Global military expenditure sees largest annual increase in a decade, reaching USD1917 billion in 2019
Total global military expenditure rose to $1917 billion in 2019, according to new data from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI). The total for 2019 represents an increase of 3.6 percent from 2018 and the largest annual growth in spending since 2010.
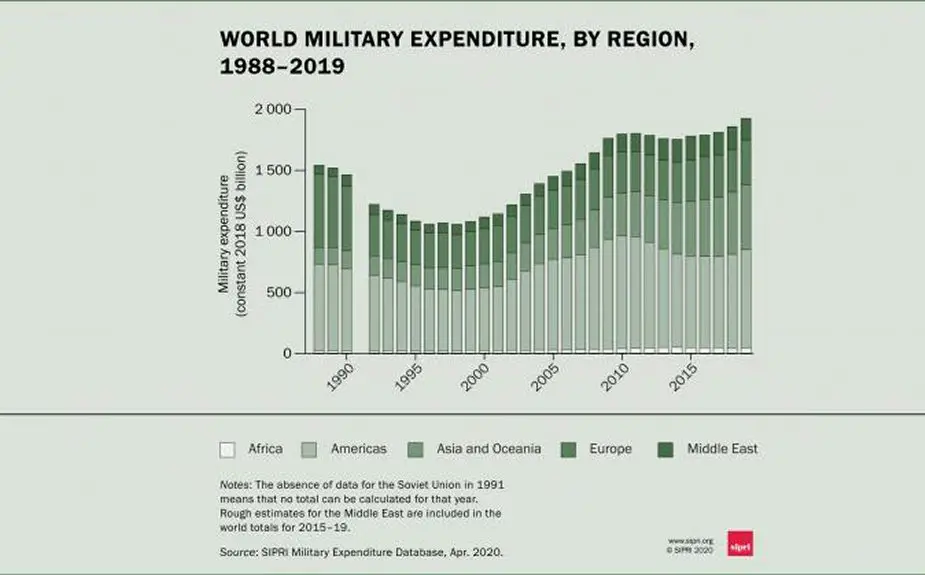
World military expenditure, by region, 1988–2019 (SIPRI)
The five largest spenders in 2019, which accounted for 62 percent of expenditure, were the United States, China, India, Russia and Saudi Arabia. This is the first time that two Asian states have featured among the top three military spenders. The comprehensive annual update of the SIPRI Military Expenditure Database is accessible at www.sipri.org.
Global military spending in 2019 represented 2.2 percent of the global gross domestic product (GDP), which equates to approximately $249 per person. ‘Global military expenditure was 7.2 percent higher in 2019 than it was in 2010, showing a trend that military spending growth has accelerated in recent years,’ says Dr. Nan Tian, SIPRI Researcher. ‘This is the highest level of spending since the 2008 global financial crisis and probably represents a peak in expenditure.’
The United States drives global growth in military spending
Military spending by the United States grew by 5.3 percent to a total of $732 billion in 2019 and accounted for 38 percent of global military spending. The increase in US spending in 2019 alone was equivalent to the entirety of Germany’s military expenditure for that year. ‘The recent growth in US military spending is largely based on a perceived return to competition between the great powers,’ says Pieter D. Wezeman, Senior Researcher at SIPRI.
China and India top Asian military spending
In 2019 China and India were, respectively, the second- and third-largest military spenders in the world. China’s military expenditure reached $261 billion in 2019, a 5.1 percent increase compared with 2018, while India’s grew by 6.8 percent to $71.1 billion. ‘India’s tensions and rivalry with both Pakistan and China are among the major drivers for its increased military spending,’ says Siemon T. Wezeman, SIPRI Senior Researcher.
In addition to China and India, Japan ($47.6 billion) and South Korea ($43.9 billion) were the largest military spenders in Asia and Oceania. Military expenditure in the region has risen every year since at least 1989.
Germany leads military expenditure increases in Europe
Germany’s military spending rose by 10 percent in 2019, to $49.3 billion. This was the largest increase in spending among the top 15 military spenders in 2019. ‘The growth in German military spending can partly be explained by the perception of an increased threat from Russia, shared by many North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) member states,’ says Diego Lopes da Silva, Researcher at SIPRI. ‘At the same time, however, military spending by France and the United Kingdom remained relatively stable.’
There were sharp increases in military expenditure among NATO member states in Central Europe: for example, Bulgaria’s increased by 127 percent—mainly due to payments for new combat aircraft—and Romania’s rose by 17 percent. Total military spending by all 29 NATO member states was $1035 billion in 2019.
In 2019, Russia was the fourth-largest spender in the world and increased its military expenditure by 4.5 percent to $65.1 billion. ‘At 3.9 percent of its GDP, Russia’s military spending burden was among the highest in Europe in 2019,’ says Alexandra Kuimova, Researcher at SIPRI.
Volatile military spending in African states in conflict
Armed conflict is one of the main drivers for the volatile nature of military spending in sub-Saharan Africa. For example, in the Sahel and Lake Chad region, where there are several ongoing armed conflicts, military spending in 2019 increased in Burkina Faso (22 percent), Cameroon (1.4 percent) and Mali (3.6 percent) but fell in Chad (–5.1 percent), Niger (–20 percent) and Nigeria (–8.2 percent). Among Central African countries that were involved in armed conflict, military spending in 2019 rose overall. The Central African Republic (8.7 percent), the Democratic Republic of the Congo (16 percent) and Uganda (52 percent) all increased military spending in 2019.
Volatile military spending in African states in conflict
South America: Military expenditure in South America was relatively unchanged in 2019, at $52.8 billion. Brazil accounted for 51 percent of total military expenditure in the sub-region.
Africa: The combined military expenditure of states in Africa grew by 1.5 percent to an estimated $41.2 billion in 2019—the region’s first spending increase for five years.
Southeast Asia: Military spending in South East Asia increased by 4.2 percent in 2019 to reach $40.5 billion.
The average military spending burden was 1.4 percent of GDP for countries in the Americas, 1.6 percent for Africa, 1.7 percent for Asia and Oceania and for Europe and 4.5 percent for the Middle East (in countries for which data is available).
Coronavirus crisis impact
Data from previous global economic downturns suggests that the economic crisis resulting from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic will probably disrupt future military spending. SIPRI is monitoring current developments to assess the extent of this crisis on military spending.
All percentage changes are expressed in real terms (constant 2018 prices). Military expenditure refers to all government spending on current military forces and activities, including salaries and benefits, operational expenses, arms and equipment purchases, military construction, research and development, and central administration, command and support. SIPRI, therefore, discourages the use of terms such as ‘arms spending’ when referring to military expenditure, as spending on armaments is usually only a minority of the total.


























