- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
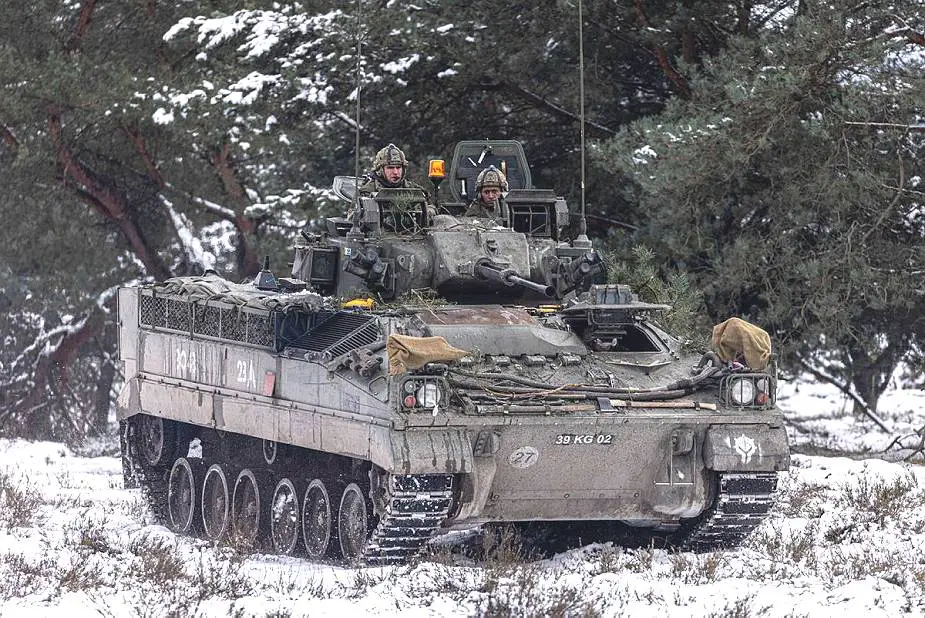
Warrior MCV-80 IFV
Warrior MCV-80 IFV
Tracked armored Infantry Fighting Vehicle - United Kingdom

Description
The Warrior MCV-80 is an Armoured Infantry Fighting Vehicle (AIFV) designed in 1977 by the British Company GKN Sankey to replace the tracked armored personnel carrier FV432, which was in service with the British Army since the 1960s. Actual design work commenced in 1977, and by 1980, three MCV-80 prototypes were running. In January 1984, the British Ministry of Defence announced negotiations with GKN Sankey for an initial production order. By 1984, 10 prototypes had been built; one of these had a highly successful demonstration in the Middle East in 1983 and again in another Gulf country in mid-1984. This has led to the development of a Desert Fighting Vehicle configuration with 25 mm, 30 mm or 90 mm cannon and a crew of 10. Production of Warrior began at Telford in January 1986, with the first production vehicles completed in December. The first production batch comprised 290 vehicles: 170 section vehicles with two-man 30 mm RARDEN turrets and 120 specialized variants. The first production of Warrior was officially handed over to the British Army in May 1987. The first Warrior Battalion in the British Army of the Rhine was fully operational in mid-1988. The second and third batches were to have totaled 763 vehicles, bringing the British Army order to 1,053 vehicles, including variants, sufficient to equip 13 armored infantry battalions. The Warrior has been upgraded with many improvements, including Bowman Communications System and Thales Battle Group Thermal Imaging (BGTI) night sights. Future upgrades will include a digital fire control system and an improved power pack. The British Army intends to upgrade its Warriors to extend their service life to 2025. The Warrior Capability Sustainment Program (WCSP) will involve upgrading 643 of its Warriors with the Warrior Modular Protection System (WMPS) and Warrior Enhanced Electronic Architecture (WEEA). Within that group, 449 vehicles will also be fitted with a new turret and weapon system under the Warrior Fightability Lethality Improvement Program (WFLIP). The remainder will be designated as Armoured Battlefield Support Vehicles (ABSV), will lack turrets, and will perform field repair and recovery using winch and crane attachments. Under the WFLI program, the current turret mounting the RARDEN cannon, which lacks stabilization and is manually loaded with three-round clips, will be replaced with a turret that mounts a stabilized 40 mm weapon developed by the Anglo-French firm CTA International, which fires Cased Telescoped ammunition. In November 2011, BAE Systems was selected by the UK Ministry of Defence (MoD) to support and provide crucial systems for the Warrior Capability Sustainment Programme. The company will provide its new 40mm cannon and ammunition, designed through a joint venture with Nexter Systems CTA International, for the program.
MCV-80 Warrior IFV variants:
- FV511 Infantry Command Vehicle: 84 of these were produced.
- FV512 Mechanised Combat Repair Vehicle: Operated by REME detachments in Armoured Infantry battalions. It is equipped with a 6.5-tonne crane and power tools, and can tow a trailer carrying two Warrior power packs or one Challenger power pack. 105 of these were produced.
- FV513 Mechanised Recovery Vehicle: Also operated by REME detachments in Armoured Infantry battalions. It is equipped with a 20 tonne winch and 6.5 tonne crane plus power tools and (like the FV512) is able to tow a trailer carrying two Warrior power packs or one Challenger power pack. 39 of these were produced.
