- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
Tochka-U SS-21 Scarab 9M79
Tochka Tochka-U SS-21 Scarab 9M79
Surface-to-surface short-range ballistic missile - Russia
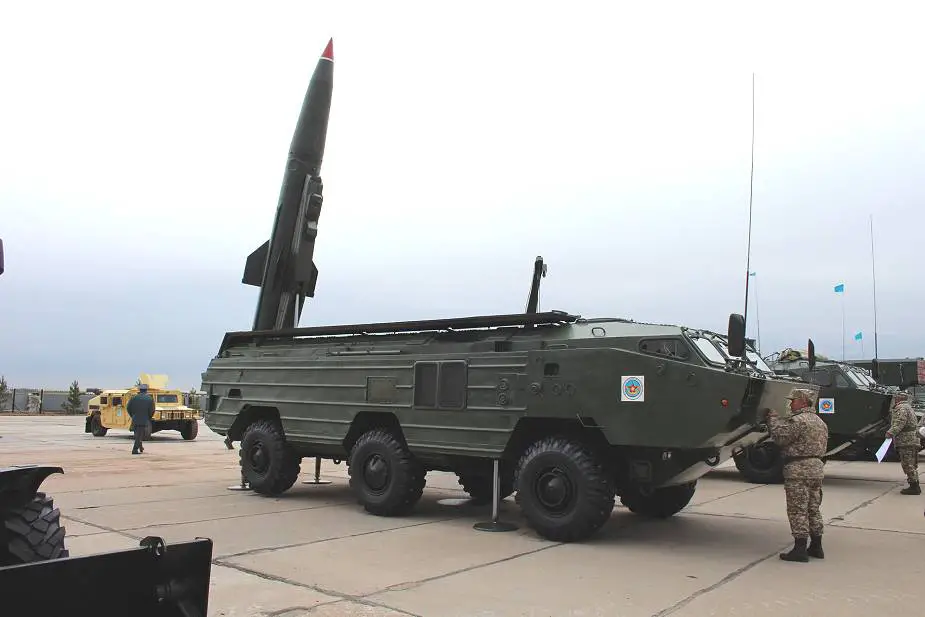

Description
The SS-21 Scarab (Russian name: 9M79 "Tochka") is a Russian-made short-range ballistic missile. In the late 1960s, the Russian decided to start the process of developing a guided successor to the unguided artillery rocket known to the West as the FROG-7, and the result was the 9M79 Tochka (SS-21 Scarab). The Tochka-U is an improved version of the Tochka using a new missile propellant to increase the range to 120 km and an improved CEP (Circular Error Probable) to less than 95 m. The improved Scarab B (Tochka-U) passed state tests from 1986 to 1988 and was introduced in 1989. This mobile missile launcher unit was developed in 1972 and in 1973 it entered service in the Soviet armed forces with infantry and armored regiments. The SS-21 is designed to effectively defeat critical targets in the tactical depth of the enemy battle formation, as nuclear strike means, missile launch positions, airfields, command posts, anti-aircraft units, artillery batteries, and other small-size targets. The vehicle crew compartment is in the forward section and the missile compartment behind. During transport, the missile is enclosed with the warhead in a temperature-controlled casing.
Model variants:
- Scarab A: The initial Scarab A entered service with the Soviet Army in 1975. It carries one of three types of warheads.
- Scarab B (Tochka-U) SS-21 Scarab-B: was introduced in 1989. Improved propellant increased the range to 120 km. CEP significantly improved, to less than 95 m.
- Scarab C: was developed in the 1990s. Range increased 185 km, and Circular Error Probable (CEP) decreased Scarab C weighs 1,800 kg.
Technical Data
| Launcher Unit |
|
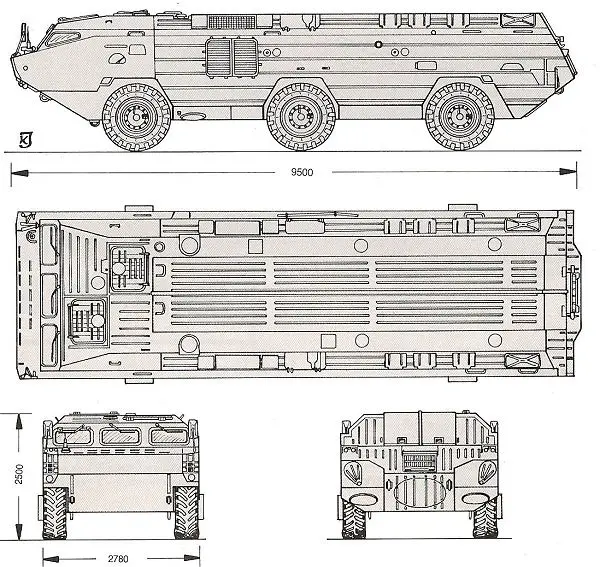
The SS-21 Scarab is based on a mobile BAZ-5921 6-wheeled launching vehicle. This vehicle has a road speed of 60 km/h and fords water obstacles with a speed of 10 km/h. The vehicle has a crew of three and carries a single missile. in the road position, the missile is stored inside the vehicle. In the firing position, roof doors are opened d before the missile is raised to its firing angle of 78° by its hydraulically‐powered launching rail, the process taking approximately 15 seconds. The vehicle is powered by a Diesel engine and is able to reach a maximum road speed of 65 km/h with a maximum cruising range of 650 km. The vehicle is amphibious and can cross water obstacles at a maximum speed of 10 km/h.
