Breaking news
Royal Navy unveils radical future submarine concepts.
| 2017
|
|
|||
 Royal Navy picture Royal Navy picture |
|||
|
|
|||
|
The UK's brightest and most talented young engineers and scientists came up with the designs after being challenged by the Royal Navy to imagine what a future submarine would look like and how it would be used to keep Britain safe in decades to come.
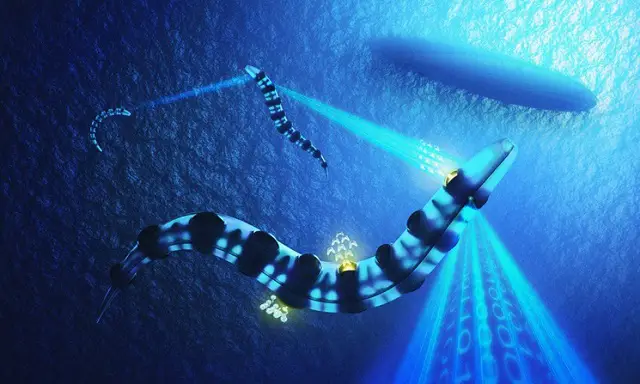
Defence Minister Harriett Baldwin said: "These remarkable designs display the great promise of our young engineers and scientists and the great ambition of the Royal Navy. "This kind of innovation is at the heart of defence and the UK's world-leading capability. That's why we are using our rising budget to invest in high-tech capability to keep our Armed Forces at the cutting-edge, and our £800 million Innovation Fund aims to take advantage of exactly these kinds of futuristic ideas." The whale shark/manta ray-shaped mothership would be built from super-strong alloys and acrylics, with surfaces which can morph in shape. With hybrid algae-electric cruising power and propulsion technologies including tunnel drives which work similarly to a Dyson bladeless fan, the submarine could travel at unprecedented speeds of up to 150 knots. |
|||
|
|
|||
 Royal Navy picture Royal Navy picture |
|||
|
|
|||
|
Commander Peter Pipkin, the Royal Navy's Fleet Robotics Officer, said: "With more than 70 per cent of the planet's surface covered by water, the oceans remain one of the world's great mysteries and untapped resources.
"It's predicted that in 50 years' time there will be more competition between nations to live and work at sea or under it. So it's with this in mind that the Royal Navy is looking at its future role, and how it will be best equipped to protect Britain's interests around the globe. "Today's Royal Navy is one of the most technologically advanced forces in the world, and that's because we have always sought to think differently and come up with ideas that challenge traditional thinking. If only 10 per cent of these ideas become reality, it will put us at the cutting edge of future warfare and defence operations." |
|||
|
|
|||
 Royal Navy picture Royal Navy picture |
|||
|
|
|||
|
This mothership would be capable of launching unmanned underwater vehicles shaped like eels, which carry pods packed with sensors for different missions. These pods can damage an enemy vessel, or dissolve on demand at the end of an operation to evade detection.
The project, named Nautilus 100, was set up to mark the 100th anniversary of the launch of the USS Nautilus, the world's first nuclear-powered submarine. Rear Admiral Tim Hodgson, the Ministry of Defence's Director of Submarine Capability, said: "We want to encourage our engineers of the future to be bold, think radically and push boundaries. From Nelson's tactics at the Battle of Trafalgar to Fisher's revolutionary Dreadnought battleships, the Royal Navy's success has always rested on a combination of technology and human skill. "The pace of global innovation is only going to increase, so for the UK to be a leader in this race it needs to maintain its leadership in skills and technology. Hopefully this project has inspired the next generation of British scientists to be bold in their ambitions and I congratulate them for their inspiring work." Young British scientists and engineers from UKNEST, a not-for-profit organisation which promotes science, engineering and technology for UK naval design, answered the challenge. More than 20 of them took part in the project, 'visioneering' a new submarine fleet for the future Royal Navy. Gemma Jefferies, 21, from Bristol, is an engineering assistant with L3 Marine Systems UK. Gemma, who took part in the project, said: "It was amazing to see a whole manner of disciplines coming together in this project. It was great to let our imaginations run with crazy ideas, some that may not actually be considered science fiction in the near future." Unlike the submarines of today, which perform multiple roles in one hull, it is envisaged that the Royal Navy of the future would operate a family of submarines of various shapes and sizes, both manned and unmanned, to fulfill a variety of tasks. The science and engineering graduates and apprentices, aged 16-34, took the complex systems required by an advanced submarine and applied the latest technological ideas to make them easier to construct, cheaper to run, and more deadly in battle. |
|||


























