- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
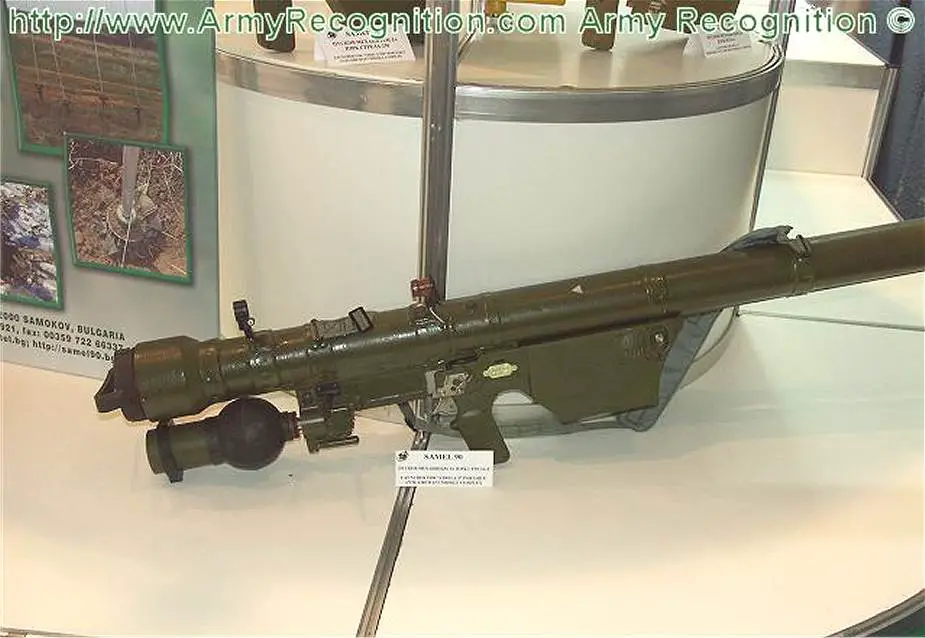
SA-14 Gremlin 9K34 Strela-3
SA-14 Gremlin 9K34 Strela-3 MANPADS
Man-portable surface-to-air defense missile system - Russia

Description
The 9K34 Strela-3 (NATO code SA-14 Gremlin) is a Russian-made man-portable air defense missile system (MANPADS) that was developed in Russia as a response to increasing the performances of the earlier 9K32 Strela 2 (SA-7 Grail) system. The missile was largely based on the earlier Strela 2, and thus development proceeded rapidly. The SA-14 Gremlin was accepted to service in the Russian Army in January 1974. Large quantities have been exported to nations in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. The SA-14 Gremlin remains in service today and has been used in a variety of conflicts.
SA-14 Gremlin 9K34 Strela-3 variants:
- SA-N-8: Naval version
Technical Data
| Launcher Unit |
|
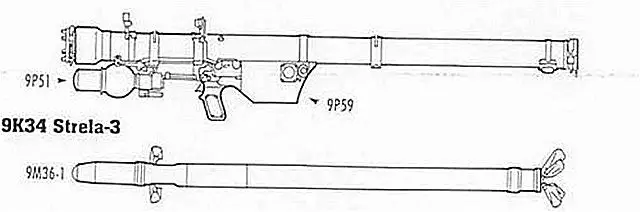
The SA-14 Gremlin is now equipped with a new infra-red homing seeker head. The new seeker worked on the FM modulation (con-scan) principle, which is less vulnerable to jamming and decoy flares than the earlier AM (spin-scan) seekers, which were easily fooled by flares and even the most primitive infrared jammers. Most importantly, the new seeker also introduced detector element cooling in the form of a pressurized nitrogen bottle attached to the launcher. The system consists of the 9P59 gripstock, 9P51 thermal battery/gas reservoir, and 9M36-1 missile. The external appearance of the SA-14 is very similar to the SA-7, and the gripstock, launch canister and aft missile body are almost identical. The most significant differences are the new seeker system and the substitution of a ball-shaped 9P51 thermal battery and gas reservoir for the SA-7's canister-shaped battery.
|
| Missile |
|
The 9M36-1 is a supersonic missile with an average maximum speed of about 410 m/s. It can engage near-supersonic targets out to 4.1 km or to altitudes of 3 km. The blast fragmentation warhead features a secondary charge to set off any remaining fuel. The new infrared seeker has an increased performance against low altitude targets over land and water and is less easily fooled by flares.
|
| Operations |
| The SA-14 Gremlin has a maximum range of 4,500 meters and a maximum altitude of 3,000 meters. |
| Combat Use |
| The SA-14 Gremlin is a very mobile system as the missile and its gripstock launcher are man-portable, even over longer ranges. The system is operated by a single soldier. |
Specifications
| Armament | Type of engaged targets |
| One 9M36-1 missile | tactical aircraft, helicopter |
| Country users | Missile |
| Angola, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Bulgaria, Cuba, Czech Rep., El Salvador, Finland, Georgia, Germany, Hungary, India, Iraq, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Moldova, Nicaragua, North Korea, Peru, Poland, Russia, Serbia, Slovakia, South Africa, Syria, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, UAE, Ukraine, Uzbekistan | - Weight: 10.3 kg - Weight Warhead: 1,17 kg - Warhead type: Blast Fragmentation - Flight speed: 410 m/s - Altitude: 30 - 2,300 m |
| Combat Weight | Reaction time |
| 16 kg ready to fire | 5 to 10 sec. |
| Target engagement | Guidance System |
| 4,100 m (Altitude) | Passive IR homing device and night vision (operating in the medium IR range) |
| Operator | Dimension Missile |
| 1 | Length: 1,47 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
Pictures - Video



























