- Army
- Air Defense Systems
- Anti-tank systems and vehicles
- Armored Vehicles
- Armoured personnel carriers
- Artillery Vehicles and Weapons
- Command Post
- Communication Vehicles and Systems
- Electronic Warfare
- Engineer | Maintenance Vehicles
- Infantry Fighting Vehicles
- Main Battle Tanks
- Missiles
- Tactical and Logistic Vehicles
- Radars
- Unmanned Systems
- Weapons
- Navy
- Air
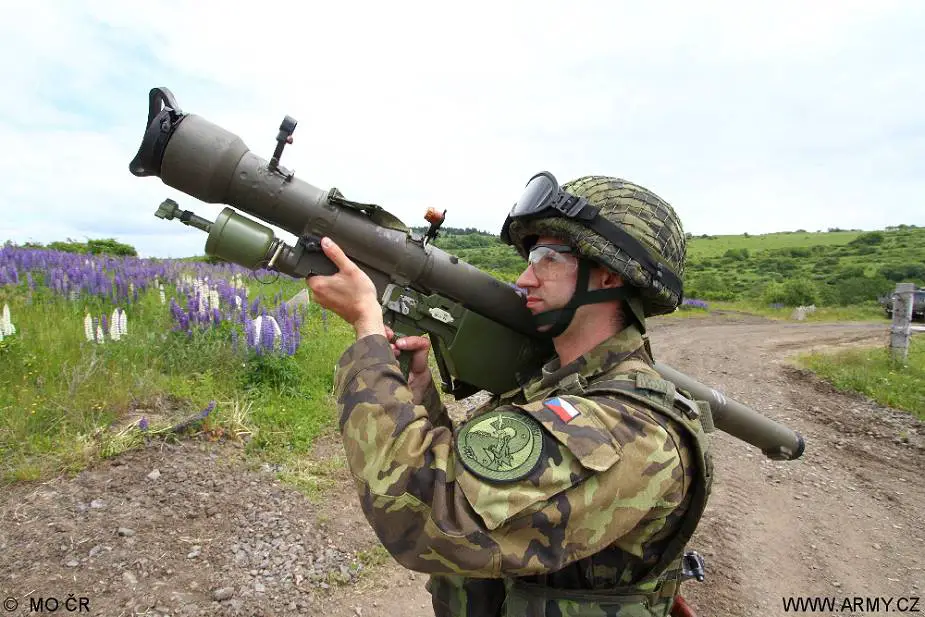
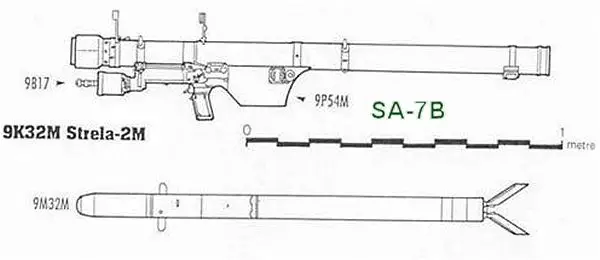
SA-7B Grail-B 9K32M Strela-2M
SA-7B Grail-b 9K32M Strela-2M MANPADS
Man-portable air defense missile system - Russia

Description
The SA-7B Grail (Russian denomination 9K32M Strela-2M) is the second generation of portable air defense missile systems, made by the Russian defense industry. In order to address the shortcomings, two improved versions were ordered already in the same as the basic version of SA-7; as an intermediate stop-gap the slightly improved 9K32M “Strela-2M” (NATO reporting name SA-7b) to replace the original, as well as the more ambitious Strela-3. The development of this relatively simple missile STRELA-2 (NATO code: SA-7A) began in 1959, and the basic version was put into service after 1966. Its advanced version STRELA-2M (SA-7B) with an improved infra-red homing system, a more effective warhead and engine, including a new detection device, has been in service since 1971. Strela-2M proved to be a considerably smaller and lighter package, the role of the Strela was changed, becoming a heavier, vehicle-mounted system with increased range and performance, to better support the ZSU-23-4 in the regimental air defense role.
