Breaking news
US Missile Defense Agency selects Northrop Grumman to lead homeland missile defense program.
Northrop Grumman has been awarded an indefinite delivery, indefinite quantity contract with a maximum amount of $3,286,745,005 by the U.S. Missile Defense Agency (MDA) for the Ground-based Midcourse Defense (GMD) Weapon System (GWS) program. The GWS program defends the United States against intermediate and intercontinental ballistic missile attacks. Under this competitively procured contract, Northrop Grumman will provide design, development, verification, deployment and sustainment support of new capabilities for GWS.
Follow Army Recognition on Google News at this link
CSIS missile defense project (Picture source: missilethreat.csis.org)
“As the GWS prime contractor, we will continue to work closely with MDA to optimize and develop modern missile defense systems to defend against evolving threats and provide advanced capabilities for the warfighter,” said Scott Lehr, vice president and general manager, launch and missile defense systems, Northrop Grumman. “GWS is part of Northrop Grumman’s land and sea-based missile defense systems that are enabled by our advanced missile warning and tracking space satellites. Together, we are delivering end-to-end capabilities that will protect the United States and its allies.”
Northrop Grumman is the leading provider of missile defense solutions. The GWS program award builds on the company’s decades of mission-proven missile defense innovation, experience and end-to-end capabilities. The Northrop Grumman-led GWS program team will primarily be located in Huntsville including our large and small business partners.
GWS will transform the current ground system component of the GMD system by utilizing a DevSecOps approach leveraging proven digital transformation processes to update and modernize legacy code, warfighter capabilities, and incorporate the Next Generation Interceptor fleet into the overall GMD system.
What is the Ground-based Midcourse Defense system?
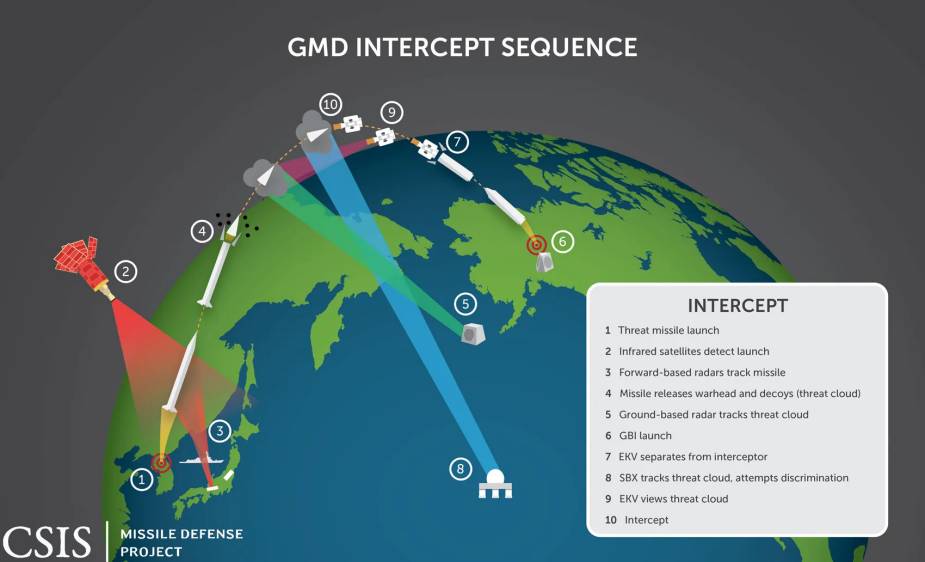
The Ground-based Midcourse Defense (GMD) system is currently the only U.S. missile defense system devoted to defending the U.S. homeland from long-range ballistic missile attacks. GMD and its associated elements span 15 time zones, including Ground-based Interceptors (GBIs) at two locations (Ft. Greely, Alaska and Vandenberg AFB, CA), seven types of sensors on land, sea, and space, and multiple and distributed fire control systems. By the end of 2017, there will be 44 deployed GBIs, 40 based at Ft. Greely, and four at Vandenberg AFB.
When ballistic missile defense sensors detect a missile launch, these data are fused and fed into the GMD fire control system, which is used to launch one or more GBIs. The GBI will fly into the path of an incoming missile before releasing an Exoatmospheric Kill Vehicle (EKV), which uses onboard sensors to hunt down and physically collide with the warhead, destroying it on impact.
What makes GMD different from other missile defense systems?
GMD is designed expressly to counter long-range, intercontinental class ballistic missiles which threaten the U.S. homeland. It uses a three-stage booster, giving the necessary “legs” to perform intercepts over great distances. This range gives GMD by far the greatest coverage area of any U.S. missile defense system, defending (to a varying degree) all fifty states and Canada. Other missile defense systems, including Aegis, THAAD, and Patriot, are generally classified as “regional” systems and are geared toward short to intermediate-range ballistic missile threats. While some may have homeland defense applications in some circumstances, they have much smaller coverage areas than GMD, and generally much less capability, if any, against ICBMs.
Conversely, GMD is not capable of shorter-range, regional defense missions. North Korea’s short and medium-range missiles threatening South Korea and Japan, for example, fall outside of GMD’s engagement envelope. These threats require other solutions, such as Aegis, THAAD, or Patriot.


























