- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
Trembita Cruise Missile
Trembita Missile
Cruise missile or flying bomb - Ukraine
Description
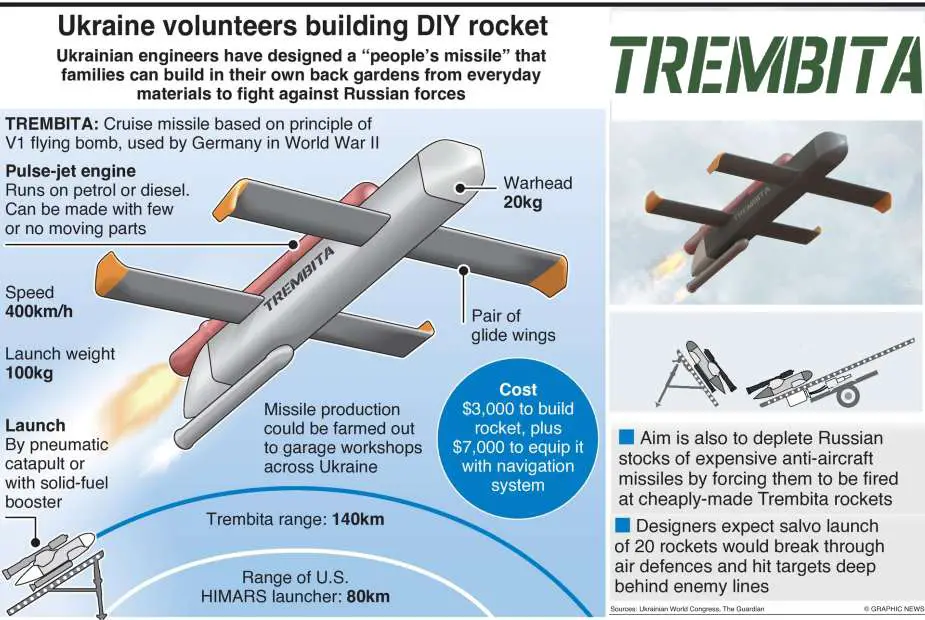
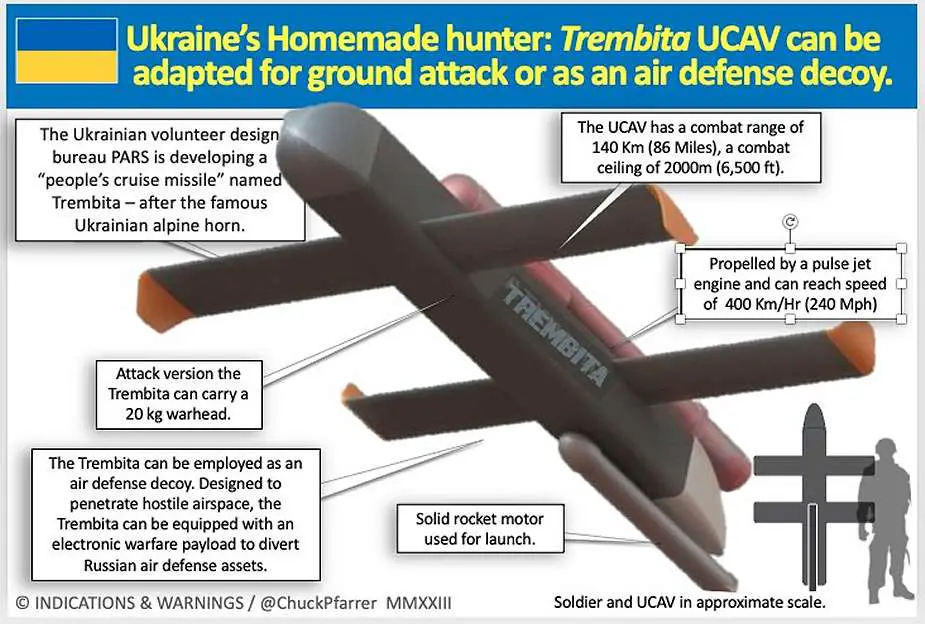
The Trembita is an affordable cruise missile, designed and developed by Ukrainian engineers, that comes at a cost significantly lower than its Western counterparts. Named after a traditional long alpine horn used by Ukrainian shepherds in the Carpathian highlands of the west, the development of this missile was the work of a dedicated team of eight Ukrainian engineers. The new missile was unveiled in July 2023 thanks to a video report by the TV News Channel France 24.
The cost of manufacturing the missile body is about $3,000, with an additional $7,000 required to fit it with a state-of-the-art navigation system. This pricing is just a small fraction of the cost of Russia's hypersonic and cruise missiles, such as the Kinzhal and Kalibr, which are estimated to cost between $1 million to $2 million each.
The design of the Trembita missile is grounded in the principles of the V1 flying bombs, which were utilized by Germany during World War II. According to the Ukrainian engineers responsible for its creation, this missile represents a new class of weaponry that can be launched from either a combat vehicle or a ship, using a pneumatic catapult or a solid-fuel booster.
The Trembita missile is designed with the capability to target a variety of land targets, including combat vehicles and air defense systems. This adaptability enhances its value on the battlefield and contributes to its overall effectiveness in combat scenarios.