SA-7 Grail 9K32 Strela variants:
- 9K32 Srela-2 SA-7
- 9K34 Strela-3 SA-14 Gremlin
- 9K310 Igla-1 SA-16 Gimlet
- 9K38 Igla SA-18 Grouse
- 9K310-1 Igla-1M
- 9K338 Igla-S SA-24 Grinch
Technical Data
| Launcher Unit |
|
The missile launcher system consists of the green missile launch tube containing the missile, a grip stock, and a cylindrical thermal battery. The launch tube is reloadable at the depot, but missile rounds are delivered to fire units in their launch tubes. As the modifications introduced with the Strela-2M were relatively minor, the process was fast and it was accepted in service already in 1970. The Strela-2M replaced Strela-2 in production lines immediately. Improvements were made particularly to increase the engagement envelope of the new system.
|
| Missile |
|
The SA-7B Grail consists of the missile 9K32M. The missile is fitted with a passive infrared homing system and a contact fuse and it is guided to contrast heat sources, usually the outlet pipe of an aircraft engine. It is powered by a two-stage solid-fuel engine. The target is detected visually by the operator; an additional IFF system can be used to identify its nationality. Activation of the homing system and electronic circuits takes 4 to 6 seconds, the engine is ignited 0.8 seconds after that. For stabilization reasons, the missile rotates about its longitudinal axis (20 rps). The target is destroyed by a pressure wave and splinters upon the initiation of the HE warhead. After launching, the operator can reload the device up to 5 times. The system includes a 9M32M missile in a 9P54M container, 9P58 launcher, 9B17 electric battery, 9V810M mobile testing and support assets, 9F620, 9F622, and 9F626 training and simulation installations.
|
| Operations |
| When engaging slow or straight-receding targets, the operator tracks the target with the iron sights in the launch tube and applies a half-trigger. This action "uncages" the seeker and allows it to attempt to track. If the target IR signature can be tracked against the background present, this is indicated by green light and buzzer sound. The shooter then pulls the trigger fully and immediately applies lead and superelevation. This method is called manual engagement. An automatic mode, which is used against fast targets, allows the shooter to fully depress the trigger in one pull followed by immediate lead and superelevation of the launch tube. The seeker will uncage and will automatically launch the missile if a strong enough signal is detected. |
| Combat Use |
| The SA-7b uses a higher thrust propellant which increases slant range from 3.4 to 4.2 km and ceiling from 1.5 to 2.3 km. The system uses a new improved guidance and control logic that allowed the engagement of propeller-driven and helicopter aircraft (but not jets) approaching at a maximum speed of 150 m/s. STRELA-2M can cooperate with a miniature elint seeker which can be fitted to the operator´s helmet and can locate sources of active radiation in an aircraft, like a radar, radar altimeter etc. Since the late 70s, an adapted version was mounted on Mil Mi-24 (HIND E) combat helicopters particularly to combat helicopters. To date, STRELA-2M has been considered a very efficient weapon to destroy air targets. Its advantages include particularly the simplicity of construction and the way of rapid and easy employment. Due to its small dimensions and low weight, it is easily portable. |
Specifications
| Missile | Type of engaged targets |
| One 9K32M | tactical aircraft, helicopter, UAV and cruise missile |
| Country users | Missile |
| Afghanistan, Albania, Algeria, Angola, Armenia, Botswana, Benin, Bulgaria, Burkina Faso, Cambodia, China, Cuba, El Salvador, Egypt, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Indonesia, India, Iraq, Iran, Kuwait, Laos, Lebanon, Libya, Mongolia, Macedonia, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Nicaragua, North Korea, Pakistan, Peru, Poland, Romania, Russia, Sierra Leone, Serbia, Slovakia, Somalia, South Yemen, Sudan, Syria, Tanzania, Ukraine, Vietnam, Zambia, Zimbabwe, | - Weight: 9.85 kg - Weight Warhead: 1.8 kg - Warhead type: HE High Explosive - Flight speed: 580 m/s |
| Combat weight | Reaction time |
| 15 kg ready to fire | 5 to 10 seconds |
| Target engagement | Guidance system |
| 800 to 4,200 m | Passive IR homing device (operating in the medium IR range) |
| Operator | Dimensions |
| 1 | Length: 1,47 m |
Details View
 |
|
 |
 |
Pictures - Video



























