Breaking News
US-made Typhon Missile Launcher System Could Place China Coast Within Philippine Reach.
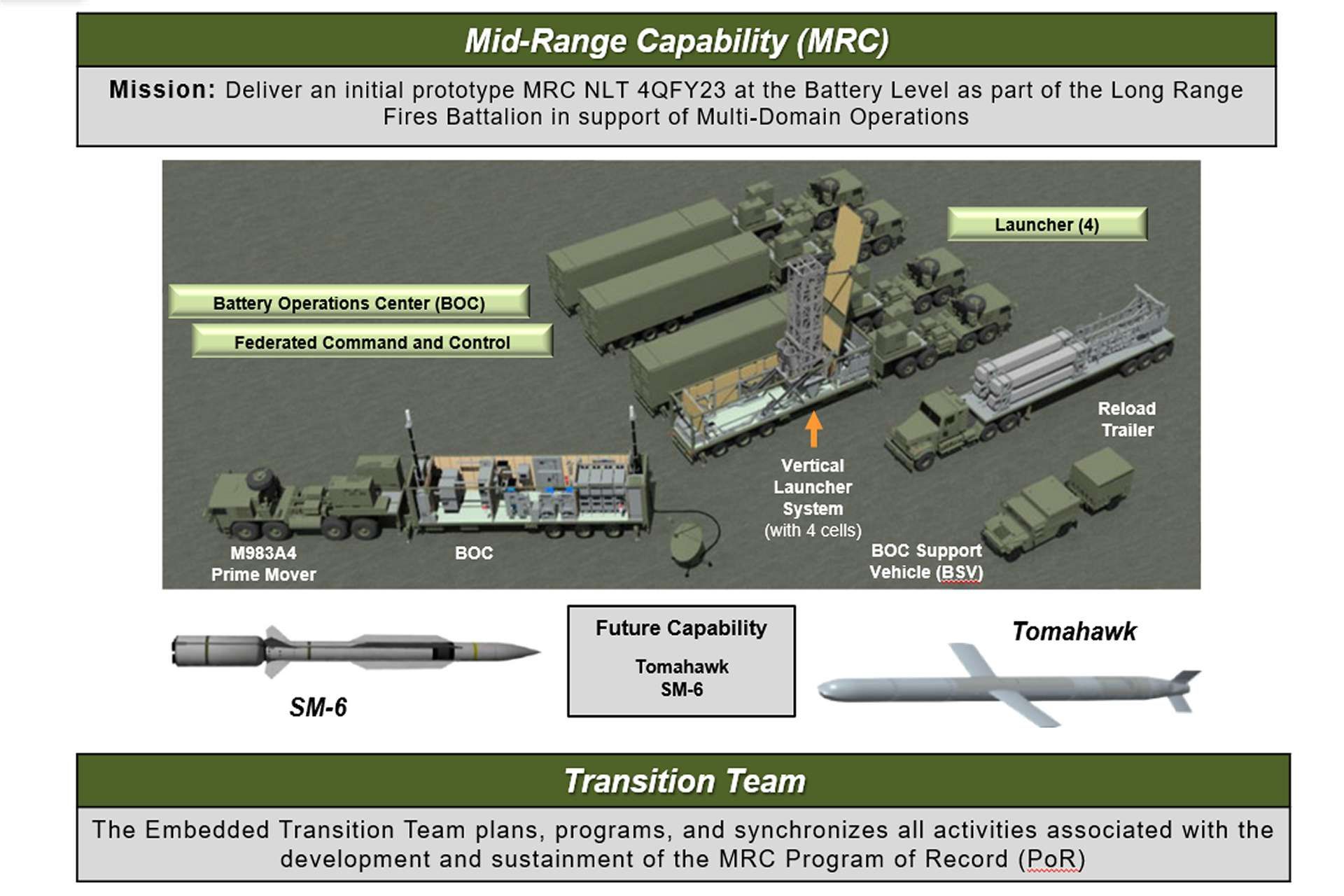
On August 31, 2024, General Romeo Brawner Jr., the head of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, announced that the Philippines is considering acquiring the Medium-Range Typhon Missile System, a significant move signaling a strategic pivot towards external defense. This announcement was made during the meeting of the Mutual Defense Board-Security Engagement Board (MDB-SEB) at the Philippine Military Academy. The Mid-Range Capability (MRC), or Typhon, is a US Army transporter erector launcher for Standard SM-6 and Tomahawk missiles.
Follow Army Recognition on Google News at this link
US Mid-Range Capability Program, MRC. (Picture source: Wikimedia)
The Typhon MRC missile system, capable of launching Tomahawk and SM-6 missiles, was last seen in the Ilocos Norte province of the Philippines. These missiles, suitable for land, air, and sea scenarios, significantly enhance the range of the country's defensive arsenal. The Typhon missiles have been operationally deployed by the U.S. Army's 1st Multi-Domain Task Force, arriving via a U.S. Air Force C-17 Globemaster at an undisclosed airfield in northern Luzon for the joint military exercises Salaknib 2024.
U.S. defense officials emphasized that from their position in Luzon, Typhon's missiles can cover not only the entire Luzon Strait but also reach the Chinese coast and various bases of the People's Liberation Army in the South China Sea. Although the system was not used in live-fire exercises, Philippine troops were trained on how to handle and maintain this missile system, which was also deployed during the Balikatan 24 exercises.
In addition to Typhon, the Philippine arsenal now includes BrahMos missiles, medium-range supersonic cruise missiles capable of hitting targets up to 400 kilometers away and traveling at a speed of Mach 2.8. These versatile missiles can be launched from submarines, ships, aircraft, or ground platforms, adding an extra layer of strategic defense.
The Medium-Range Capability (MRC) system, also known as the Typhon system, is a key component of the U.S. Army's modernization portfolio for long-range precision fires. The system is designed to bridge the gap between the Army's Precision Strike Missile (PrSM), which has a maximum range of 300 miles, and the developing long-range hypersonic weapon, capable of reaching up to 1,725 miles. Typhon uses SM-6 and Tomahawk missiles, adapted for ground launch, enhancing operational capabilities in multi-domain situations.
The Typhon's Mk 70 Mod 1 launcher system, a modified version of the Navy's vertical launch system Mk 41, allows for the integration and launching of missiles from a standard 40-foot ISO container, thus facilitating its rapid deployment and compatibility with various launching platforms. This sophisticated system enables effective target detection, tracking, engagement, launch, guidance, and interception, bolstering the Philippines' defense posture in a geopolitically tense region.
The Medium-Range Capability (MRC), or Typhon, plays a crucial role in the detection and tracking of targets within an integrated command and control network. Utilizing radars and other sensors, the MRC receives essential data to identify and track aerial threats such as enemy aircraft and missiles.
Once a target is detected and tracked, the MRC's command system selects the most appropriate missile for interception. The SM-6 missile is particularly favored for this role, due to its ability to engage high-velocity targets at long distances, a critical feature for air defense.
The missile launch is executed from the Mk 70 Mod 1 launch system, designed for a rapid response to identified threats. Its modular and mobile structure allows for easy and quick deployment in various environments, thus enhancing the interception system's effectiveness.
After launch, the SM-6 missile is guided towards its target using advanced navigation systems. It receives in-flight updates from the command system, allowing for trajectory adjustments to maximize the chances of effectively hitting the target.
Finally, interception is achieved through the SM-6 missile's terminal guidance system, which enables it to complete its course towards the target with high precision. The missile is equipped with a payload designed to neutralize the target, either through direct impact or proximity detonation, depending on the type of threat encountered.


