Trembita missile flying bomb variants:
- No variants at this time.
Technical Data
| Design |
|
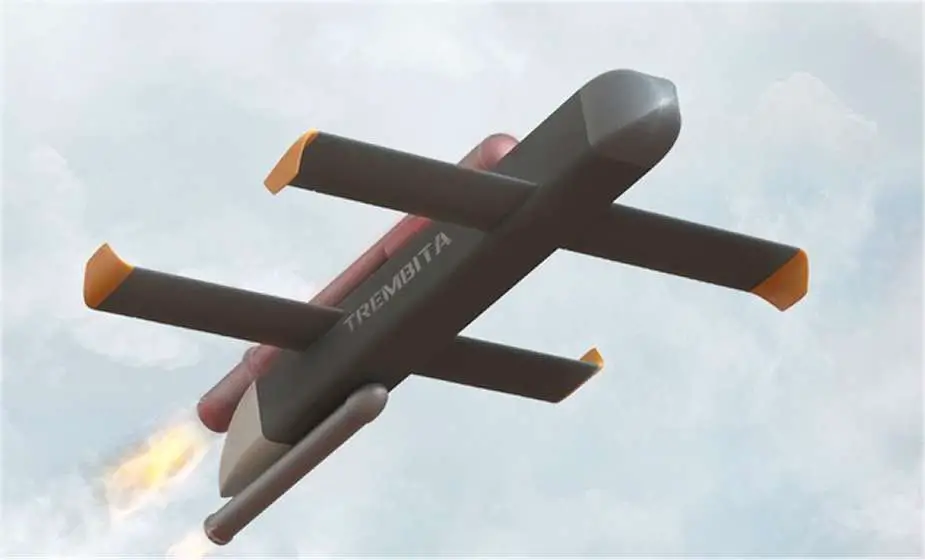
The design of the Trembita missile is based on a fuselage approximately 2 meters in length, with the explosive head mounted at the front. The missile has two stabilization wings mounted on the lower front part of the fuselage, and two others at the rear fixed on the upper part. The upper part of the fuselage is equipped with a propulsion engine.
|
 |
| Warhead |
|
The Trembita missile is designed to be capable of transporting a warhead weighing 20 kilograms. This warhead can be equipped with one of two different types of explosive charges. One option is a thermobaric charge, which creates a blast wave of extremely high pressure by rapidly releasing a large amount of energy in the form of heat and light. Alternatively, it can carry a high-explosive charge, which detonates more quickly and with more concentrated energy output. In some cases, a combined high-explosive charge is used, which blends features of both types for a multipurpose effect.
|
| Propulsion |
| The Trembita missile operates using a jet pulse engine, an innovative propulsion system that functions by intermittent combustion. This engine type is fueled by a reservoir that holds 30 liters of either diesel or petrol, making it versatile as these types of fuel are commonly available from local sources. It can reach a maximum speed of 400 kilometers per hour. It also boasts a significant cruising range, being capable of covering up to 140 kilometers before needing to refuel. A distinct advantage of this type of propulsion system is its mechanical simplicity. Because it lacks moving parts, manufacturing and maintenance become straightforward, making the missile more cost-effective to produce and upkeep. For the launching, the Trembita missile features a solid rocket motor, which is mounted to the lower rear section at the rear of the fuselage. |
| Guidance System |
| If the Trembita missile works as the German V1 missile, the primary guidance will be delivered by a compass-based autopilot system. This incorporated a magnetic compass and a gyroscope. The purpose of the gyroscope was to stabilize the compass against potential disturbances such as wind and turbulence, and the autopilot was designed to maintain the missile on a consistent bearing. The missile is also equipped with a modern navigation system. |
| Combat Use |
| According to details shared by the manufacturer of the Trembita missile, the main objective of Ukraine's first indigenously-developed cruise missile is to effectively counter Russia's defense mechanisms. The strategic plan involves launching these missiles as part of a coordinated battery, wherein 20 to 30 missiles would be dispatched simultaneously.
Interestingly, not all of these missiles are intended to carry explosive warheads. Some are designed for specific strategic objectives such as targeting ammunition depots and command and control centres. These targets have been selected due to their crucial role in maintaining effective enemy operations. By disrupting these sites, the Ukrainian forces aim to impede Russia's capacity to respond or retaliate effectively. Furthermore, an additional effect of the Trembita missiles, as stated by the producer, is the significant psychological impact they have on the Russian soldiers. These missiles generate a thunderous noise of around 100 decibels, which is expected to lead to a "negative psycho-emotional" effect. This could cause disorientation, fear, and demoralization among the Russian forces, potentially leading to reduced combat effectiveness. In this way, the Trembita missiles serve as not just physical, but also psychological, weapons of warfare. |
Specifications
| Type | Range |
| Cruise missile / Flying bomb | 140 km |
| Country users | Missile Launch Weight |
| Ukraine | 100 kg |
| Designer Country | Speed |
| Ukraine | 400 km |
| Type of Warheads | Altitude |
| Thermobaric or HE High-Explosive | 2,000 m |
| Weight Warhead | Dimensions |
| 25 kg | Length: 2 m; Diameter:? m;Wingspan : ? m |
Details View
 |
|
Pictures - Video




