|
| Missile and warhead |
|
This is a solid-propellant missile of the single-stage type. The basic missile has a range of 70 km. The SS-21 can carry a number of tactical warhead types including 9N123F HE-fragmentation type with 120 kg of explosive with a terminal guidance package (radar and terrain-comparison) yielding a CEP of 30m. Other warheads are the AA60 tactical nuclear, 9N123K carrier with 'smart' sub-munitions, and chemical. The SS-21 Scarab uses two missiles, the 9M79F with the 9N123F fragmentation-HE warhead, and the 9M79K with the 9N123K cluster warhead. The 9M79 Tochka missile has a pointed nose, roughly cylindrical main body, and a truncated conical tail. The nose of the missile is divided into three varying taper conic sections – the tip, the middle, and the rear. It has a length of 6.4 m and a diameter of 0.65 m. The missile can be also fitted with a nuclear or chemical warhead. The Tochka-U or 9M79-1 missile differs from the Tochka missile with the placement of the wings which are located slightly forwards. The 9M791 missile can be armed with the 9N123F HE (High Explosive) blast fragmentation warhead, the 9N123K submunition warhead and 9N39, 9N64, and 9N65 nuclear warheads. The missile has a length of 6.4m and a launch weight of 2,010 kg.
|
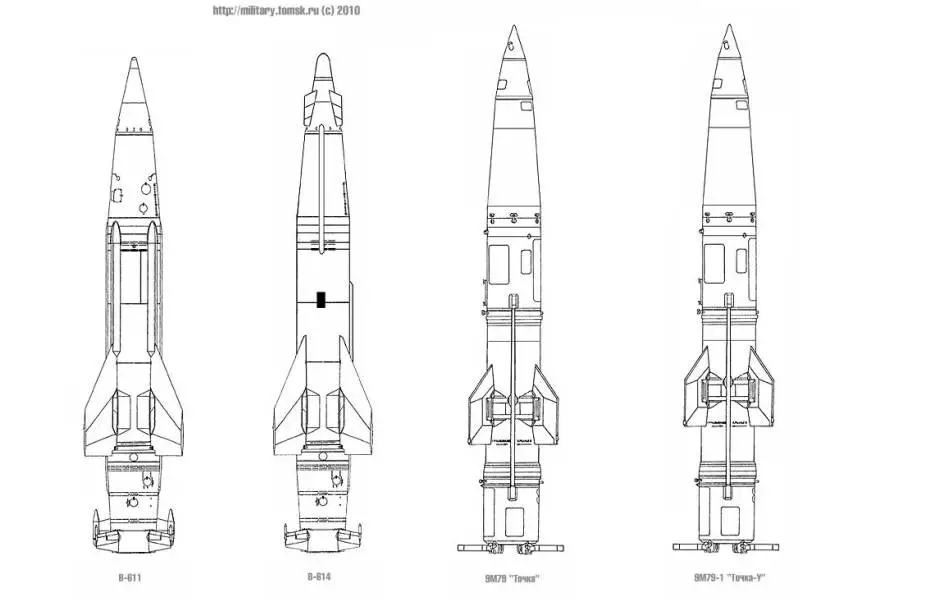 |
| Guidance |
| The missile's guidance is supplemented with terminal guidance, based on a passive radar seeker. The seeker‐equipped warheads are used when attacking radar‐emitting targets, such as radar systems used with SAM (Surface to Air Missile) sites. The missile flight is controlled using an inertial guidance system. |
| Combat Use |
| The SS-21 Scarab missile system ensures the performance of missions in all types of land combat in any theatres of war during any season and at any time of the day with both exposed and entrenched deployment of the self-propelled launcher (SPL) without surveying or meteorological support and without preparing the firing position within a combat application temperature range of -40° to +50°C. Components: - 9P129: Launcher unit - 9T218: transporter loader (TL) - 9T222 (9T238): transport vehicle - 9V819: automated checkup and testing vehicle - 9V844: maintenance vehicle - 9F370: ammunition equipment set - 9Ya234 missile and 9Ya warhead containers. |
Specifications
| Type of Missile | Vehicle Weight |
| Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile | 16,000 kg |
| Country users | Effective range missile |
| Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Czech Republic, Hungary, Iran, Kazakhstan, Libya, Nort Korea, Russia, Slovakia, Ukraine, Syria, Yemen. | Scarab A Tochka: 70 km Scarab B Tochka-U: 120 km Scarab C: 185 km |
| Launcher | Accuracy of fire missile |
| Mobile truck transporter - erector - launcher | Scarab A Tochka: 160 m Scarab B Tochka-U: 95 m Scarab C: 70 m |
| Warhead | Guidance |
| HE fragmentation, nuclear, chemical | Inertial system |
| Crew | Dimensions |
| 4 | Length: 9.5 m; Width: 2,78 m; Height: 2,5 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
Pictures - Video

























