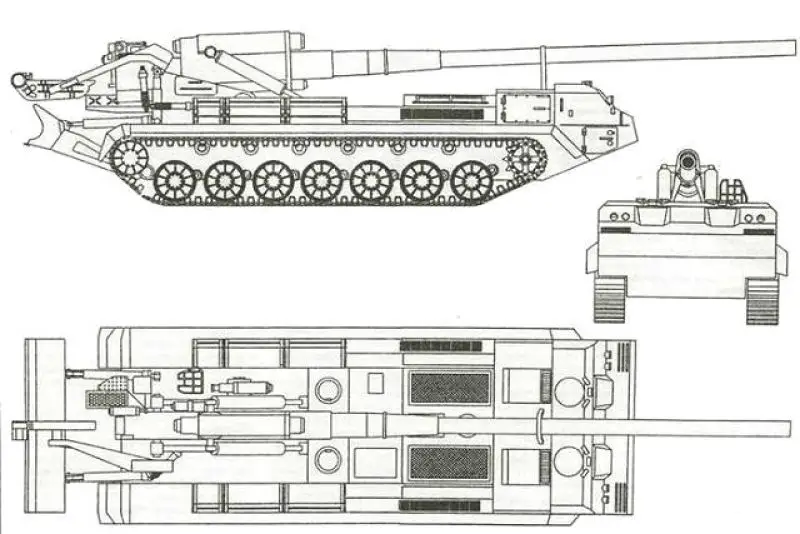
Self-propelled howitzers.
2S7 Pion M1975 SO-203 2S7M Malka.
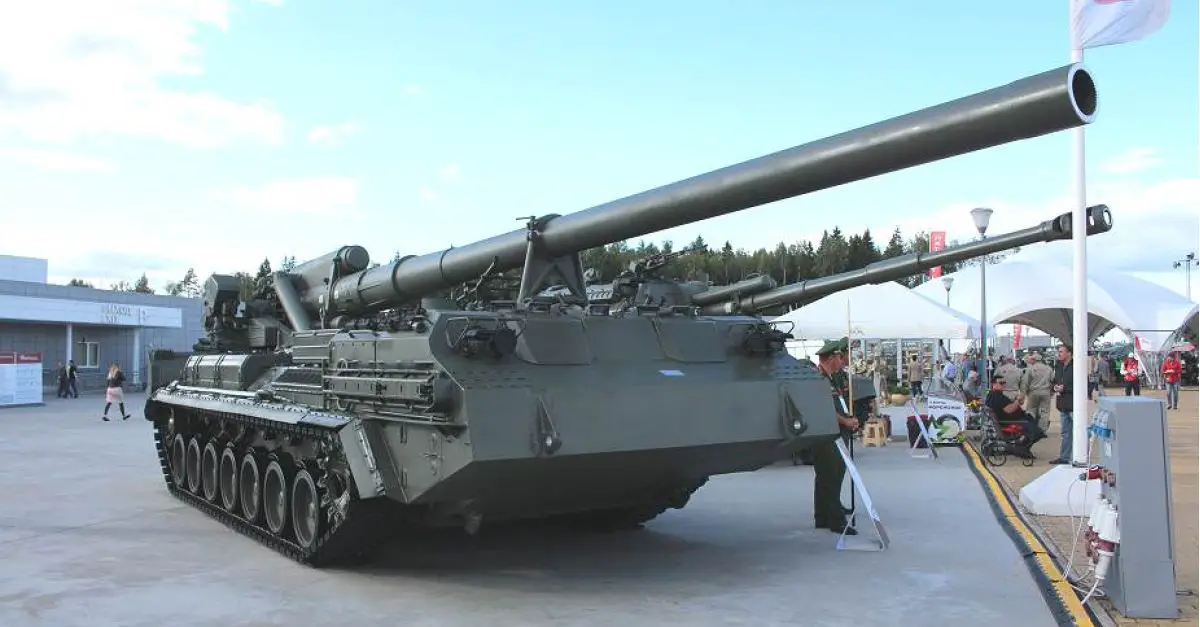

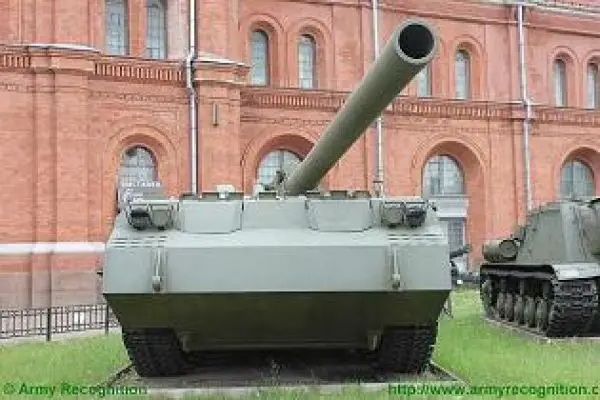
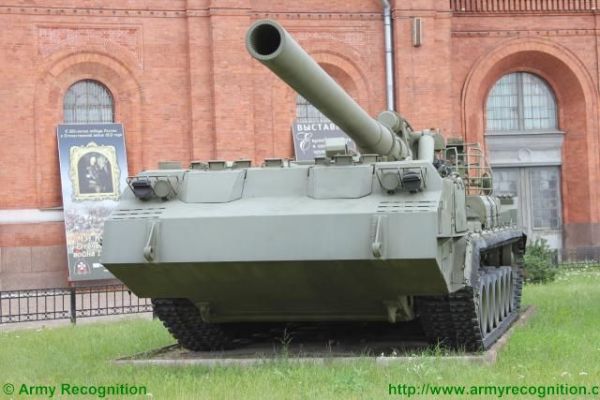
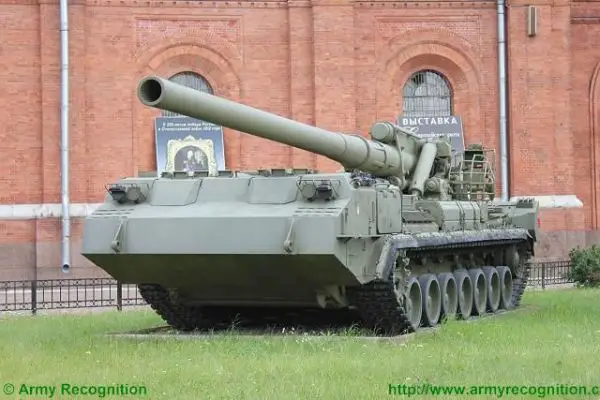
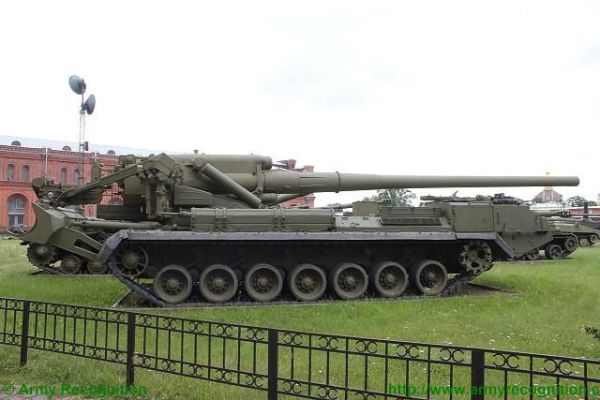
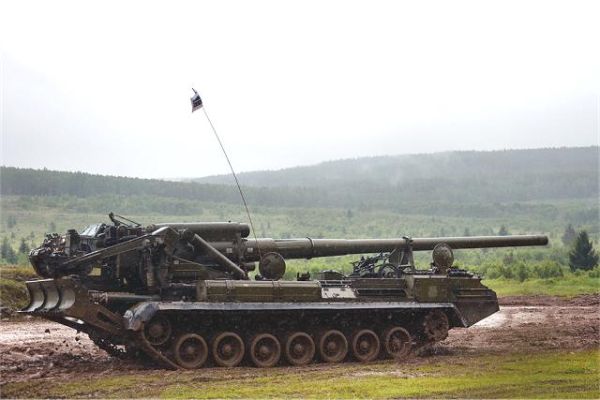
The 2S7 Pion M-1975 (Soviet name SO-203) is a tracked 203mm self-propelled gun designed and manufactured by the Russian defense industry. The 2S7 chassis was developed by the Kirov Factory under the designation of the Obiekt 216, with the gun and mount being developed by the Barrikady plant. The 2S7M is a modernized version of the previous 2S7 using the same 203mm cannon but with many new improvements.