- FV 514 Mechanised Artillery Observation Vehicle: This is operated by the Royal Artillery as an Artillery Observation Post Vehicle (OPV) and is fitted with mast-mounted Man-packable Surveillance and Target Acquisition Radar (MSTAR) and Position and Azimuth Determining System (PADS), with Image Intensifying and Infra Red equipment. The only armament is the 7.62 mm machine gun, as the 30 mm Rarden cannon is replaced with a dummy weapon. This allows space for the targeting and surveillance equipment while still keeping largely the same outward appearance of a standard Warrior in order to avoid becoming a priority target. 52 of these were produced.
- FV 515 Battery Command Vehicle: This is operated by the Royal Artillery. 19 of these were produced.
- Warrior with MILAN: This conversion was originally developed for Operation Desert Storm with a number of kits supplied to convert existing vehicles to carry out this role. Basically, the Euromissile MILAN ATGW launcher is pintle-mounted on the right side of the turret roof, with racks provided internally for additional missiles. Late in 1991, the UK MoD ordered another batch of Warriors to carry the MILAN ATGW system, a role previously undertaken by FV432s which lack the cross-country mobility to work with Warrior vehicles and Challenger 1 and 2 MBTs.
- Desert Warrior: This was an export version adapted for operations in hostile desert conditions. It was fitted with the Delco turret as used on the LAV-25 wheeled IFV, mounting a stabilised M242 Bushmaster 25 mm chain gun with coaxial 7.62 mm chain gun and 2 x Hughes TOW ATGM launchers (one mounted on each side). In 1993, Kuwait purchased 254 Desert Warrior vehicles.
Technical Data
| Armament |
|
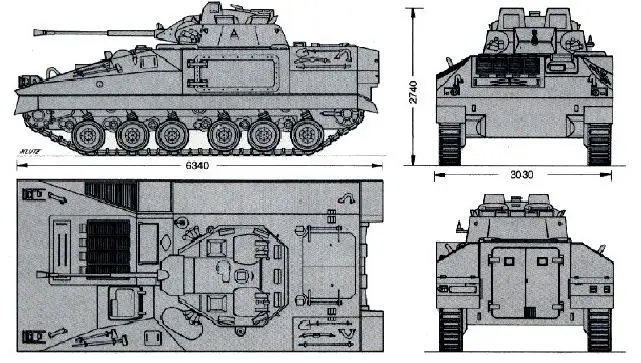
The Warrior MCV-80 IFV is fitted with a two-man electrically operated turret that can rotate on 360°. The turret is armed with a non-stabilized L21A1 30 mm RARDEN cannon capable of destroying most modern APCs at a maximum range of 1,500 meters. A 7.62mm coaxial machine gun L94A1 is mounted to the left side of the main armament. The gunner's station has an optical sight and can be fitted with an electro-optical day/night thermal sight. The commander has seven optical periscopes that provide 360° observation and a dedicated sight for weapon aiming. Six grenade dischargers are mounted on each side at the front of the turret.
|
| Design and protection |
|
The hull of Warrior MCV-80 IFV is made of all-welded aluminum, which provides protection against the firing of small arms and shell splinters. The driver sits at the front of the vehicle with the two-man steel turret located in the center of the vehicle and the troop compartment at the rear. The troops enter and exit through a single power-operated door at the rear of the hull, which has a vision block. In the roof of the troop compartment are two-day rotating periscopes, on either side, for use by the infantry. Over the top of the troop compartment are double roof hatches. The Warrior carries eight infantry, one of which also commands the vehicle and therefore dismounts with the infantry. The remaining seven sit in the troop compartment, four on the right and three on the left, in separate seats with seat belts.
|
| Mobility |
| The Warrior MCV-80 IFV is powered by a Perkins Engines Company CV-8 TCA V-8 diesel developing 550 hp. at 2,300 rpm coupled to a Perkins Engines Company X-300-4B fully automatic transmission with torque converter and lock-up clutch, 4 forward and 2 reverse gears. The torsion bar suspension of Warrior MCV-80 consists of six rubber-tired aluminum roadwheels on either side, with the drive sprocket at the front, idler at the rear, and three track-return rollers. The Warrior can run at a maximum road speed of 75 km/h with a maximum cruising range of 660 km. The vehicle is able to negotiate a gradient up to 60%, side slopes to 40%, and natural and engineered trenches to 2.5 m. The Warrior can climb a vertical obstacle of 0.75 m and a fording depth of 1.3 m without preparation. |
| Combat Equipment |
| Standard equipment of the Warrior MCV-80 IFV includes an NBC system, which is mounted on the side of the hull to the left rear of the driver, and a full range of passive night vision equipment. On either side of the rear troop doors is a storage box. All Warrior IFVs are now equipped with Bowman radios, which replace the earlier Clansman radios, for enhanced communications, command, and control. The old IR night vision sights is now replaced by Thales Optronics Battle Group Thermal Imaging (BGTI) sights to upgrade night fighting capabilities, with 8x magnification. |
Specifications
| Armament | Armor |
| One 30mm cannon, one 7.62mm machine gun | Protection against the firing of small arms and artillery shell splinters |
| Country users | Weight |
| United Kingdom | 28,000 kg combat weight |
| Designer Country | Speed |
| United Kingdom | 75 km/h |
| Combat Equipment | Range |
| NBC protection system, passive night vision, night vision, Optronics Battle Group Thermal Imaging | 660 km |
| Crew | Dimensions |
| 3 + 7 | Length: 6.34 m; Width: 3.0 m; Height: 2.79 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pictures - Video



























