco, Mozambique, Myanmar, Namibia, Nicaragua, Pakistan, Peru, Poland, Russia, Serbia and Montenegro, Seychelles, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, Tajikistan, Tanzania, Turkmenistan, Uganda, Ukraine, Uzbekistan, Vietnam, Yemen, Croatia, Zambia | 13,700 kg fully loaded |
| Designer Country | Speed Truck |
| Russia | 80 km/h |
| Accessories | Range Truck |
| PG-1M panoramic telescope | 800 km |
| Crew | Dimensions |
| 6 | Length: 7.35 m; Width: 2.04 m; Height: 3.09 m |
| Weight Rocket | Armour |
| 77 kg | No protection |
| Firing Range | Engine truck |
| 20 km with standard rockets and 35 to 40 km with new-generation of rockets | V-8 gasoline ZiL-375 180 hp (130 kW) |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pictures - Video

