Country users: Azerbaijan, Angola, Belarus, Georgia, Russia, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan.
Description
The 2S7 Pion M-1975 (Soviet name SO-203) is a tracked 203mm self-propelled gun designed and manufactured by the Russian defense industry. The 2S7 chassis was developed by the Kirov Factory under the designation of the Obiekt 216, with the gun and mount being developed by the Barrikady plant. The vehicle enters into service with the Russian army in 1975, and it has been referred to as the M-1975 as this is the year when the system was first observed. It is estimated that well over 1,000 of these systems have been completed, although the Russian Federation and many Eastern European countries have also used this vehicle. The 2s7 is still in service with the Russian army reserve forces and other countries in East Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, but production is stopped and it is no longer being marketed. The 2S7 was also used by the Ukrainian armed forces during the conflict of the Pro-Russian rebels. The 2S7 takes 5 to 6 minutes to come into action and 3 to 5 minutes to come out of action. The 2S7M is a modernized version of the previous 2S7 using the same 203mm cannon but with many new improvements.
2S7 Pion variants:
- 2S7M Malka: latest variant is equipped with R-173 communications equipment and can carry a total of eight 203 mm projectiles and charges. In addition, the rate of fire is increased from 1.5 to 2.5 rds/min.
Technical Data
-
Armament
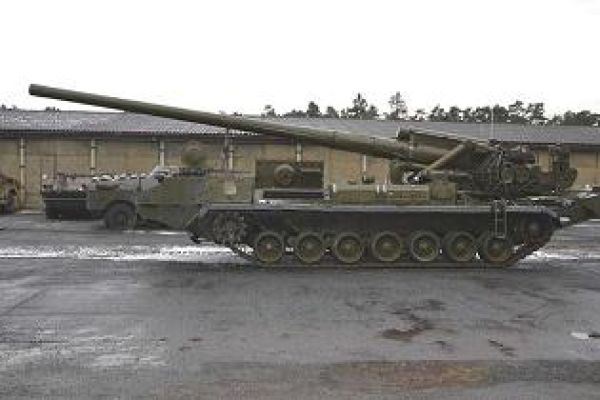
