- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
SA-7 Grail 9K32 Strela-2
SA-7 Grail 9K32 Strela-2 MANPADS
Man-portable air defense missile system - Russia
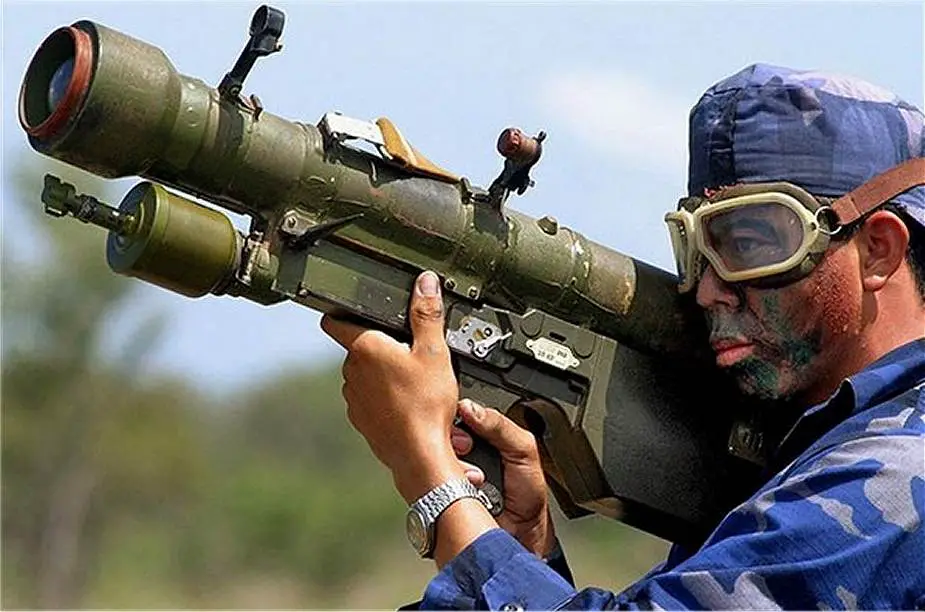

Description
The SA-7 Grail (Russian denomination 9K32M Strela-2) is the first generation of portable air defense missile system (MANPADS), made by the Russian defense industry. The SA-7a (9K32 Strela-2) was introduced for service in 1968 but was soon replaced by the SA-7b (9K32M Strela-2M) which became the most common production model. The SA-7 GRAIL (Strela-2) is a man-portable, shoulder-fired, low-altitude SAM, with a high explosive warhead and passive infrared homing guidance. The SA-7a has an effective range from 800 m to 3.2 km and a kill zone between 15 and 1500 meters in altitude, with a speed of about 430 meters per second (Mach 1.4). The SA-7 Grail is able to destroy all aerial targets flying at low altitudes such as combat helicopters, low-flying fighter aircraft, and UAVs. The STRELA-2 is considerably widespread; it is in service with many armies throughout the world and was produced in many countries based on a license. The total number of missiles that have been manufactured is estimated at 50,000 pieces.
SA-7 Grail 9K32 Strela 2 main variants:
- 9K32M Srela-2M SA-7 B
- 9K34 Strela-3 SA-14 Gremlin
- 9K310 Igla-1 SA-16 Gimlet
- 9K38 Igla SA-18 Grouse
- 9K310-1 Igla-1M
- 9K338 Igla-S SA-24 Grinch
Technical Data
| Launcher Unit |
|
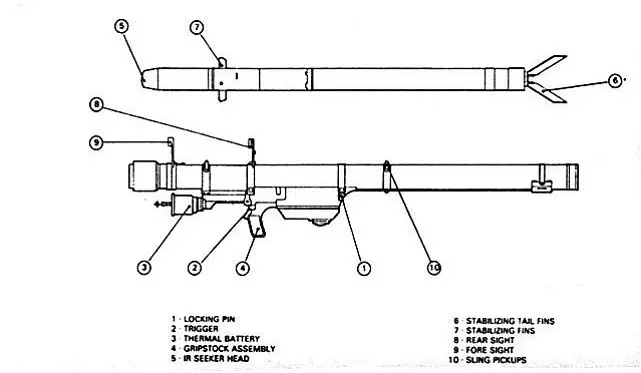
The SA-7 Grail consists of the missile (9K32 & 9K32M), a reloadable gripstock (9P54 & 9P54M), and a thermal battery (9B17). The launch tube is reloadable at the depot, but missile rounds are delivered to fire units in their launch tubes. The device can be reloaded up to five times. An identification friend or foe (IFF) system can be fitted to the operator's helmet. Further, a supplementary early warning system consisting of a passive RF antenna and headphones can be used to provide early cues about the approach and rough direction of an enemy aircraft. The launch unit of the SA-7 Grail has a length of 1.43 m with a combat weight of 9.15 kg.
|
| Missile |
|
The SA-7 Grail missile is launched from a portable cylindrical launcher. It has two rectangular movable control ailerons in the front section, and four tilting rectangular stabilization ailerons in the rear. It is an infrared-guided missile with the seeker in the nose. The initial series of the STRELA-2 missiles were fitted with a non-cooled IR detector with a limited possibility of homing from the aft hemisphere and they had no protection against IR decoys and modulated jammers. The starting (booster) engine burns for about 0.5 seconds, driving engine for another 2 sec. The missile has a maximum firing range of 3.4 km with an altitude from 50 m to 1.5 km. The missile is fitted with a HE (High Explosive) fragmentation warhead weighing 1.17 kg.
|
| Operations |
| When engaging slow or straight-receding targets, the operator tracks the target with the iron sights in the launch tube and applies a half-trigger. This action "uncages" the seeker and allows it to attempt to track. If the target IR signature can be tracked against the background present, this is indicated by green light and buzzer sound. The shooter then pulls the trigger fully and immediately applies lead and superelevation. This method is called manual engagement. An automatic mode, which is used against fast targets, allows the shooter to fully depress the trigger in one pull followed by immediate lead and superelevation of the launch tube. The seeker will uncage and will automatically launch the missile if a strong enough signal is detected. |
| Combat use |
| The SA-7 Grail or 9M32 STRELA-2 is a first-generation man-portable, shoulder-fired short-range anti-aircraft missile system, intended for destruction of both subsonic and supersonic air targets (fixed-wing aircraft, helicopters, UAV) in ground and low altitudes. Development of this relatively simple system (STRELA-2, or SA-7A) started in 1959 and its basic version was introduced after 1966. |
Specifications
| Type | Type of engaged targets |
| Man-portable air defense missile system MANPADS | Tactical aircraft, helicopter, UAV, and cruise missile |
| Country users | Missile |
| Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Angola, Armenia, Botswana, Benin, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, China, Cuba, El Salvador, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Indonesia, India, Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Laos, Lebanon, Libya, Mongolia, Macedonia, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Nicaragua, North Korea, Pakistan, Peru, Poland, Romania, Russia, Sierra Leone, Serbia, Slovakia, Somalia, South Yemen, Sudan, Syria, Tanzania, Ukraine, Vietnam, Zambia, Zimbabwe. | - One 9K32 missile - Weight: 9.2 kg - Weight Warhead: 1.15 kg - Warhead type: HE High Explosive - Flight speed: 430 m/s |
| Designer Country | Reaction Time |
| Russia | 5 to 10 sec |
| Combat weight | Guidance System |
| 14.5 kg ready to fire | Passive IR homing device (operating in the medium IR range) |
| Operator | Dimensions |
| 1 | Length: 1,49 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
Pictures - Video

























