- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
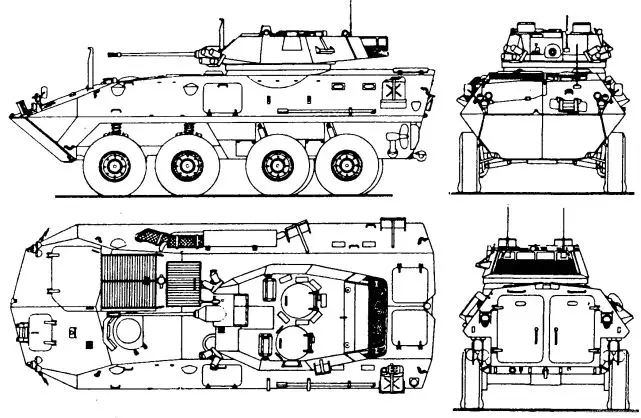
LAV 25
|
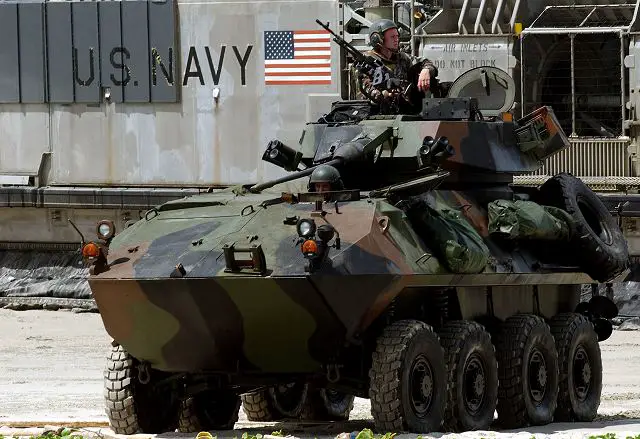
LAV-25 Light Armoured Vehicle
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The LAV-25 is an 8x8 amphibious reconnaissance armored vehicle designed and manufactured by the American Company General Dynamics Land Systems. The vehicle is mainly used by the United States Marine Corps. The LAV-25 is based on the Swiss 8x8 armored vehicle Piranha I manufactured by the Swiss Company Mowag, now a subdivision of General Dynamics Land Systems. In September 1981, General Motors of Canada (now General Dynamics Land Systems - Canada), was awarded a $3.1 U.S. million contract by the United States Marine Corps to supply four 8 × 8 models of the Swiss MOWAG Piranha vehicle. In September 1982, it was announced that the then Diesel Division, General Motors of Canada, had won the LAV competition. The original five-year contract was to have been for 969 LAVs, 680 for the US Army and 289 for the US Marine Corps with a total value of US$477.8 million, and an option for a further 598 vehicles. In 1994, the U.S. military withdrew from the program, and all the vehicles were delivered to the U.S. Marine Corps. Final deliveries of the LAV were made to the US Marine Corps in 1988. The LAV was also delivered to the U.S. Marine Corps in several variants. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Variants | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
- LAV-25A1: upgrade of standard LAV vehicle under the program SLEP (Service Life Extension System). The new modification or SLEP has changed the LAV-25 to the LAV-25A1 standard and has been completely fielded. The basic SLEP program encompasses two primary components, survivability, and reliability. The survivability parts include add-on camouflage panels for visual and thermal signature reduction as well as thermal treatment for the exhaust. The first basic SLEP LAV vehicles entered service in May 2003 and are designated A1.
- LAV-25A2: with new external and internal ballistic armor upgrades, improved fire suppression equipment, and upgrading the vehicle's suspension to the Generation II standard. The LAV-25A2 includes the Improved Thermal Sight System (ITSS) developed by Raytheon. The ITSS provides the gunner and commander with thermal images, an eye-safe laser range finder, a fire-control solution, and far-target location target grid information. - LAV-AT: equipped with an Emerson 901A1 TOW-2 ATGM (Anti-Tank Guided Missile) launcher. - LAV-M: mortar carrier with an 81mm mortar mounted at the rear of the vehicle - LAV-AD: equipped with an electric turret mounting a General Dynamics GAU-12 Equalizer 25 mm (0.984 in) 5-barreled Gatling cannon, and two missile pods each with 4× FIM-92 Stinger missiles for Short Range Air Defense (SHORAD) duties. - LAV-R: recovery vehicle with a boom crane and recovery winch. - LAV-C2: command vehicle with a raised roof to accommodate several VHF, UHF, and HF radios. - LAV-LOG: modified vehicle for lgistic role. - LAV-MEWSS (Mobile Electronic Warfare Support System): LAV equipped with electronic warfare equipment. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Technical Data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back to top | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Back to top | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||





