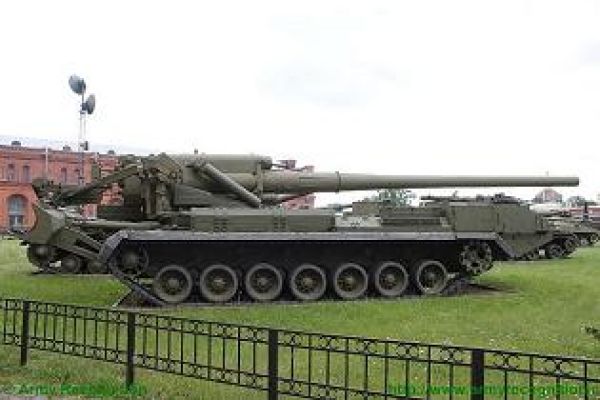
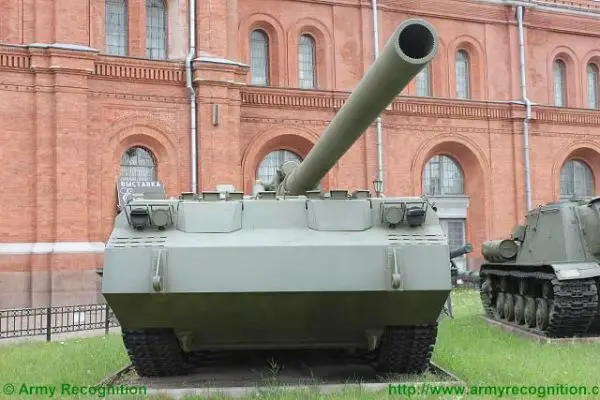
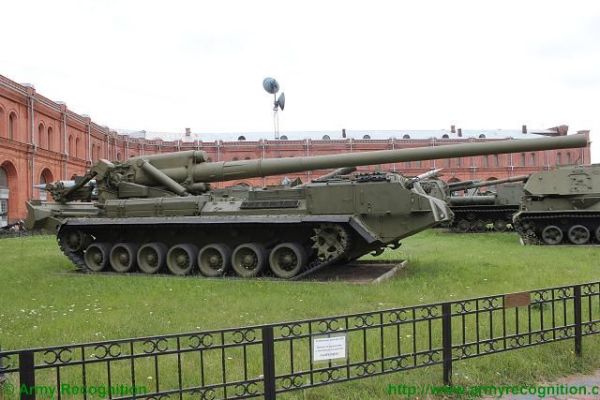
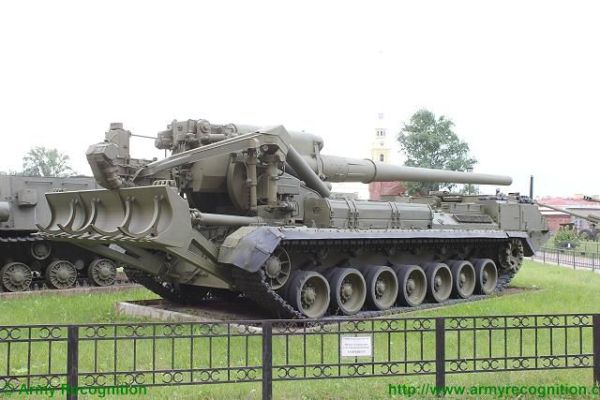
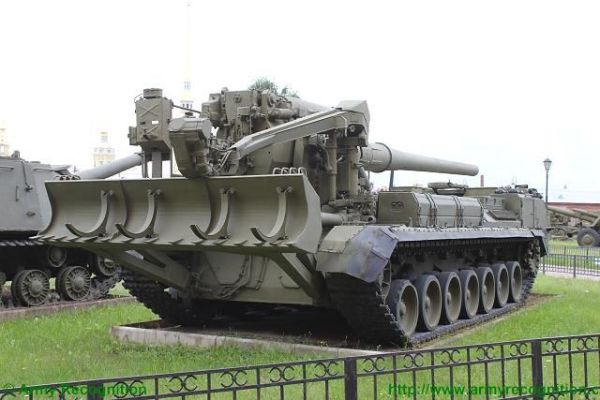
The 2S7 Pion M-1975 (SO-203) main armament consists of a 2A44 203mm cannon. The 203 mm barrel has an overall length of 56.2 calibers and weighs a total of 7,800 kg and has a barrel life of about 450 rounds. When traveling, the 203 mm cannon is held in position by a manually operated travel lock mounted on top of the cab. Gun elevation, traverse, loading and operation of the spade are all hydraulic with manual controls for emergency use. Mounted at the very rear of the tracked chassis is a large recoil spade that, when lowered to the ground, provides stability during firing. The gun operator is seated at the rear of the vehicle on the left side and for the engagement of targets has a standard PG-1M panoramic day telescope that is used in conjunction with the K-1 collimator. Ammunition is of the separate loading type, projectile and charge, with a maximum muzzle velocity of 960 m/s. The maximum range, using unassisted ammunition, is 37.5 km. The standard 203 mm HE round is designated the ZOF 43 and weighs 110 kg, with a total of four projectiles and charges being carried on the 2S7 for immediate use. The remainder of the ammunition load is carried by another vehicle, usually a truck. In addition, there is a rocket-assisted high-explosive projectile that weighs 103 kg and has a maximum range of 47,500 m. The 2S7 is also able to fire chemical and nuclear shells.
-
Design and protection
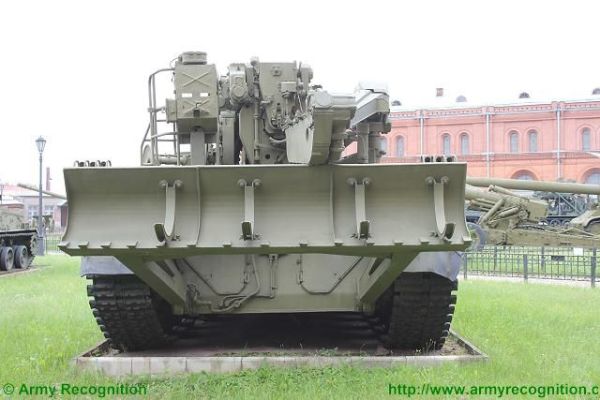
The chassis of the 2S7 Pion M-1975 (SO-203) is of all-welded steel armor construction that provides protection against the firing of small arms and shell splinters. It is divided into four compartments: driver's, engine, crew, and rear compartment. When traveling, the commander, gunner, and driver/mechanic are seated in the driver's compartment at the front of the vehicle. The commander and driver are each provided with a circular roof hatch and in front of these are day periscopes for forwarding observation. At the front of the crew compartment, there are two small windows that can be covered by an armored shutter hinged at the top. To the rear of the engine is another crew compartment for the remaining four crew members who enter the vehicle via two circular roof hatches.
-
Mobility
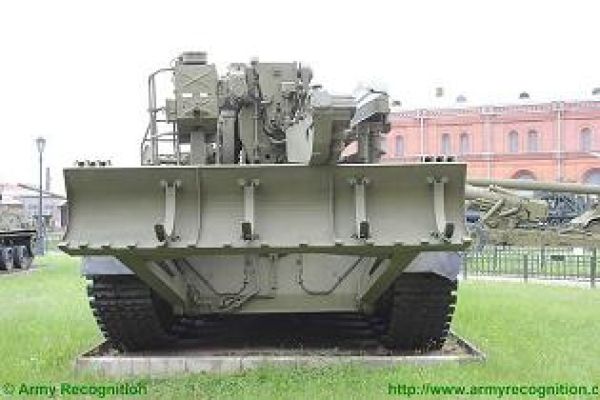
The 2S7 Pion M-1975 (SO-203) is motorized with a V-46-I V-12 liquid-cooled diesel engine coupled to a manual transmission with eight speeds. The engine is located at the rear of the crew compartment cab. The suspension of the 2S7 pion consists of seven dual rubber-tired road wheels on either side, with the drive sprocket at the front and the idler at the rear, and six track-return rollers that support the inside of the track only. Shock-absorbers are provided for the first, second, third, sixth,, and seventh roadwheel stations. When deployed in the firing position, the chassis is lowered at the rear to help provide a more stable firing platform. The 2S7 can run at a maximum road speed of 50 km/h with a maximum cruising range of 600M The vehicle can cross a vertical obstacle of 0.7 m and trench of 2.5 m.
-
Combat Equipment
Standard equipment of the 2S7 Pion M-1975 (SO-203) includes an NBC system of the overpressure type, a heater, a 24 hp 9R4-6U2 auxiliary power unit, and night vision equipment. The 2S7 is provided with an ammunition handling system that enables a rate of fire of 2 rds/min to be achieved, this being operated by the loader.
Specifications
-
Armament
One 2A44 203mm cannon
-
Country users
Azerbaijan, Angola, Belarus, Georgia, Russia, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan.
-
Designer Country
Russia
-
Combat Equipment
NBC system of the overpressure type, heater, a 24 hp 9R4-6U2 auxiliary power unit, and night vision equipment
-
Crew
7
-
Armor
Protection against the firing of small arms and shell splinters
-
Weight
46,500 kg
-
Speed
50 km/h road speed
-
Range
650 km
-
Dimensions
Length: 13.12m; Width: 3.38 m; Height: 3.0 m